铰链接头的无损运动-Unity
我已经在Unity中创建了一个简单的摆锤-GameObject,带有Rigidbody和Hinge Joint组件。我都将拖动角度和角度拖动都设置为0。在90度的起始位置,我希望钟摆能从90度到-90度来回摆动。但是,情况并非如此-幅度衰减非常快,但是对于小角度,摆似乎永远不会停止。
我的问题是:我应该如何配置铰链接头,以完全控制物理和抵抗运动的力?我的目标是即使以性能为代价,也要尽可能精确地进行物理模拟。
我已经尝试减少固定步长的时间间隔并增加求解器迭代-这些都没有解决。
我为什么需要它?我打算为一个推车上的多个倒立摆设计一个控制系统。我有一个在Matlab中实现的摆锤的数学模型,我想使用Unity中的一个简单模型进行验证(因为在这种情况下,我会调整所有参数,初始条件等,而物理引擎正在为我计算一切)。如果事实证明支持Unity的物理引擎不够可靠,您还会推荐我使用什么其他软件?
2 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:0)
我的理解是,由于Unity物理学的运行方式,如果仅使用铰链关节,则这种摆运动会随着时间的流逝而失去动能。基本上,如果要进行精确的摆锤模拟,则必须绕过物理引擎并直接实现。
a very good post on the gamedev stackexchange最初发布了MLM,内容涉及如何在Unity中实现更精确的摆锤模拟,我在下面粘贴了该
我认为这将是一个相对简单的问题,但是我花了几天的时间试图弄清楚如何模拟摆运动。我不想作弊,只是根据sin(theta)和cos(theta)曲线更改x,y位置。相反,我想处理现实生活中应用的两种力量,即重力和张力。我所缺少的主要部件是向心力。
Pendulum (mathematics) wikipedia page有一个很好的动画(在左下),说明了摆运动。您可以看到我的结果(右)与该图非常相似
“ bob”是摆动的对象,“ pivot”是起点/根。
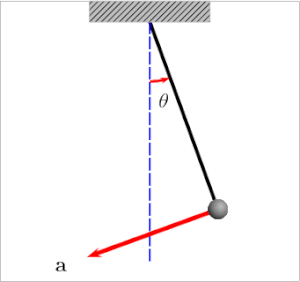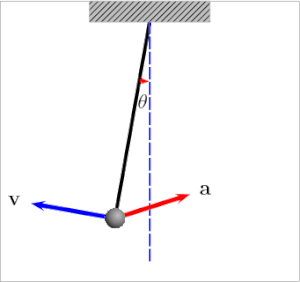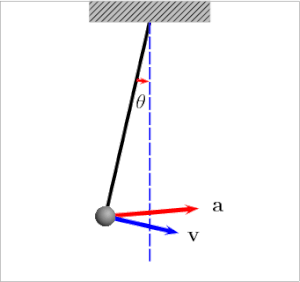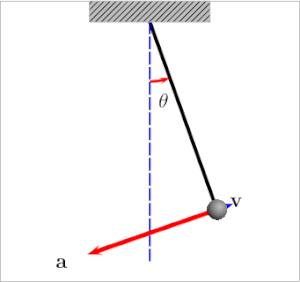

我还发现this article和下面的图表很有帮助:

Theta等于绳索和重力方向之间的角度。
当摆锤位于左侧或右侧时,张力等于:

当鲍勃接近平衡点(中间)时,张力较大的原因是由于centripetal force:

所以随着鲍勃摆动,总体张力公式如下:

摆系统中有两种作用力:
- 重力
-
GravityForce = mass * gravity.magnitude -
GravityDirection = gravity.normalized
-
- 张力
-
TensionForce = (mass * gravity * Cos(theta)) + ((mass * velocityTangent^2)/ropeLength) -
TensionDirection = ropeDirection = bob to pivot
-
只需像对待普通物体一样对物体施加重力,然后施加拉力即可。施加力时,只需将力乘以方向和deltaTime。
下面是Pendulum.cs脚本(也作为GitHub Gist)。它工作得很好,但是如果您将其放置一段时间(不会返回到完全相同的位置),则会出现一些舍入误差漂移。
该脚本可在3D模式下工作,但当然,钟摆只能在2D平面内摆动。它也可以在任何方向上与重力共同作用。因此,例如,如果您反转重力,则钟摆将上下颠倒。 Edit->Project Settings->Physics->Gravity
在更新钟摆时,始终保持相对较小的deltaTime是非常重要的,这样就不会在曲线周围反弹。我正在使用本文FIX YOUR TIMESTEP! by Glenn Fiedler中发现的技术来完成此任务。检查下面的Update()函数,看看我是如何实现的。

Also as a GitHub Gist
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
// Author: Eric Eastwood (ericeastwood.com)
//
// Description:
// Written for this gd.se question: http://gamedev.stackexchange.com/a/75748/16587
// Simulates/Emulates pendulum motion in code
// Works in any 3D direction and with any force/direciton of gravity
//
// Demonstration: https://i.imgur.com/vOQgFMe.gif
//
// Usage: https://i.imgur.com/BM52dbT.png
public class Pendulum : MonoBehaviour {
public GameObject Pivot;
public GameObject Bob;
public float mass = 1f;
float ropeLength = 2f;
Vector3 bobStartingPosition;
bool bobStartingPositionSet = false;
// You could define these in the `PendulumUpdate()` loop
// But we want them in the class scope so we can draw gizmos `OnDrawGizmos()`
private Vector3 gravityDirection;
private Vector3 tensionDirection;
private Vector3 tangentDirection;
private Vector3 pendulumSideDirection;
private float tensionForce = 0f;
private float gravityForce = 0f;
// Keep track of the current velocity
Vector3 currentVelocity = new Vector3();
// We use these to smooth between values in certain framerate situations in the `Update()` loop
Vector3 currentStatePosition;
Vector3 previousStatePosition;
// Use this for initialization
void Start () {
// Set the starting position for later use in the context menu reset methods
this.bobStartingPosition = this.Bob.transform.position;
this.bobStartingPositionSet = true;
this.PendulumInit();
}
float t = 0f;
float dt = 0.01f;
float currentTime = 0f;
float accumulator = 0f;
void Update()
{
/* */
// Fixed deltaTime rendering at any speed with smoothing
// Technique: http://gafferongames.com/game-physics/fix-your-timestep/
float frameTime = Time.time - currentTime;
this.currentTime = Time.time;
this.accumulator += frameTime;
while (this.accumulator >= this.dt)
{
this.previousStatePosition = this.currentStatePosition;
this.currentStatePosition = this.PendulumUpdate(this.currentStatePosition, this.dt);
//integrate(state, this.t, this.dt);
accumulator -= this.dt;
this.t += this.dt;
}
float alpha = this.accumulator/this.dt;
Vector3 newPosition = this.currentStatePosition*alpha + this.previousStatePosition*(1f-alpha);
this.Bob.transform.position = newPosition; //this.currentStatePosition;
/* */
//this.Bob.transform.position = this.PendulumUpdate(this.Bob.transform.position, Time.deltaTime);
}
// Use this to reset forces and go back to the starting position
[ContextMenu("Reset Pendulum Position")]
void ResetPendulumPosition()
{
if(this.bobStartingPositionSet)
this.MoveBob(this.bobStartingPosition);
else
this.PendulumInit();
}
// Use this to reset any built up forces
[ContextMenu("Reset Pendulum Forces")]
void ResetPendulumForces()
{
this.currentVelocity = Vector3.zero;
// Set the transition state
this.currentStatePosition = this.Bob.transform.position;
}
void PendulumInit()
{
// Get the initial rope length from how far away the bob is now
this.ropeLength = Vector3.Distance(Pivot.transform.position, Bob.transform.position);
this.ResetPendulumForces();
}
void MoveBob(Vector3 resetBobPosition)
{
// Put the bob back in the place we first saw it at in `Start()`
this.Bob.transform.position = resetBobPosition;
// Set the transition state
this.currentStatePosition = resetBobPosition;
}
Vector3 PendulumUpdate(Vector3 currentStatePosition, float deltaTime)
{
// Add gravity free fall
this.gravityForce = this.mass * Physics.gravity.magnitude;
this.gravityDirection = Physics.gravity.normalized;
this.currentVelocity += this.gravityDirection * this.gravityForce * deltaTime;
Vector3 pivot_p = this.Pivot.transform.position;
Vector3 bob_p = this.currentStatePosition;
Vector3 auxiliaryMovementDelta = this.currentVelocity * deltaTime;
float distanceAfterGravity = Vector3.Distance(pivot_p, bob_p + auxiliaryMovementDelta);
// If at the end of the rope
if(distanceAfterGravity > this.ropeLength || Mathf.Approximately(distanceAfterGravity, this.ropeLength))
{
this.tensionDirection = (pivot_p - bob_p).normalized;
this.pendulumSideDirection = (Quaternion.Euler(0f, 90f, 0f) * this.tensionDirection);
this.pendulumSideDirection.Scale(new Vector3(1f, 0f, 1f));
this.pendulumSideDirection.Normalize();
this.tangentDirection = (-1f * Vector3.Cross(this.tensionDirection, this.pendulumSideDirection)).normalized;
float inclinationAngle = Vector3.Angle(bob_p-pivot_p, this.gravityDirection);
this.tensionForce = this.mass * Physics.gravity.magnitude * Mathf.Cos(Mathf.Deg2Rad * inclinationAngle);
float centripetalForce = ((this.mass * Mathf.Pow(this.currentVelocity.magnitude, 2))/this.ropeLength);
this.tensionForce += centripetalForce;
this.currentVelocity += this.tensionDirection * this.tensionForce * deltaTime;
}
// Get the movement delta
Vector3 movementDelta = Vector3.zero;
movementDelta += this.currentVelocity * deltaTime;
//return currentStatePosition + movementDelta;
float distance = Vector3.Distance(pivot_p, currentStatePosition + movementDelta);
return this.GetPointOnLine(pivot_p, currentStatePosition + movementDelta, distance <= this.ropeLength ? distance : this.ropeLength);
}
Vector3 GetPointOnLine(Vector3 start, Vector3 end, float distanceFromStart)
{
return start + (distanceFromStart * Vector3.Normalize(end - start));
}
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
// purple
Gizmos.color = new Color(.5f, 0f, .5f);
Gizmos.DrawWireSphere(this.Pivot.transform.position, this.ropeLength);
Gizmos.DrawWireCube(this.bobStartingPosition, new Vector3(.5f, .5f, .5f));
// Blue: Auxilary
Gizmos.color = new Color(.3f, .3f, 1f); // blue
Vector3 auxVel = .3f * this.currentVelocity;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, auxVel);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + auxVel, .2f);
// Yellow: Gravity
Gizmos.color = new Color(1f, 1f, .2f);
Vector3 gravity = .3f * this.gravityForce*this.gravityDirection;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, gravity);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + gravity, .2f);
// Orange: Tension
Gizmos.color = new Color(1f, .5f, .2f); // Orange
Vector3 tension = .3f * this.tensionForce*this.tensionDirection;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, tension);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + tension, .2f);
// Red: Resultant
Gizmos.color = new Color(1f, .3f, .3f); // red
Vector3 resultant = gravity + tension;
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, resultant);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + resultant, .2f);
/* * /
// Green: Pendulum side direction
Gizmos.color = new Color(.3f, 1f, .3f);
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, 3f*this.pendulumSideDirection);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + 3f*this.pendulumSideDirection, .2f);
/* */
/* * /
// Cyan: tangent direction
Gizmos.color = new Color(.2f, 1f, 1f); // cyan
Gizmos.DrawRay(this.Bob.transform.position, 3f*this.tangentDirection);
Gizmos.DrawSphere(this.Bob.transform.position + 3f*this.tangentDirection, .2f);
/* */
}
}
更多魅力镜头:


答案 1 :(得分:0)
将刚体上的 maxAngularVelocity 设置为 Mathf.Infinity 。
我知道这个话题已经9个月了,但是由于这个问题,我最近一直在撞墙。由于某种原因,Unity开发人员认为将刚性体的最大旋转速度限制为每秒 7弧度是一个好主意!每秒仅旋转一圈多一点,对于任何人来说都太低了需要物理精度的应用程序。最重要的是,属性在检查器或物理设置中不可见!
我希望这会为您(如果您还没有自己解决这个问题)和将来可能与这个问题作斗争的其他人提供帮助!
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?