еҲ—иЎЁз»ҷеҮәдәҶз»ҶеҲҶй”ҷиҜҜ
жҲ‘дёҚжҳҺзҷҪдёәд»Җд№ҲжӯӨC ++д»Јз Ғдјҡдә§з”ҹеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜгҖӮ
жҲ‘жӯЈеңЁе°қиҜ•е°Ҷж•°жҚ®жҸ’е…ҘйӮ»жҺҘиЎЁ
иҜ·жңүдәәе‘ҠиҜүжҲ‘еҰӮдҪ•зә жӯЈе®ғжҲ–еҰӮдҪ•д»Ҙе…¶д»–ж–№ејҸеҒҡеҲ°иҝҷдёҖзӮ№...
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
list<int> *adj;
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].push_back(w); // Add w to vвҖҷs list.
adj[w].push_back(v);
}
int main()
{
int n, m, t;
cin >> n >> m >> t;
int u, v;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
cin >> u >> v;
addEdge(u, v);
}
}
1 дёӘзӯ”жЎҲ:
зӯ”жЎҲ 0 :(еҫ—еҲҶпјҡ2)
В ВжҲ‘иҜҘжҖҺд№ҲеҠһпјҹ
жҲ‘дјҡдҪҝз”ЁеҲ—иЎЁеҲ—иЎЁпјҡ
#include <cstdlib>
#include <limits>
#include <map>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
class adjacency_list_t {
private:
using list_type = std::map<int, std::list<int>>;
list_type list;
public:
adjacency_list_t() = default;
void add_edge(int v1, int v2)
{
list[v1].push_back(v2);
list[v2].push_back(v1);
}
std::list<int> const& get_neighbours(int v) const { return list.at(v); }
bool are_neighbours(int v1, int v2) const
{
auto const &v1_list = list.at(v1);
return std::find(v1_list.cbegin(), v1_list.cend(), v2) != v1_list.end();
}
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &os, adjacency_list_t const &list)
{
for (auto const &v : list.list) {
os << v.first << ' ';
for (auto const &u : v.second) {
os << u << ' ';
}
os << '\n';
}
return os;
}
};
int main()
{
std::cout << "number of edges? ";
size_t num_edges;
if (!(std::cin >> num_edges)) {
std::cerr << "Input error. Bye :(\n\n";
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
adjacency_list_t list;
for (std::size_t i{}; i < num_edges; ++i) {
std::cout << "edge #" << i + 1 << "? ";
int v1, v2;
std::cin >> v1 >> v2;
list.add_edge(v1, v2);
}
std::cout << "\n\n";
bool run{ true };
do {
int choice;
while (std::cout << "[1] print\n[2] print neighbours of\n"
"[3] are neighbours?\n[4] exit\n\n",
!(std::cin >> choice) || choice < 1 || 4 < choice)
{
std::cerr << "Input error :(\n\n";
std::cin.clear();
std::cin.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(), '\n');
}
switch (choice) {
case 1: // print
std::cout << "full list:\n" << list;
break;
case 2: // print neighbours of
{
std::cout << "vertex? ";
int v;
if (std::cin >> v) {
auto const &neighbours{ list.get_neighbours(v) };
for (auto const &n : neighbours)
std::cout << n << ' ';
}
break;
}
case 3: // are neighbours?
{
int v1;
int v2;
std::cout << "vertices? ";
if (std::cin >> v1 >> v2) {
std::cout << std::boolalpha << list.are_neighbours(v1, v2);
}
break;
}
case 4:
std::cout << "Bye.";
run = false;
}
std::cout << "\n\n";
} while (run);
}
ж ·жң¬иҫ“еҮәпјҡ
number of edges? 7
edge #1? 6 4
edge #2? 4 3
edge #3? 4 5
edge #4? 5 2
edge #5? 3 2
edge #6? 5 1
edge #7? 2 1
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
1
full list:
1 5 2
2 5 3 1
3 4 2
4 6 3 5
5 4 2 1
6 4
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
2
vertex? 3
4 2
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
2
vertex? 5
4 2 1
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
2
vertex? 1
5 2
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
3
vertices? 4 3
true
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
3
vertices? 2 6
false
[1] print
[2] print neighbours of
[3] are neighbours?
[4] exit
4
Bye.
еҜ№еә”еӣҫпјҡ
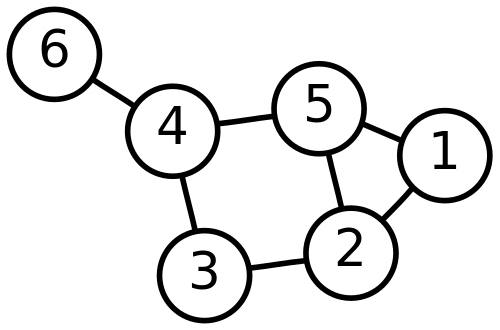
дҪҶжҳҜеҫҲйҡҫе‘ҠиҜүжӮЁд»Җд№ҲжҳҜжңҖдҪізҡ„ж•°жҚ®з»“жһ„пјҢеӣ дёәжҲ‘们дёҚзҹҘйҒ“жӮЁе°ҶдҪҝз”Ёд»Җд№Ҳж•°жҚ®з»“жһ„гҖӮ
зӣёе…ій—®йўҳ
- strtokз»ҷеҮәеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- putcз»ҷеҮәеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜпјҹ
- memcache_getпјҲпјүз»ҷеҮәеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- еҲҶж®өж•…йҡңзӨәдҫӢжңӘз»ҷеҮәеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- glxMakeCurrentз»ҷеҮәеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- strcmpз»ҷеҮәеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- zmq_socketпјҲпјүз»ҷеҮәдәҶеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- д»ҘдёӢд»Јз Ғз»ҷеҮәдәҶеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- MPIеҸ‘йҖҒз»ҷеҮәдәҶеҲҶж®өй”ҷиҜҜ
- еҲ—иЎЁз»ҷеҮәдәҶз»ҶеҲҶй”ҷиҜҜ
жңҖж–°й—®йўҳ
- жҲ‘еҶҷдәҶиҝҷж®өд»Јз ҒпјҢдҪҶжҲ‘ж— жі•зҗҶи§ЈжҲ‘зҡ„й”ҷиҜҜ
- жҲ‘ж— жі•д»ҺдёҖдёӘд»Јз Ғе®һдҫӢзҡ„еҲ—иЎЁдёӯеҲ йҷӨ None еҖјпјҢдҪҶжҲ‘еҸҜд»ҘеңЁеҸҰдёҖдёӘе®һдҫӢдёӯгҖӮдёәд»Җд№Ҳе®ғйҖӮз”ЁдәҺдёҖдёӘз»ҶеҲҶеёӮеңәиҖҢдёҚйҖӮз”ЁдәҺеҸҰдёҖдёӘз»ҶеҲҶеёӮеңәпјҹ
- жҳҜеҗҰжңүеҸҜиғҪдҪҝ loadstring дёҚеҸҜиғҪзӯүдәҺжү“еҚ°пјҹеҚўйҳҝ
- javaдёӯзҡ„random.expovariate()
- Appscript йҖҡиҝҮдјҡи®®еңЁ Google ж—ҘеҺҶдёӯеҸ‘йҖҒз”өеӯҗйӮ®д»¶е’ҢеҲӣе»әжҙ»еҠЁ
- дёәд»Җд№ҲжҲ‘зҡ„ Onclick з®ӯеӨҙеҠҹиғҪеңЁ React дёӯдёҚиө·дҪңз”Ёпјҹ
- еңЁжӯӨд»Јз ҒдёӯжҳҜеҗҰжңүдҪҝз”ЁвҖңthisвҖқзҡ„жӣҝд»Јж–№жі•пјҹ
- еңЁ SQL Server е’Ң PostgreSQL дёҠжҹҘиҜўпјҢжҲ‘еҰӮдҪ•д»Һ第дёҖдёӘиЎЁиҺ·еҫ—第дәҢдёӘиЎЁзҡ„еҸҜи§ҶеҢ–
- жҜҸеҚғдёӘж•°еӯ—еҫ—еҲ°
- жӣҙж–°дәҶеҹҺеёӮиҫ№з•Ң KML ж–Ү件зҡ„жқҘжәҗпјҹ