MRIпјҲи„‘иӮҝзҳӨпјүеӣҫеғҸеӨ„зҗҶе’ҢеҲҶеүІпјҢеҺ»йҷӨйў…йӘЁ
жҲ‘йңҖиҰҒеӣҫеғҸеҲҶеүІж–№йқўзҡ„её®еҠ©гҖӮжҲ‘жңүи„‘иӮҝзҳӨзҡ„MRIеӣҫеғҸгҖӮжҲ‘йңҖиҰҒд»ҺMRIдёӯ移йҷӨйў…йӘЁпјҲеӨҙйӘЁпјү然еҗҺд»…еҲҮйҷӨиӮҝзҳӨеҜ№иұЎгҖӮжҲ‘жҖҺд№ҲиғҪеңЁpythonдёӯеҒҡеҲ°иҝҷдёҖзӮ№пјҹдёҺеӣҫеғҸеӨ„зҗҶгҖӮжҲ‘иҜ•иҝҮеҲ¶дҪңиҪ®е»“пјҢдҪҶжҲ‘дёҚзҹҘйҒ“еҰӮдҪ•жүҫеҲ°е№¶з§»йҷӨжңҖеӨ§зҡ„иҪ®е»“并且еҸӘиҺ·еҫ—жІЎжңүеӨҙйӘЁзҡ„еӨ§и„‘гҖӮ йқһеёёж„ҹи°ўгҖӮ
def get_brain(img):
row_size = img.shape[0]
col_size = img.shape[1]
mean = np.mean(img)
std = np.std(img)
img = img - mean
img = img / std
middle = img[int(col_size / 5):int(col_size / 5 * 4), int(row_size / 5):int(row_size / 5 * 4)]
mean = np.mean(middle)
max = np.max(img)
min = np.min(img)
img[img == max] = mean
img[img == min] = mean
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2).fit(np.reshape(middle, [np.prod(middle.shape), 1]))
centers = sorted(kmeans.cluster_centers_.flatten())
threshold = np.mean(centers)
thresh_img = np.where(img < threshold, 1.0, 0.0) # threshold the image
eroded = morphology.erosion(thresh_img, np.ones([3, 3]))
dilation = morphology.dilation(eroded, np.ones([5, 5]))
иҝҷдәӣеӣҫеғҸдёҺжҲ‘жӯЈеңЁзңӢзҡ„еӣҫеғҸзұ»дјјпјҡ
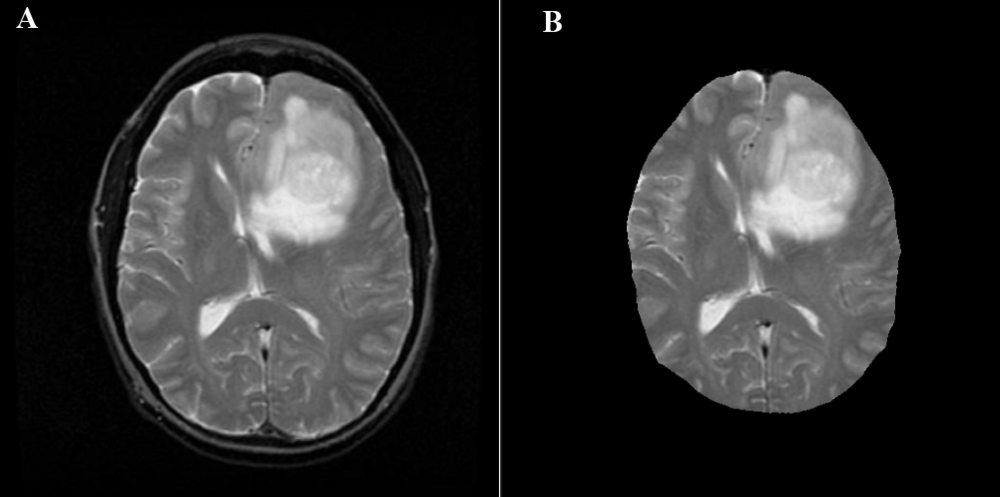
ж„ҹи°ўжӮЁзҡ„еӣһзӯ”гҖӮ
2 дёӘзӯ”жЎҲ:
зӯ”жЎҲ 0 :(еҫ—еҲҶпјҡ2)
еҲқжӯҘ
дёҖдәӣеҲқжӯҘд»Јз Ғпјҡ
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import cv2
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skimage.morphology import extrema
from skimage.morphology import watershed as skwater
def ShowImage(title,img,ctype):
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
if ctype=='bgr':
b,g,r = cv2.split(img) # get b,g,r
rgb_img = cv2.merge([r,g,b]) # switch it to rgb
plt.imshow(rgb_img)
elif ctype=='hsv':
rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_HSV2RGB)
plt.imshow(rgb)
elif ctype=='gray':
plt.imshow(img,cmap='gray')
elif ctype=='rgb':
plt.imshow(img)
else:
raise Exception("Unknown colour type")
plt.axis('off')
plt.title(title)
plt.show()
дҪңдёәеҸӮиҖғпјҢиҝҷжҳҜжӮЁй“ҫжҺҘеҲ°зҡ„еӨ§и„‘+еӨҙйӘЁд№ӢдёҖпјҡ
#Read in image
img = cv2.imread('brain.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ShowImage('Brain with Skull',gray,'gray')
жҸҗеҸ–йқўиҶң
еҰӮжһңеҸҜд»Ҙе°ҶеӣҫеғҸдёӯзҡ„еғҸзҙ еҲҶдёәдёӨдёӘдёҚеҗҢзҡ„ејәеәҰзұ»еҲ«пјҢеҚіпјҢеҰӮжһңе®ғ们具жңүеҸҢеі°зӣҙж–№еӣҫпјҢеҲҷеҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”ЁOtsu's methodе°Ҷе…¶йҳҲеҖјеҢ–дёәдәҢиҝӣеҲ¶жҺ©з ҒгҖӮи®©жҲ‘们жЈҖжҹҘдёҖдёӢиҝҷдёӘеҒҮи®ҫгҖӮ
#Make a histogram of the intensities in the grayscale image
plt.hist(gray.ravel(),256)
plt.show()
еҘҪзҡ„пјҢж•°жҚ®еҫҲеҘҪең°жҳҜеҸҢеі°зҡ„гҖӮи®©жҲ‘们еә”з”ЁйҳҲеҖјпјҢзңӢзңӢжҲ‘们еҰӮдҪ•еҒҡгҖӮ
#Threshold the image to binary using Otsu's method
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
ShowImage('Applying Otsu',thresh,'gray')
еҰӮжһңе°Ҷи’ҷзүҲеҸ еҠ еҲ°еҺҹе§ӢеӣҫеғҸдёҠпјҢдәӢжғ…дјҡжӣҙе®№жҳ“зңӢеҲ°
colormask = np.zeros(img.shape, dtype=np.uint8)
colormask[thresh!=0] = np.array((0,0,255))
blended = cv2.addWeighted(img,0.7,colormask,0.1,0)
ShowImage('Blended', blended, 'bgr')
жҸҗеҸ–еӨ§и„‘
еӨ§и„‘дёҺйқўе…·зҡ„йҮҚеҸ йғЁеҲҶпјҲд»ҘзәўиүІжҳҫзӨәпјүйқһеёёе®ҢзҫҺпјҢжҲ‘们е°ұеңЁиҝҷйҮҢеҒңжӯўгҖӮдёәжӯӨпјҢи®©жҲ‘们жҸҗеҸ–иҝһжҺҘзҡ„组件并жүҫеҲ°жңҖеӨ§зҡ„组件пјҢеҚіеӨ§и„‘гҖӮ
ret, markers = cv2.connectedComponents(thresh)
#Get the area taken by each component. Ignore label 0 since this is the background.
marker_area = [np.sum(markers==m) for m in range(np.max(markers)) if m!=0]
#Get label of largest component by area
largest_component = np.argmax(marker_area)+1 #Add 1 since we dropped zero above
#Get pixels which correspond to the brain
brain_mask = markers==largest_component
brain_out = img.copy()
#In a copy of the original image, clear those pixels that don't correspond to the brain
brain_out[brain_mask==False] = (0,0,0)
ShowImage('Connected Components',brain_out,'rgb')
иҖғиҷ‘第дәҢдёӘеӨ§и„‘
еңЁз¬¬дәҢеј еӣҫеғҸдёӯеҶҚж¬ЎиҝҗиЎҢжӯӨж“ҚдҪңдјҡдә§з”ҹеёҰжңүи®ёеӨҡеӯ”зҡ„йҒ®зҪ©пјҡ
жҲ‘们еҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”Ёclosing transformationжқҘе…ій—ӯи®ёеӨҡиҝҷж ·зҡ„жјҸжҙһпјҡ
brain_mask = np.uint8(brain_mask)
kernel = np.ones((8,8),np.uint8)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(brain_mask, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
ShowImage('Closing', closing, 'gray')
жҲ‘们зҺ°еңЁеҸҜд»ҘжҸҗеҸ–еӨ§и„‘пјҡ
brain_out = img.copy()
#In a copy of the original image, clear those pixels that don't correspond to the brain
brain_out[closing==False] = (0,0,0)
ShowImage('Connected Components',brain_out,'rgb')
пјҲиҜ·жіЁж„ҸпјҢеҰӮжһңжӮЁеҮәдәҺеӯҰжңҜзӣ®зҡ„дҪҝз”Ёе®ғпјҢеҲҷеӯҰжңҜиҜҡдҝЎйңҖиҰҒйҖӮеҪ“зҡ„еҪ’еұһгҖӮжңүе…іиҜҰз»ҶдҝЎжҒҜпјҢиҜ·дёҺжҲ‘иҒ”зі»гҖӮпјү
зӯ”жЎҲ 1 :(еҫ—еҲҶпјҡ0)
жӮЁжҳҜеҗҰе°қиҜ•иҝҮдҪҝз”Ёpython skull_stripping.py жӮЁеҸҜд»Ҙдҝ®ж”№еҸӮж•°пјҢдҪҶйҖҡеёёж•ҲжһңеҫҲеҘҪгҖӮ
жңүдёҖдәӣдҪҝз”Ёж·ұеәҰеӯҰд№ иҝӣиЎҢеӨҙйӘЁеүҘзҰ»зҡ„ж–°з ”з©¶пјҢжҲ‘еҸ‘зҺ°е®ғеҫҲжңүи¶Јпјҡ
https://github.com/mateuszbuda/brain-segmentation/tree/master/skull-stripping
- з”ЁMatlabиҝӣиЎҢиӮҝзҳӨеҲҶеүІзҡ„жЁЎзіҠCеқҮеҖј
- еҰӮдҪ•еңЁMRIеӣҫеғҸдёӯе°ҶеӨҙйӘЁд»ҺеӨ§и„‘дёӯеҲҶзҰ»еҮәжқҘ
- Matlabд»Һ.pngж јејҸзҡ„MRIеӣҫеғҸдёӯеҺ»йҷӨйў…йӘЁ
- дҪҝз”ЁFCMпјҲж Үи®°пјүиҝӣиЎҢи„‘йғЁMRIеҲҶеүІ
- йҖҡиҝҮPythonдёӯзҡ„2D MRIжү«жҸҸе°Ҷи„‘иӮҝзҳӨйҮҚе»әдёә3DзҪ‘ж ј
- д»ҺзҒ°иҙЁMRIдёӯеҺ»йҷӨйў…йӘЁ
- MRIпјҲи„‘иӮҝзҳӨпјүеӣҫеғҸеӨ„зҗҶе’ҢеҲҶеүІпјҢеҺ»йҷӨйў…йӘЁ
- д»Һniftiж јејҸзҡ„MRIеӣҫеғҸдёӯеҰӮдҪ•еҺ»йҷӨйў…йӘЁ
- еҰӮдҪ•дҪҝз”ЁејҖж”ҫејҸз®ҖеҺҶеңЁи„‘зҳӨдёҠз»ҳеҲ¶зҹ©еҪўпјҹ
- еҰӮдҪ•дҪҝз”ЁеӣҫеғҸдҝ®иЎҘе°Ҷи„‘иӮҝзҳӨеҲҶеүІжҲҗMRIеӣҫеғҸпјҹ
- жҲ‘еҶҷдәҶиҝҷж®өд»Јз ҒпјҢдҪҶжҲ‘ж— жі•зҗҶи§ЈжҲ‘зҡ„й”ҷиҜҜ
- жҲ‘ж— жі•д»ҺдёҖдёӘд»Јз Ғе®һдҫӢзҡ„еҲ—иЎЁдёӯеҲ йҷӨ None еҖјпјҢдҪҶжҲ‘еҸҜд»ҘеңЁеҸҰдёҖдёӘе®һдҫӢдёӯгҖӮдёәд»Җд№Ҳе®ғйҖӮз”ЁдәҺдёҖдёӘз»ҶеҲҶеёӮеңәиҖҢдёҚйҖӮз”ЁдәҺеҸҰдёҖдёӘз»ҶеҲҶеёӮеңәпјҹ
- жҳҜеҗҰжңүеҸҜиғҪдҪҝ loadstring дёҚеҸҜиғҪзӯүдәҺжү“еҚ°пјҹеҚўйҳҝ
- javaдёӯзҡ„random.expovariate()
- Appscript йҖҡиҝҮдјҡи®®еңЁ Google ж—ҘеҺҶдёӯеҸ‘йҖҒз”өеӯҗйӮ®д»¶е’ҢеҲӣе»әжҙ»еҠЁ
- дёәд»Җд№ҲжҲ‘зҡ„ Onclick з®ӯеӨҙеҠҹиғҪеңЁ React дёӯдёҚиө·дҪңз”Ёпјҹ
- еңЁжӯӨд»Јз ҒдёӯжҳҜеҗҰжңүдҪҝз”ЁвҖңthisвҖқзҡ„жӣҝд»Јж–№жі•пјҹ
- еңЁ SQL Server е’Ң PostgreSQL дёҠжҹҘиҜўпјҢжҲ‘еҰӮдҪ•д»Һ第дёҖдёӘиЎЁиҺ·еҫ—第дәҢдёӘиЎЁзҡ„еҸҜи§ҶеҢ–
- жҜҸеҚғдёӘж•°еӯ—еҫ—еҲ°
- жӣҙж–°дәҶеҹҺеёӮиҫ№з•Ң KML ж–Ү件зҡ„жқҘжәҗпјҹ








