圆 - 矩形碰撞检测(交叉)
如何判断圆形和矩形在2D欧几里德空间中是否相交? (即经典的二维几何)
25 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:263)
我将如何做到这一点:
bool intersects(CircleType circle, RectType rect)
{
circleDistance.x = abs(circle.x - rect.x);
circleDistance.y = abs(circle.y - rect.y);
if (circleDistance.x > (rect.width/2 + circle.r)) { return false; }
if (circleDistance.y > (rect.height/2 + circle.r)) { return false; }
if (circleDistance.x <= (rect.width/2)) { return true; }
if (circleDistance.y <= (rect.height/2)) { return true; }
cornerDistance_sq = (circleDistance.x - rect.width/2)^2 +
(circleDistance.y - rect.height/2)^2;
return (cornerDistance_sq <= (circle.r^2));
}
以下是它的工作原理:

-
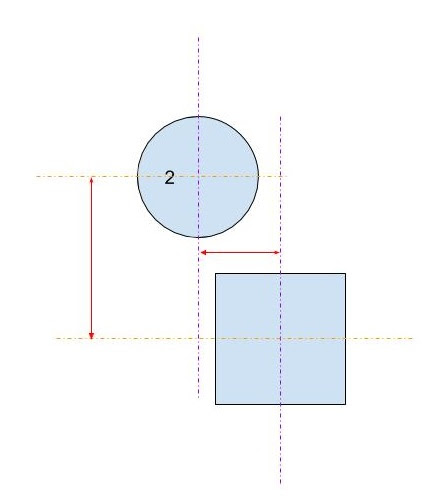
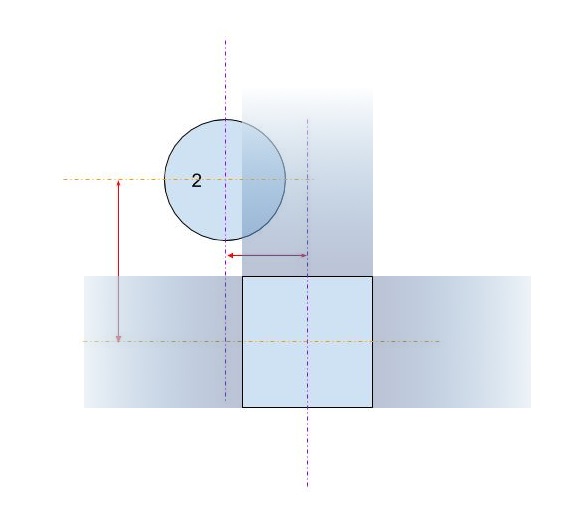
第一对线计算圆心和矩形中心之间的x和y差的绝对值。这将四个象限折叠成一个,因此计算不必进行四次。图像显示圆圈中心现在必须位于的区域。请注意,仅显示单个象限。矩形是灰色区域,红色边框勾勒出临界区域,该区域与矩形边缘恰好相差一个半径。圆的中心必须在红色边界内,才能发生交叉。
-
第二对线消除了圆形远离矩形(在任一方向上)远离任何交叉点的简单情况。这对应于图像中的绿色区域。
-
第三对线处理容易的情况,其中圆圈足够接近矩形(在任一方向上),保证交叉点。这对应于图像中的橙色和灰色部分。请注意,必须在步骤2之后执行此步骤才能使逻辑有意义。
-
剩余的线条计算圆圈可能与矩形的角相交的困难情况。要求解,请计算圆心和拐角的距离,然后验证距离是否不大于圆的半径。对于中心位于红色阴影区域内的所有圆圈,此计算返回false,对于中心位于白色阴影区域内的所有圆圈,此计算返回true。
答案 1 :(得分:157)
当圆与矩形相交时,只有两种情况:
- 圆圈的中心位于矩形内,或
- 矩形的一个边缘在圆圈中有一个点。
请注意,这不要求矩形是轴平行的。
(一种看待这种情况的方法:如果没有一个边缘在圆圈中有一个点(如果所有的边都完全“在圆圈外面”),那么圆圈仍然可以与多边形相交的唯一方法就是完全在多边形内部。)
通过这种洞察力,以下内容将起作用,其中圆圈具有居中P和半径R,并且矩形具有顶点A,B,{ {1}},C按此顺序(不是完整代码):
D如果您正在编写任何几何图形,则可能已在库中具有上述功能。否则,def intersect(Circle(P, R), Rectangle(A, B, C, D)):
S = Circle(P, R)
return (pointInRectangle(P, Rectangle(A, B, C, D)) or
intersectCircle(S, (A, B)) or
intersectCircle(S, (B, C)) or
intersectCircle(S, (C, D)) or
intersectCircle(S, (D, A)))
可以通过多种方式实施;任何一般的point in polygon方法都可以使用,但是对于一个矩形,你可以检查它是否有效:
pointInRectangle()并且0 ≤ AP·AB ≤ AB·AB and 0 ≤ AP·AD ≤ AD·AD
也很容易实现:一种方法是检查从intersectCircle()到线的垂线的脚是否足够接近并且在端点之间,否则检查端点。
很酷的是,相同的想法不仅适用于矩形,而且适用于圆与任何simple polygon的交叉 - 甚至不必是凸的!
答案 2 :(得分:118)
这是另一个非常简单的解决方案(也非常快)。它将捕获所有交叉点,包括球体完全进入矩形时。
// clamp(value, min, max) - limits value to the range min..max
// Find the closest point to the circle within the rectangle
float closestX = clamp(circle.X, rectangle.Left, rectangle.Right);
float closestY = clamp(circle.Y, rectangle.Top, rectangle.Bottom);
// Calculate the distance between the circle's center and this closest point
float distanceX = circle.X - closestX;
float distanceY = circle.Y - closestY;
// If the distance is less than the circle's radius, an intersection occurs
float distanceSquared = (distanceX * distanceX) + (distanceY * distanceY);
return distanceSquared < (circle.Radius * circle.Radius);
任何体面的数学库,可以缩短为3或4行。
答案 3 :(得分:10)
你的球体和矩形相交IIF
圆心与矩形的一个顶点之间的距离小于球体的半径
或
圆心与矩形的一条边之间的距离小于球体的半径([point-line distance])
或
圆心位于矩形内
点 - 点距离:
P1 = [x1,y1] P2 = [x2,y2] Distance = sqrt(abs(x1 - x2)+abs(y1-y2))
点线距离:
L1 = [x1,y1],L2 = [x2,y2] (two points of your line, ie the vertex points) P1 = [px,py] some point Distance d = abs( (x2-x1)(y1-py)-(x1-px)(y2-y1) ) / Distance(L1,L2)
圆形中心内部矩形:
采取分离轴方法:如果在一条线上有一个投影,从该点分隔矩形,它们不相交
将点投影在平行于矩形边的线上,然后可以轻松确定它们是否相交。如果它们不与所有4个投影相交,则它们(点和矩形)不能相交。
你只需要内积(x = [x1,x2],y = [y1,y2],x * y = x1 * y1 + x2 * y2)
你的测试看起来像那样:
//rectangle edges: TL (top left), TR (top right), BL (bottom left), BR (bottom right)
//point to test: POI
seperated = false
for egde in { {TL,TR}, {BL,BR}, {TL,BL},{TR-BR} }: // the edges
D = edge[0] - edge[1]
innerProd = D * POI
Interval_min = min(D*edge[0],D*edge[1])
Interval_max = max(D*edge[0],D*edge[1])
if not ( Interval_min ≤ innerProd ≤ Interval_max )
seperated = true
break // end for loop
end if
end for
if (seperated is true)
return "no intersection"
else
return "intersection"
end if
这不假设是一个轴对齐的矩形,并且可以很容易地扩展以测试凸集之间的交叉点。
答案 4 :(得分:6)
这是最快的解决方案:
public static boolean intersect(Rectangle r, Circle c)
{
float cx = Math.abs(c.x - r.x - r.halfWidth);
float xDist = r.halfWidth + c.radius;
if (cx > xDist)
return false;
float cy = Math.abs(c.y - r.y - r.halfHeight);
float yDist = r.halfHeight + c.radius;
if (cy > yDist)
return false;
if (cx <= r.halfWidth || cy <= r.halfHeight)
return true;
float xCornerDist = cx - r.halfWidth;
float yCornerDist = cy - r.halfHeight;
float xCornerDistSq = xCornerDist * xCornerDist;
float yCornerDistSq = yCornerDist * yCornerDist;
float maxCornerDistSq = c.radius * c.radius;
return xCornerDistSq + yCornerDistSq <= maxCornerDistSq;
}
请注意执行顺序,预先计算宽度/高度的一半。平方也是“手动”完成的,以节省一些时钟周期。
答案 5 :(得分:3)
我提出的最简单的解决方案非常简单。
它的工作原理是找到距离圆最近的矩形点,然后比较距离。
您可以通过一些操作完成所有这些操作,甚至可以避免使用sqrt功能。
public boolean intersects(float cx, float cy, float radius, float left, float top, float right, float bottom)
{
float closestX = (cx < left ? left : (cx > right ? right : cx));
float closestY = (cy < top ? top : (cy > bottom ? bottom : cy));
float dx = closestX - cx;
float dy = closestY - cy;
return ( dx * dx + dy * dy ) <= radius * radius;
}
就是这样!上述解决方案假定世界左上角有一个原点,x轴指向下方。
如果你想要一个处理移动圆和矩形之间碰撞的解决方案,那就复杂得多,涵盖in another answer of mine.
答案 6 :(得分:3)
这是我的C代码,用于解决球体和非轴对齐框之间的碰撞。它依赖于我自己的几个库例程,但它可能对某些人有用。我在游戏中使用它并且效果很好。
float physicsProcessCollisionBetweenSelfAndActorRect(SPhysics *self, SPhysics *actor)
{
float diff = 99999;
SVector relative_position_of_circle = getDifference2DBetweenVectors(&self->worldPosition, &actor->worldPosition);
rotateVector2DBy(&relative_position_of_circle, -actor->axis.angleZ); // This aligns the coord system so the rect becomes an AABB
float x_clamped_within_rectangle = relative_position_of_circle.x;
float y_clamped_within_rectangle = relative_position_of_circle.y;
LIMIT(x_clamped_within_rectangle, actor->physicsRect.l, actor->physicsRect.r);
LIMIT(y_clamped_within_rectangle, actor->physicsRect.b, actor->physicsRect.t);
// Calculate the distance between the circle's center and this closest point
float distance_to_nearest_edge_x = relative_position_of_circle.x - x_clamped_within_rectangle;
float distance_to_nearest_edge_y = relative_position_of_circle.y - y_clamped_within_rectangle;
// If the distance is less than the circle's radius, an intersection occurs
float distance_sq_x = SQUARE(distance_to_nearest_edge_x);
float distance_sq_y = SQUARE(distance_to_nearest_edge_y);
float radius_sq = SQUARE(self->physicsRadius);
if(distance_sq_x + distance_sq_y < radius_sq)
{
float half_rect_w = (actor->physicsRect.r - actor->physicsRect.l) * 0.5f;
float half_rect_h = (actor->physicsRect.t - actor->physicsRect.b) * 0.5f;
CREATE_VECTOR(push_vector);
// If we're at one of the corners of this object, treat this as a circular/circular collision
if(fabs(relative_position_of_circle.x) > half_rect_w && fabs(relative_position_of_circle.y) > half_rect_h)
{
SVector edges;
if(relative_position_of_circle.x > 0) edges.x = half_rect_w; else edges.x = -half_rect_w;
if(relative_position_of_circle.y > 0) edges.y = half_rect_h; else edges.y = -half_rect_h;
push_vector = relative_position_of_circle;
moveVectorByInverseVector2D(&push_vector, &edges);
// We now have the vector from the corner of the rect to the point.
float delta_length = getVector2DMagnitude(&push_vector);
float diff = self->physicsRadius - delta_length; // Find out how far away we are from our ideal distance
// Normalise the vector
push_vector.x /= delta_length;
push_vector.y /= delta_length;
scaleVector2DBy(&push_vector, diff); // Now multiply it by the difference
push_vector.z = 0;
}
else // Nope - just bouncing against one of the edges
{
if(relative_position_of_circle.x > 0) // Ball is to the right
push_vector.x = (half_rect_w + self->physicsRadius) - relative_position_of_circle.x;
else
push_vector.x = -((half_rect_w + self->physicsRadius) + relative_position_of_circle.x);
if(relative_position_of_circle.y > 0) // Ball is above
push_vector.y = (half_rect_h + self->physicsRadius) - relative_position_of_circle.y;
else
push_vector.y = -((half_rect_h + self->physicsRadius) + relative_position_of_circle.y);
if(fabs(push_vector.x) < fabs(push_vector.y))
push_vector.y = 0;
else
push_vector.x = 0;
}
diff = 0; // Cheat, since we don't do anything with the value anyway
rotateVector2DBy(&push_vector, actor->axis.angleZ);
SVector *from = &self->worldPosition;
moveVectorBy2D(from, push_vector.x, push_vector.y);
}
return diff;
}
答案 7 :(得分:3)
实际上,这要简单得多。你只需要两件事。
首先,您需要找到从圆心到矩形每条线的四个正交距离。如果它们中的任何三个大于圆半径,则圆圈将不会与矩形相交。
其次,你需要找到圆心和矩形中心之间的距离,如果距离大于矩形对角线长度的一半,你就不会在圆形内部。
祝你好运!答案 8 :(得分:2)
要想象,请拿出键盘的小键盘。如果键'5'代表您的矩形,则所有键1-9代表9个象限的空间除以构成矩形的线(5为内部。)
1)如果圆的中心位于象限5(即矩形内),则两个形状相交。
除此之外,有两种可能的情况: a)圆与矩形的两个或多个相邻边相交。 b)圆与矩形的一条边相交。
第一种情况很简单。如果圆与矩形的两个相邻边相交,则它必须包含连接这两个边的角。 (那个,或者它的中心位于我们已经覆盖过的象限5中。另请注意,圆圈与矩形的两个相对的边相交的情况也被覆盖。)
2)如果矩形的任何角A,B,C,D位于圆内,则两个形状相交。
第二种情况比较棘手。我们应该注意到它可能只发生在圆的中心位于象限2,4,6或8中的一个时。(事实上,如果中心位于象限1,3,7,8中的任何一个,相应的角落将是最接近它的点。)
现在我们得到圆的中心位于“边缘”象限之一的情况,它只与相应的边相交。然后,最靠近圆心的边缘上的点必须位于圆圈内。
3)对于每条线AB,BC,CD,DA,通过圆的中心构建垂直线p(AB,P),p(BC,P),p(CD,P),p(DA,P) P.对于每条垂直线,如果与原始边缘的交点位于圆内,则两个形状相交。
最后一步有一个快捷方式。如果圆的中心位于象限8并且边AB是顶边,则交点将具有A和B的y坐标以及中心P的x坐标。
您可以构造四个线交叉点并检查它们是否位于相应的边缘,或找出P所在的象限并检查相应的交叉点。两者都应简化为相同的布尔方程。要小心,上面的第2步并不排除P在一个“角落”象限中;它只是寻找一个交叉点。
编辑:事实证明,我忽略了一个简单的事实,#2是上面#3的子句。毕竟,角落也是边缘上的点。请参阅下面的@ ShreevatsaR的答案,以获得很好的解释。同时,除非您想要快速但冗余的检查,否则请忘记上面的#2。
答案 9 :(得分:2)
此功能检测圆形和矩形之间的碰撞(交叉点)。他在答案中的工作方式与e.James方法类似,但是这个方法可以检测所有矩形角度(不仅是右上角)的碰撞。
注意:
aRect.origin.x 和 aRect.origin.y 是矩形左下角的坐标!
aCircle.x 和 aCircle.y 是Circle Center的坐标!
static inline BOOL RectIntersectsCircle(CGRect aRect, Circle aCircle) {
float testX = aCircle.x;
float testY = aCircle.y;
if (testX < aRect.origin.x)
testX = aRect.origin.x;
if (testX > (aRect.origin.x + aRect.size.width))
testX = (aRect.origin.x + aRect.size.width);
if (testY < aRect.origin.y)
testY = aRect.origin.y;
if (testY > (aRect.origin.y + aRect.size.height))
testY = (aRect.origin.y + aRect.size.height);
return ((aCircle.x - testX) * (aCircle.x - testX) + (aCircle.y - testY) * (aCircle.y - testY)) < aCircle.radius * aCircle.radius;
}
答案 10 :(得分:1)
我创建了用于处理形状的类 希望你喜欢
public class Geomethry {
public static boolean intersectionCircleAndRectangle(int circleX, int circleY, int circleR, int rectangleX, int rectangleY, int rectangleWidth, int rectangleHeight){
boolean result = false;
float rectHalfWidth = rectangleWidth/2.0f;
float rectHalfHeight = rectangleHeight/2.0f;
float rectCenterX = rectangleX + rectHalfWidth;
float rectCenterY = rectangleY + rectHalfHeight;
float deltax = Math.abs(rectCenterX - circleX);
float deltay = Math.abs(rectCenterY - circleY);
float lengthHypotenuseSqure = deltax*deltax + deltay*deltay;
do{
// check that distance between the centerse is more than the distance between the circumcircle of rectangle and circle
if(lengthHypotenuseSqure > ((rectHalfWidth+circleR)*(rectHalfWidth+circleR) + (rectHalfHeight+circleR)*(rectHalfHeight+circleR))){
//System.out.println("distance between the centerse is more than the distance between the circumcircle of rectangle and circle");
break;
}
// check that distance between the centerse is less than the distance between the inscribed circle
float rectMinHalfSide = Math.min(rectHalfWidth, rectHalfHeight);
if(lengthHypotenuseSqure < ((rectMinHalfSide+circleR)*(rectMinHalfSide+circleR))){
//System.out.println("distance between the centerse is less than the distance between the inscribed circle");
result=true;
break;
}
// check that the squares relate to angles
if((deltax > (rectHalfWidth+circleR)*0.9) && (deltay > (rectHalfHeight+circleR)*0.9)){
//System.out.println("squares relate to angles");
result=true;
}
}while(false);
return result;
}
public static boolean intersectionRectangleAndRectangle(int rectangleX, int rectangleY, int rectangleWidth, int rectangleHeight, int rectangleX2, int rectangleY2, int rectangleWidth2, int rectangleHeight2){
boolean result = false;
float rectHalfWidth = rectangleWidth/2.0f;
float rectHalfHeight = rectangleHeight/2.0f;
float rectHalfWidth2 = rectangleWidth2/2.0f;
float rectHalfHeight2 = rectangleHeight2/2.0f;
float deltax = Math.abs((rectangleX + rectHalfWidth) - (rectangleX2 + rectHalfWidth2));
float deltay = Math.abs((rectangleY + rectHalfHeight) - (rectangleY2 + rectHalfHeight2));
float lengthHypotenuseSqure = deltax*deltax + deltay*deltay;
do{
// check that distance between the centerse is more than the distance between the circumcircle
if(lengthHypotenuseSqure > ((rectHalfWidth+rectHalfWidth2)*(rectHalfWidth+rectHalfWidth2) + (rectHalfHeight+rectHalfHeight2)*(rectHalfHeight+rectHalfHeight2))){
//System.out.println("distance between the centerse is more than the distance between the circumcircle");
break;
}
// check that distance between the centerse is less than the distance between the inscribed circle
float rectMinHalfSide = Math.min(rectHalfWidth, rectHalfHeight);
float rectMinHalfSide2 = Math.min(rectHalfWidth2, rectHalfHeight2);
if(lengthHypotenuseSqure < ((rectMinHalfSide+rectMinHalfSide2)*(rectMinHalfSide+rectMinHalfSide2))){
//System.out.println("distance between the centerse is less than the distance between the inscribed circle");
result=true;
break;
}
// check that the squares relate to angles
if((deltax > (rectHalfWidth+rectHalfWidth2)*0.9) && (deltay > (rectHalfHeight+rectHalfHeight2)*0.9)){
//System.out.println("squares relate to angles");
result=true;
}
}while(false);
return result;
}
}
答案 11 :(得分:1)
这是100%工作的修改代码:
public static bool IsIntersected(PointF circle, float radius, RectangleF rectangle)
{
var rectangleCenter = new PointF((rectangle.X + rectangle.Width / 2),
(rectangle.Y + rectangle.Height / 2));
var w = rectangle.Width / 2;
var h = rectangle.Height / 2;
var dx = Math.Abs(circle.X - rectangleCenter.X);
var dy = Math.Abs(circle.Y - rectangleCenter.Y);
if (dx > (radius + w) || dy > (radius + h)) return false;
var circleDistance = new PointF
{
X = Math.Abs(circle.X - rectangle.X - w),
Y = Math.Abs(circle.Y - rectangle.Y - h)
};
if (circleDistance.X <= (w))
{
return true;
}
if (circleDistance.Y <= (h))
{
return true;
}
var cornerDistanceSq = Math.Pow(circleDistance.X - w, 2) +
Math.Pow(circleDistance.Y - h, 2);
return (cornerDistanceSq <= (Math.Pow(radius, 2)));
}
Bassam Alugili
答案 12 :(得分:1)
这是一个快速的单行测试:
if (length(max(abs(center - rect_mid) - rect_halves, 0)) <= radius ) {
// They intersect.
}
这是轴对齐的情况,其中rect_halves是从矩形中间指向角的正向量。 length()内的表达式是从center到矩形中最近点的增量矢量。这适用于任何方面。
答案 13 :(得分:1)
- 首先检查矩形和圆的正方形是否重叠(简单)。如果它们没有重叠,它们就不会发生碰撞。
- 检查圆圈的中心是否在矩形内(简单)。如果它在里面,它们会发生碰撞。
- 计算从矩形边到圆的中心(稍微硬)的最小平方距离。如果它低于平方半径,那么它们会发生碰撞,否则它们就不会发生。
效率很高,因为:
- 首先,它使用便宜的算法检查最常见的场景,当它确定它们不会发生碰撞时,它就会结束。
- 然后用廉价算法检查下一个最常见的场景(不计算平方根,使用平方值),当它确定它们碰撞时就结束了。
- 然后它执行更昂贵的算法来检查与矩形边界的碰撞。
答案 14 :(得分:1)
为我工作(仅在矩形角度为180度时工作)
function intersects(circle, rect) {
let left = rect.x + rect.width > circle.x - circle.radius;
let right = rect.x < circle.x + circle.radius;
let top = rect.y < circle.y + circle.radius;
let bottom = rect.y + rect.height > circle.y - circle.radius;
return left && right && bottom && top;
}
答案 15 :(得分:1)
double dx = abs(circle.x - rect.x) - rect.w / 2,
dy = abs(circle.y - rect.y) - rect.h / 2;
if (dx > circle.r || dy > circle.r) { return false; }
if (dx <= 0 || dy <= 0) { return true; }
return (dx * dx + dy * dy <= circle.r * circle.r);
这会将rect.w / 2和rect.h / 2减去一次,而不是三倍。
答案 16 :(得分:0)
我有一种方法可以避免昂贵的毕达哥拉斯,如果没有必要 - 即。当矩形的边界框和圆不相交时。
它也适用于非欧几里德:
class Circle {
// create the bounding box of the circle only once
BBox bbox;
public boolean intersect(BBox b) {
// test top intersect
if (lat > b.maxLat) {
if (lon < b.minLon)
return normDist(b.maxLat, b.minLon) <= normedDist;
if (lon > b.maxLon)
return normDist(b.maxLat, b.maxLon) <= normedDist;
return b.maxLat - bbox.minLat > 0;
}
// test bottom intersect
if (lat < b.minLat) {
if (lon < b.minLon)
return normDist(b.minLat, b.minLon) <= normedDist;
if (lon > b.maxLon)
return normDist(b.minLat, b.maxLon) <= normedDist;
return bbox.maxLat - b.minLat > 0;
}
// test middle intersect
if (lon < b.minLon)
return bbox.maxLon - b.minLon > 0;
if (lon > b.maxLon)
return b.maxLon - bbox.minLon > 0;
return true;
}
}
- minLat,maxLat可以替换为minY,maxY和minLon,maxLon相同:将其替换为minX,maxX
- normDist只是比全距离计算快一点的方法。例如。没有欧几里德空间中的平方根(或者没有很多其他的东西):
dLat=(lat-circleY); dLon=(lon-circleX); normed=dLat*dLat+dLon*dLon。当然,如果您使用该normDist方法,则需要为圆圈创建normedDist = dist*dist;
查看我BBox项目的完整Circle和GraphHopper代码。
答案 17 :(得分:0)
工作,一周前刚想出来,现在才开始测试。
double theta = Math.atan2(cir.getX()-sqr.getX()*1.0,
cir.getY()-sqr.getY()*1.0); //radians of the angle
double dBox; //distance from box to edge of box in direction of the circle
if((theta > Math.PI/4 && theta < 3*Math.PI / 4) ||
(theta < -Math.PI/4 && theta > -3*Math.PI / 4)) {
dBox = sqr.getS() / (2*Math.sin(theta));
} else {
dBox = sqr.getS() / (2*Math.cos(theta));
}
boolean touching = (Math.abs(dBox) >=
Math.sqrt(Math.pow(sqr.getX()-cir.getX(), 2) +
Math.pow(sqr.getY()-cir.getY(), 2)));
答案 18 :(得分:0)
对于那些必须使用SQL计算地理坐标中的圆/矩形碰撞的人,
这是我在e.James suggested algorithm的oracle 11中的实现。
在输入中,它需要圆坐标,以km为单位的圆半径和矩形的两个顶点坐标:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION "DETECT_CIRC_RECT_COLLISION"
(
circleCenterLat IN NUMBER, -- circle Center Latitude
circleCenterLon IN NUMBER, -- circle Center Longitude
circleRadius IN NUMBER, -- circle Radius in KM
rectSWLat IN NUMBER, -- rectangle South West Latitude
rectSWLon IN NUMBER, -- rectangle South West Longitude
rectNELat IN NUMBER, -- rectangle North Est Latitude
rectNELon IN NUMBER -- rectangle North Est Longitude
)
RETURN NUMBER
AS
-- converts km to degrees (use 69 if miles)
kmToDegreeConst NUMBER := 111.045;
-- Remaining rectangle vertices
rectNWLat NUMBER;
rectNWLon NUMBER;
rectSELat NUMBER;
rectSELon NUMBER;
rectHeight NUMBER;
rectWIdth NUMBER;
circleDistanceLat NUMBER;
circleDistanceLon NUMBER;
cornerDistanceSQ NUMBER;
BEGIN
-- Initialization of remaining rectangle vertices
rectNWLat := rectNELat;
rectNWLon := rectSWLon;
rectSELat := rectSWLat;
rectSELon := rectNELon;
-- Rectangle sides length calculation
rectHeight := calc_distance(rectSWLat, rectSWLon, rectNWLat, rectNWLon);
rectWidth := calc_distance(rectSWLat, rectSWLon, rectSELat, rectSELon);
circleDistanceLat := abs( (circleCenterLat * kmToDegreeConst) - ((rectSWLat * kmToDegreeConst) + (rectHeight/2)) );
circleDistanceLon := abs( (circleCenterLon * kmToDegreeConst) - ((rectSWLon * kmToDegreeConst) + (rectWidth/2)) );
IF circleDistanceLon > ((rectWidth/2) + circleRadius) THEN
RETURN -1; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
END IF;
IF circleDistanceLat > ((rectHeight/2) + circleRadius) THEN
RETURN -1; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
END IF;
IF circleDistanceLon <= (rectWidth/2) THEN
RETURN 0; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
END IF;
IF circleDistanceLat <= (rectHeight/2) THEN
RETURN 0; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
END IF;
cornerDistanceSQ := POWER(circleDistanceLon - (rectWidth/2), 2) + POWER(circleDistanceLat - (rectHeight/2), 2);
IF cornerDistanceSQ <= POWER(circleRadius, 2) THEN
RETURN 0; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
ELSE
RETURN -1; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
END IF;
RETURN -1; -- -1 => NO Collision ; 0 => Collision Detected
END;
答案 19 :(得分:0)
def colision(rect, circle):
dx = rect.x - circle.x
dy = rect.y - circle.y
distance = (dy**2 + dx**2)**0.5
angle_to = (rect.angle + math.atan2(dx, dy)/3.1415*180.0) % 360
if((angle_to>135 and angle_to<225) or (angle_to>0 and angle_to<45) or (angle_to>315 and angle_to<360)):
if distance <= circle.rad/2.+((rect.height/2.0)*(1.+0.5*abs(math.sin(angle_to*math.pi/180.)))):
return True
else:
if distance <= circle.rad/2.+((rect.width/2.0)*(1.+0.5*abs(math.cos(angle_to*math.pi/180.)))):
return True
return False
答案 20 :(得分:0)
我在制作这款游戏时开发了此算法:https://mshwf.github.io/mates/
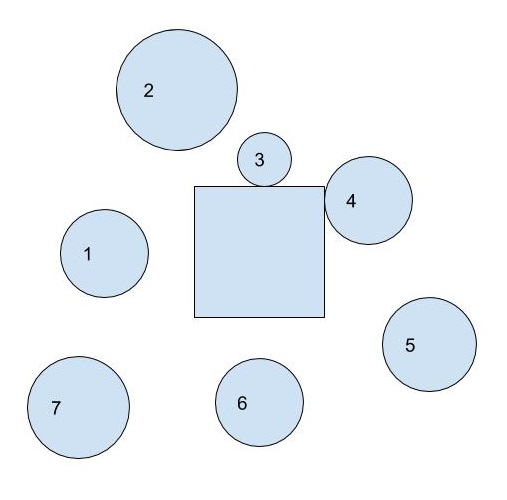
如果圆接触正方形,则圆的中心线与正方形的中心线之间的距离应等于(diameter+side)/2。
因此,我们有一个名为touching的变量来保持该距离。问题是:我应该考虑哪个中心线:水平还是垂直?
考虑以下框架:
每个中心线都给出不同的距离,只有一个是正确表示无碰撞的,但是利用我们的直觉,才开始了解自然算法的工作原理。
它们没有接触,这意味着两条中心线之间的距离应大于touching,这意味着自然算法会选择水平中心线(垂直中心线表示发生碰撞!)。通过注意多个圆,您可以知道:如果圆与正方形的垂直延伸线相交,则我们选择垂直距离(水平中心线之间),如果圆与水平延伸线相交,则我们选择水平距离:
另一个例子,圆号4:它与正方形的水平延伸线相交,然后我们考虑等于触摸的水平距离。
好吧,最困难的部分是神秘的,现在我们知道算法将如何工作,但是我们如何知道圆与哪个扩展相交呢?
实际上很容易:我们计算出最右边的x和最左边的x(在圆和正方形中)之间的距离,对于y轴也是如此,值更大的那个是具有与圆相交的扩展名的轴(如果它大于diameter+side,则该圆在两个方形扩展名的外部,如圆#7)。代码如下:
right = Math.max(square.x+square.side, circle.x+circle.rad);
left = Math.min(square.x, circle.x-circle.rad);
bottom = Math.max(square.y+square.side, circle.y+circle.rad);
top = Math.min(square.y, circle.y-circle.rad);
if (right - left > down - top) {
//compare with horizontal distance
}
else {
//compare with vertical distance
}
/*These equations assume that the reference point of the square is at its top left corner, and the reference point of the circle is at its center*/
答案 21 :(得分:0)
- 预先检查是否完全封装了矩形的圆与圆碰撞。
- 检查圆内的矩形角。
- 对于每个边,查看与圆是否存在线相交。将中心点C投影到直线AB上以获得点D。如果CD的长度小于半径,则发生碰撞。
projectionScalar=dot(AC,AB)/(mag(AC)*mag(AB));
if(projectionScalar>=0 && projectionScalar<=1) {
D=A+AB*projectionScalar;
CD=D-C;
if(mag(CD)<circle.radius){
// there was a collision
}
}
答案 22 :(得分:0)
有一种非常简单的方法,您必须在x和y处夹点,但要在正方形内,而圆心在所需的垂直轴之一的两个正方形边界点之间要将这些坐标钳位到平行轴上,只需确保所钳位的坐标没有超出平方的范围即可。 然后只需获取圆心与所夹持坐标之间的距离,并检查该距离是否小于圆心。
这是我的操作方式(前4个点是方形坐标,其余是圆点):
bool DoesCircleImpactBox(float x, float y, float x1, float y1, float xc, float yc, float radius){
float ClampedX=0;
float ClampedY=0;
if(xc>=x and xc<=x1){
ClampedX=xc;
}
if(yc>=y and yc<=y1){
ClampedY=yc;
}
radius = radius+1;
if(xc<x) ClampedX=x;
if(xc>x1) ClampedX=x1-1;
if(yc<y) ClampedY=y;
if(yc>y1) ClampedY=y1-1;
float XDif=ClampedX-xc;
XDif=XDif*XDif;
float YDif=ClampedY-yc;
YDif=YDif*YDif;
if(XDif+YDif<=radius*radius) return true;
return false;
}
答案 23 :(得分:-2)
假设您有矩形的四个边缘,检查从边缘到圆心的距离,如果它小于半径,则形状相交。
if sqrt((rectangleRight.x - circleCenter.x)^2 +
(rectangleBottom.y - circleCenter.y)^2) < radius
// then they intersect
if sqrt((rectangleRight.x - circleCenter.x)^2 +
(rectangleTop.y - circleCenter.y)^2) < radius
// then they intersect
if sqrt((rectangleLeft.x - circleCenter.x)^2 +
(rectangleTop.y - circleCenter.y)^2) < radius
// then they intersect
if sqrt((rectangleLeft.x - circleCenter.x)^2 +
(rectangleBottom.y - circleCenter.y)^2) < radius
// then they intersect
答案 24 :(得分:-2)
如果矩形与圆相交,则矩形的一个或多个角点应位于圆内。假设矩形的四个点是A,B,C,D。其中至少有一个应与圆相交。因此,如果从一个点到圆心的距离小于圆的半径,它应该与圆相交。为了获得距离,你可以使用毕达哥拉斯定理,
H^2 = A^2 + B^2
这种技术有一些限制。但它对游戏开发者来说会更好。特别是碰撞检测
这是对Arvo算法的一个很好的更新
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?