iOS - 圆形渐变
我正在尝试绘制圆形渐变。
let backgroundView:UIView = UIView()
let backgroundLayer:CAShapeLayer = CAShapeLayer()
let gradient:CAGradientLayer = CAGradientLayer()
...
backgroundLayer.frame = CGRectMake(0, 0, backgroundDiameter, backgroundDiameter)
backgroundLayer.backgroundColor = UIColor.clearColor().CGColor
backgroundLayer.strokeColor = backgroundStrokeColor
backgroundLayer.fillColor = backgroundFillColor
gradient.colors = [UIColor(red: 0.5, green: 0.5, blue: 0.9, alpha: 1.0).CGColor,
UIColor(red: 0.9, green: 0.9, blue: 0.3, alpha: 1.0).CGColor]
gradient.locations = [0.01, 0.8]
gradient.frame = backgroundLayer.frame
backgroundView.frame = CGRectMake(0, 0, backgroundDiameter, backgroundDiameter)
backgroundView.backgroundColor = UIColor.clearColor()
backgroundView.center = ringControlCenter
backgroundLayer.insertSublayer(gradient, atIndex: 1)
backgroundLayer.path = CGPathCreateWithEllipseInRect(backgroundLayer.frame, nil)
backgroundView.layer.addSublayer(backgroundLayer)
self.addSubview(backgroundView)
然而,渐变似乎没有受到以下因素的影响:
backgroundLayer.path = CGPathCreateWithEllipseInRect(backgroundLayer.frame, nil)
仍然有它的初始形状。 有没有办法用椭圆形图层掩盖渐变而不使用CGContext *指令?
谢谢,
MG
6 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:11)
我已经在 Swift 3.x 中翻译了Leo library's,换句话说,好的 WCGradientCircleLayer 在目标C中写了(它完全正常工作)如预期的那样)
import UIKit
class WCGraintCircleLayer: CALayer {
override init () {
super.init()
}
convenience init(bounds:CGRect,position:CGPoint,fromColor:UIColor,toColor:UIColor,linewidth:CGFloat,toValue:CGFloat) {
self.init()
self.bounds = bounds
self.position = position
let colors : [UIColor] = self.graint(fromColor: fromColor, toColor:toColor, count:4)
for i in 0..<colors.count-1 {
let graint = CAGradientLayer()
graint.bounds = CGRect(origin:CGPoint.zero, size: CGSize(width:bounds.width/2,height:bounds.height/2))
let valuePoint = self.positionArrayWith(bounds: self.bounds)[i]
graint.position = valuePoint
print("iesimo graint position: \(graint.position)")
let fromColor = colors[i]
let toColor = colors[i+1]
let colors : [CGColor] = [fromColor.cgColor,toColor.cgColor]
let stopOne: CGFloat = 0.0
let stopTwo: CGFloat = 1.0
let locations : [CGFloat] = [stopOne,stopTwo]
graint.colors = colors
graint.locations = locations as [NSNumber]? // with Swift 2 and Swift 3 you can cast directly a `CGFloat` value to `NSNumber` and back
graint.startPoint = self.startPoints()[i]
graint.endPoint = self.endPoints()[i]
self.addSublayer(graint)
//Set mask
let shapelayer = CAShapeLayer()
let rect = CGRect(origin:CGPoint.zero,size:CGSize(width:self.bounds.width - 2 * linewidth,height: self.bounds.height - 2 * linewidth))
shapelayer.bounds = rect
shapelayer.position = CGPoint(x:self.bounds.width/2,y: self.bounds.height/2)
shapelayer.strokeColor = UIColor.blue.cgColor
shapelayer.fillColor = UIColor.clear.cgColor
shapelayer.path = UIBezierPath(roundedRect: rect, cornerRadius: rect.width/2).cgPath
shapelayer.lineWidth = linewidth
shapelayer.lineCap = kCALineCapRound
shapelayer.strokeStart = 0.010
let finalValue = (toValue*0.99)
shapelayer.strokeEnd = finalValue//0.99;
self.mask = shapelayer
}
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
func layerWithWithBounds(bounds:CGRect, position:CGPoint, fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, linewidth : CGFloat,toValue:CGFloat) -> WCGraintCircleLayer {
let layer = WCGraintCircleLayer(bounds: bounds,position: position,fromColor:fromColor, toColor: toColor,linewidth: linewidth,toValue:toValue )
return layer
}
func graint(fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, count:Int) -> [UIColor]{
var fromR:CGFloat = 0.0,fromG:CGFloat = 0.0,fromB:CGFloat = 0.0,fromAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
fromColor.getRed(&fromR,green: &fromG,blue: &fromB,alpha: &fromAlpha)
var toR:CGFloat = 0.0,toG:CGFloat = 0.0,toB:CGFloat = 0.0,toAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
toColor.getRed(&toR,green: &toG,blue: &toB,alpha: &toAlpha)
var result : [UIColor]! = [UIColor]()
for i in 0...count {
let oneR:CGFloat = fromR + (toR - fromR)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneG : CGFloat = fromG + (toG - fromG)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneB : CGFloat = fromB + (toB - fromB)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneAlpha : CGFloat = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneColor = UIColor.init(red: oneR, green: oneG, blue: oneB, alpha: oneAlpha)
result.append(oneColor)
print(oneColor)
}
return result
}
func positionArrayWith(bounds:CGRect) -> [CGPoint]{
let first = CGPoint(x:(bounds.width/4)*3,y: (bounds.height/4)*1)
let second = CGPoint(x:(bounds.width/4)*3,y: (bounds.height/4)*3)
let third = CGPoint(x:(bounds.width/4)*1,y: (bounds.height/4)*3)
let fourth = CGPoint(x:(bounds.width/4)*1,y: (bounds.height/4)*1)
print([first,second,third,fourth])
return [first,second,third,fourth]
}
func startPoints() -> [CGPoint] {
return [CGPoint.zero,CGPoint(x:1,y:0),CGPoint(x:1,y:1),CGPoint(x:0,y:1)]
}
func endPoints() -> [CGPoint] {
return [CGPoint(x:1,y:1),CGPoint(x:0,y:1),CGPoint.zero,CGPoint(x:1,y:0)]
}
func midColorWithFromColor(fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, progress:CGFloat) -> UIColor {
var fromR:CGFloat = 0.0,fromG:CGFloat = 0.0,fromB:CGFloat = 0.0,fromAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
fromColor.getRed(&fromR,green: &fromG,blue: &fromB,alpha: &fromAlpha)
var toR:CGFloat = 0.0,toG:CGFloat = 0.0,toB:CGFloat = 0.0,toAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
toColor.getRed(&toR,green: &toG,blue: &toB,alpha: &toAlpha)
let oneR = fromR + (toR - fromR) * progress
let oneG = fromG + (toG - fromG) * progress
let oneB = fromB + (toB - fromB) * progress
let oneAlpha = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha) * progress
let oneColor = UIColor.init(red: oneR, green: oneG, blue: oneB, alpha: oneAlpha)
return oneColor
}
// This is what you call if you want to draw a full circle.
func animateCircle(duration: TimeInterval) {
animateCircleTo(duration: duration, fromValue: 0.010, toValue: 0.99)
}
// This is what you call to draw a partial circle.
func animateCircleTo(duration: TimeInterval, fromValue: CGFloat, toValue: CGFloat){
// We want to animate the strokeEnd property of the circleLayer
let animation = CABasicAnimation(keyPath: "strokeEnd")
animation.isRemovedOnCompletion = true
// Set the animation duration appropriately
animation.duration = duration
// Animate from 0.010 (no circle) to 0.99 (full circle)
animation.fromValue = 0.010
animation.toValue = toValue
// Do an easeout. Don't know how to do a spring instead
//animation.timingFunction = CAMediaTimingFunction(name: kCAMediaTimingFunctionEaseOut)
animation.timingFunction = CAMediaTimingFunction(name: kCAMediaTimingFunctionEaseOut)
// Set the circleLayer's strokeEnd property to 0.99 now so that it's the
// right value when the animation ends.
let circleMask = self.mask as! CAShapeLayer
circleMask.strokeEnd = toValue
// Do the actual animation
circleMask.removeAllAnimations()
circleMask.add(animation, forKey: "animateCircle")
}
}
这是一个小例子,如何在Swift 3.x中使用:
let gradientRingLayer = WCGraintCircleLayer(bounds: CGRect(origin: CGPoint.zero,size:CGSize(width: 150, height: 150)), position:CGPoint(x: 200, y: 300),fromColor:UIColor.blue, toColor:UIColor.white, linewidth:4.0, toValue:0)
self.view.layer.addSublayer(gradientRingLayer)
let duration = 3.0
gradientRingLayer.animateCircleTo(duration: duration, fromValue: 0, toValue: 0.99)
这是 Swift 2.x:
中的代码import UIKit
class WCGraintCircleLayer: CALayer {
override init () {
super.init()
}
convenience init(bounds:CGRect,position:CGPoint,fromColor:UIColor,toColor:UIColor,linewidth:CGFloat,toValue:CGFloat) {
self.init()
self.bounds = bounds
self.position = position
let colors : [UIColor] = self.graintFromColor(fromColor, toColor:toColor, count:4)
for i in 0..<colors.count-1 {
let graint = CAGradientLayer()
graint.bounds = CGRectMake(0,0,CGRectGetWidth(bounds)/2,CGRectGetHeight(bounds)/2)
let valuePoint = self.positionArrayWithMainBounds(self.bounds)[i]
graint.position = valuePoint
print("iesimo graint position: \(graint.position)")
let fromColor = colors[i]
let toColor = colors[i+1]
let colors : [CGColorRef] = [fromColor.CGColor,toColor.CGColor]
let stopOne: CGFloat = 0.0
let stopTwo: CGFloat = 1.0
let locations : [CGFloat] = [stopOne,stopTwo]
graint.colors = colors
graint.locations = locations
graint.startPoint = self.startPoints()[i]
graint.endPoint = self.endPoints()[i]
self.addSublayer(graint)
//Set mask
let shapelayer = CAShapeLayer()
let rect = CGRectMake(0,0,CGRectGetWidth(self.bounds) - 2 * linewidth, CGRectGetHeight(self.bounds) - 2 * linewidth)
shapelayer.bounds = rect
shapelayer.position = CGPointMake(CGRectGetWidth(self.bounds)/2, CGRectGetHeight(self.bounds)/2)
shapelayer.strokeColor = UIColor.blueColor().CGColor
shapelayer.fillColor = UIColor.clearColor().CGColor
shapelayer.path = UIBezierPath(roundedRect: rect, cornerRadius: CGRectGetWidth(rect)/2).CGPath
shapelayer.lineWidth = linewidth
shapelayer.lineCap = kCALineCapRound
shapelayer.strokeStart = 0.010
let finalValue = (toValue*0.99)
shapelayer.strokeEnd = finalValue//0.99;
self.mask = shapelayer
}
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
func layerWithWithBounds(bounds:CGRect, position:CGPoint, fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, linewidth : CGFloat,toValue:CGFloat) -> WCGraintCircleLayer {
let layer = WCGraintCircleLayer(bounds: bounds,position: position,fromColor:fromColor, toColor: toColor,linewidth: linewidth,toValue:toValue )
return layer
}
func graintFromColor(fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, count:Int) -> [UIColor]{
var fromR:CGFloat = 0.0,fromG:CGFloat = 0.0,fromB:CGFloat = 0.0,fromAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
fromColor.getRed(&fromR,green: &fromG,blue: &fromB,alpha: &fromAlpha)
var toR:CGFloat = 0.0,toG:CGFloat = 0.0,toB:CGFloat = 0.0,toAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
toColor.getRed(&toR,green: &toG,blue: &toB,alpha: &toAlpha)
var result : [UIColor]! = [UIColor]()
for i in 0...count {
let oneR:CGFloat = fromR + (toR - fromR)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneG : CGFloat = fromG + (toG - fromG)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneB : CGFloat = fromB + (toB - fromB)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneAlpha : CGFloat = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneColor = UIColor.init(red: oneR, green: oneG, blue: oneB, alpha: oneAlpha)
result.append(oneColor)
print(oneColor)
}
return result
}
func positionArrayWithMainBounds(bounds:CGRect) -> [CGPoint]{
let first = CGPointMake((CGRectGetWidth(bounds)/4)*3, (CGRectGetHeight(bounds)/4)*1)
let second = CGPointMake((CGRectGetWidth(bounds)/4)*3, (CGRectGetHeight(bounds)/4)*3)
let third = CGPointMake((CGRectGetWidth(bounds)/4)*1, (CGRectGetHeight(bounds)/4)*3)
let fourth = CGPointMake((CGRectGetWidth(bounds)/4)*1, (CGRectGetHeight(bounds)/4)*1)
print([first,second,third,fourth])
return [first,second,third,fourth]
}
func startPoints() -> [CGPoint] {
return [CGPointMake(0,0),CGPointMake(1,0),CGPointMake(1,1),CGPointMake(0,1)]
}
func endPoints() -> [CGPoint] {
return [CGPointMake(1,1),CGPointMake(0,1),CGPointMake(0,0),CGPointMake(1,0)]
}
func midColorWithFromColor(fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, progress:CGFloat) -> UIColor {
var fromR:CGFloat = 0.0,fromG:CGFloat = 0.0,fromB:CGFloat = 0.0,fromAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
fromColor.getRed(&fromR,green: &fromG,blue: &fromB,alpha: &fromAlpha)
var toR:CGFloat = 0.0,toG:CGFloat = 0.0,toB:CGFloat = 0.0,toAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
toColor.getRed(&toR,green: &toG,blue: &toB,alpha: &toAlpha)
let oneR = fromR + (toR - fromR) * progress
let oneG = fromG + (toG - fromG) * progress
let oneB = fromB + (toB - fromB) * progress
let oneAlpha = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha) * progress
let oneColor = UIColor.init(red: oneR, green: oneG, blue: oneB, alpha: oneAlpha)
return oneColor
}
// This is what you call if you want to draw a full circle.
func animateCircle(duration: NSTimeInterval) {
animateCircleTo(duration, fromValue: 0.010, toValue: 0.99)
}
// This is what you call to draw a partial circle.
func animateCircleTo(duration: NSTimeInterval, fromValue: CGFloat, toValue: CGFloat){
// We want to animate the strokeEnd property of the circleLayer
let animation = CABasicAnimation(keyPath: "strokeEnd")
animation.removedOnCompletion = true
// Set the animation duration appropriately
animation.duration = duration
// Animate from 0.010 (no circle) to 0.99 (full circle)
animation.fromValue = 0.010
animation.toValue = toValue
// Do an easeout. Don't know how to do a spring instead
//animation.timingFunction = CAMediaTimingFunction(name: kCAMediaTimingFunctionEaseOut)
animation.timingFunction = CAMediaTimingFunction(name: kCAMediaTimingFunctionEaseOut)
// Set the circleLayer's strokeEnd property to 0.99 now so that it's the
// right value when the animation ends.
let circleMask = self.mask as! CAShapeLayer
circleMask.strokeEnd = toValue
// Do the actual animation
circleMask.removeAllAnimations()
circleMask.addAnimation(animation, forKey: "animateCircle")
}
}
这是一个小例子,如何在Swift 2.x中使用:
let gradientRingLayer = WCGraintCircleLayer(bounds: CGRectMake(0, 0, 150, 150), position:CGPointMake(200,300) ,fromColor:UIColor.blueColor(), toColor:UIColor.whiteColor(),linewidth:4.0, toValue:0)
self.view.layer.addSublayer(gradientRingLayer)
let duration = 3.0
gradientRingLayer.animateCircleTo(duration, fromValue: 0, toValue: 0.99)
这是快速复制/粘贴远程pastebin code
还可以使用动画:
答案 1 :(得分:4)
我碰巧访问了这个问题,并希望发表我的回答。
唯一需要做的就是使用CAShapeLayer设置Mask
[graintLayer setMask:shapeLayer]
我写了一个关于如何构建Circle Graint Layer的简单库
这是截图
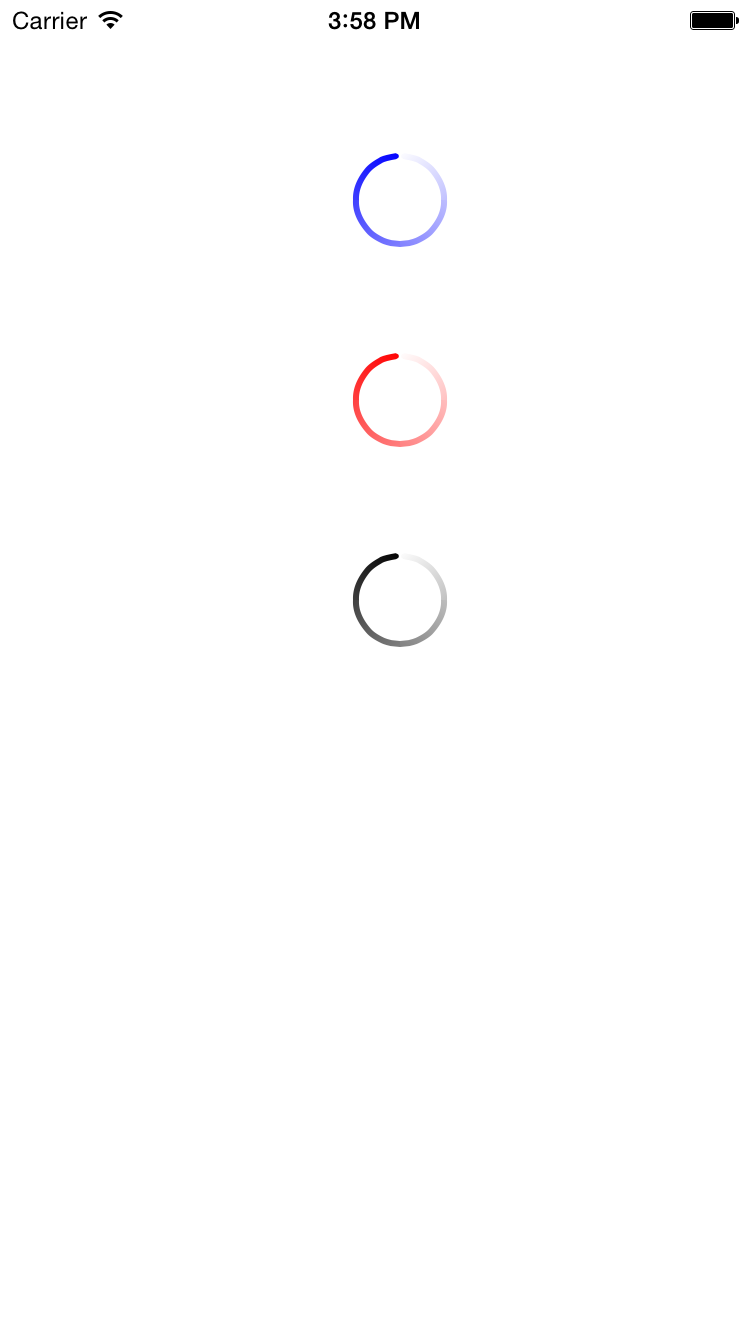
答案 2 :(得分:3)
如果您的backgroundLayer只是作为渐变图层的蒙版,请使用
gradient.mask = backgroundLayer
并将渐变添加到视图的图层
backgroundView.layer.addSublayer(gradient)
否则创建一个新的CAShapeLayer作为渐变
答案 3 :(得分:0)
以下Leo's library转换为Swift 3.感谢Alessandro Ornano的Swift 2.3翻译。
代码:
import UIKit
class WCGraintCircleLayer: CALayer {
override init () {
super.init()
}
convenience init(bounds:CGRect,position:CGPoint,fromColor:UIColor,toColor:UIColor,linewidth:CGFloat,toValue:CGFloat) {
self.init()
self.bounds = bounds
self.position = position
let colors : [UIColor] = self.graintFromColor(fromColor: fromColor, toColor:toColor, count:4)
for i in 0..<colors.count-1 {
let graint = CAGradientLayer()
graint.bounds = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: bounds.width/2, height: bounds.height/2)
let valuePoint = self.positionArrayWithMainBounds(bounds: self.bounds)[i]
graint.position = valuePoint
print("iesimo graint position: \(graint.position)")
let fromColor = colors[i]
let toColor = colors[i+1]
let colors : [CGColor] = [fromColor.cgColor,toColor.cgColor]
let stopOne: CGFloat = 0.0
let stopTwo: CGFloat = 1.0
let locations : [CGFloat] = [stopOne,stopTwo]
graint.colors = colors
graint.locations = locations as [NSNumber]?
graint.startPoint = self.startPoints()[i]
graint.endPoint = self.endPoints()[i]
self.addSublayer(graint)
//Set mask
let shapelayer = CAShapeLayer()
let rect = CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: bounds.width - 2 * linewidth, height: bounds.height - 2 * linewidth)
shapelayer.bounds = rect
shapelayer.position = CGPoint(x: bounds.width/2, y: bounds.height/2)
shapelayer.strokeColor = UIColor.blue.cgColor
shapelayer.fillColor = UIColor.clear.cgColor
shapelayer.path = UIBezierPath(roundedRect: rect, cornerRadius: rect.width/2).cgPath
shapelayer.lineWidth = linewidth
shapelayer.lineCap = kCALineCapRound
shapelayer.strokeStart = 0.010
let finalValue = (toValue*0.99)
shapelayer.strokeEnd = finalValue//0.99;
self.mask = shapelayer
}
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
fatalError("init(coder:) has not been implemented")
}
func layerWithWithBounds(bounds:CGRect, position:CGPoint, fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, linewidth : CGFloat,toValue:CGFloat) -> WCGraintCircleLayer {
let layer = WCGraintCircleLayer(bounds: bounds,position: position,fromColor:fromColor, toColor: toColor,linewidth: linewidth,toValue:toValue )
return layer
}
func graintFromColor(fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, count:Int) -> [UIColor]{
var fromR:CGFloat = 0.0,fromG:CGFloat = 0.0,fromB:CGFloat = 0.0,fromAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
fromColor.getRed(&fromR,green: &fromG,blue: &fromB,alpha: &fromAlpha)
var toR:CGFloat = 0.0,toG:CGFloat = 0.0,toB:CGFloat = 0.0,toAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
toColor.getRed(&toR,green: &toG,blue: &toB,alpha: &toAlpha)
var result : [UIColor]! = [UIColor]()
for i in 0...count {
let oneR:CGFloat = fromR + (toR - fromR)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneG : CGFloat = fromG + (toG - fromG)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneB : CGFloat = fromB + (toB - fromB)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneAlpha : CGFloat = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha)/CGFloat(count) * CGFloat(i)
let oneColor = UIColor.init(red: oneR, green: oneG, blue: oneB, alpha: oneAlpha)
result.append(oneColor)
print(oneColor)
}
return result
}
func positionArrayWithMainBounds(bounds:CGRect) -> [CGPoint]{
let first = CGPoint(x: (bounds.width/4)*3, y: (bounds.height/4)*1)
let second = CGPoint(x: (bounds.width/4)*3, y: (bounds.height/4)*3)
let third = CGPoint(x: (bounds.width/4)*1, y: (bounds.height/4)*3)
let fourth = CGPoint(x: (bounds.width/4)*1, y: (bounds.height/4)*1)
print([first,second,third,fourth])
return [first,second,third,fourth]
}
func startPoints() -> [CGPoint] {
return [CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0),CGPoint(x: 1, y: 0),CGPoint(x: 1, y: 1),CGPoint(x: 0, y: 1)]
}
func endPoints() -> [CGPoint] {
return [CGPoint(x: 1, y: 1),CGPoint(x: 0, y: 1),CGPoint(x: 0, y: 0),CGPoint(x: 1, y: 0)]
}
func midColorWithFromColor(fromColor:UIColor, toColor:UIColor, progress:CGFloat) -> UIColor {
var fromR:CGFloat = 0.0,fromG:CGFloat = 0.0,fromB:CGFloat = 0.0,fromAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
fromColor.getRed(&fromR,green: &fromG,blue: &fromB,alpha: &fromAlpha)
var toR:CGFloat = 0.0,toG:CGFloat = 0.0,toB:CGFloat = 0.0,toAlpha:CGFloat = 0.0
toColor.getRed(&toR,green: &toG,blue: &toB,alpha: &toAlpha)
let oneR = fromR + (toR - fromR) * progress
let oneG = fromG + (toG - fromG) * progress
let oneB = fromB + (toB - fromB) * progress
let oneAlpha = fromAlpha + (toAlpha - fromAlpha) * progress
let oneColor = UIColor.init(red: oneR, green: oneG, blue: oneB, alpha: oneAlpha)
return oneColor
}
// This is what you call if you want to draw a full circle.
func animateCircle(duration: TimeInterval) {
animateCircleTo(duration: duration, fromValue: 0.010, toValue: 0.99)
}
// This is what you call to draw a partial circle.
func animateCircleTo(duration: TimeInterval, fromValue: CGFloat, toValue: CGFloat){
// We want to animate the strokeEnd property of the circleLayer
let animation = CABasicAnimation(keyPath: "strokeEnd")
animation.isRemovedOnCompletion = true
// Set the animation duration appropriately
animation.duration = duration
// Animate from 0.010 (no circle) to 0.99 (full circle)
animation.fromValue = 0.010
animation.toValue = toValue
// Do an easeout. Don't know how to do a spring instead
//animation.timingFunction = CAMediaTimingFunction(name: kCAMediaTimingFunctionEaseOut)
animation.timingFunction = CAMediaTimingFunction(name: kCAMediaTimingFunctionEaseOut)
// Set the circleLayer's strokeEnd property to 0.99 now so that it's the
// right value when the animation ends.
let circleMask = self.mask as! CAShapeLayer
circleMask.strokeEnd = toValue
// Do the actual animation
circleMask.removeAllAnimations()
circleMask.add(animation, forKey: "animateCircle")
}
}
使用方法:
let gradientRingLayer = WCGraintCircleLayer(bounds: CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: 150, height: 150), position:CGPoint(x: 200, y: 300),fromColor:UIColor.blue, toColor:UIColor.white, linewidth:4.0, toValue:0)
self.view.layer.addSublayer(gradientRingLayer)
let duration = 3.0
gradientRingLayer.animateCircleTo(duration: duration, fromValue: 0, toValue: 0.99)
答案 4 :(得分:0)
我找到了一个不使用多个图层的简单答案,将多个图层混合可能会影响动画效果,通常应尽可能避免使用
。override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
let lineWidth: CGFloat = CGFloat(2)
let strokeColor: UIColor = UIColor.black
let startAngle: CGFloat = 0
let maxAngle: CGFloat = CGFloat(Double.pi * 2)
let lineCapStyle: CGLineCap = .round
let gradations = 255
let center = CGPoint(x: bounds.origin.x + bounds.size.width / 2, y: bounds.origin.y + bounds.size.height / 2)
let radius = (min(bounds.size.width, bounds.size.height) - lineWidth) / 2
for i in 1 ... gradations {
let percent0 = CGFloat(i - 1) / CGFloat(gradations)
let percent1 = CGFloat(i) / CGFloat(gradations)
let angle0 = startAngle + (maxAngle - startAngle) * percent0
let angle1 = startAngle + (maxAngle - startAngle) * percent1
let context = UIGraphicsGetCurrentContext()!
context.setLineWidth(lineWidth)
context.setLineCap(lineCapStyle)
let path = CGMutablePath()
path.addArc(center: center, radius: radius + lineWidth / 2, startAngle: angle0, endAngle: angle1, clockwise: true)
path.addArc(center: center, radius: radius - lineWidth / 2, startAngle: angle1, endAngle: angle0, clockwise: false)
path.closeSubpath()
let colors = [strokeColor.withAlphaComponent(percent0).cgColor, strokeColor.withAlphaComponent(percent1).cgColor]
let colorSpace = CGColorSpaceCreateDeviceRGB()
let colorLocations: [CGFloat] = [0.0, 1.0]
let gradient = CGGradient(colorsSpace: colorSpace, colors: colors as CFArray, locations: colorLocations)!
let startPoint = CGPoint.init(x: center.x + cos(angle0) * radius, y: center.y + sin(angle0) * radius)
let endPoint = CGPoint.init(x: center.x + cos(angle1) * radius, y: center.y + sin(angle1) * radius)
context.saveGState()
context.addPath(path)
context.clip()
context.drawLinearGradient(gradient, start: startPoint, end: endPoint, options: [])
context.restoreGState()
}
}
答案 5 :(得分:-1)
相关问题
最新问题
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?


