计算阶乘10 .. 100而不重复任何代码?
我可以通过使用for循环来实现它,但它太长了。我必须做大约10个for循环。
System.out.println("factorial of 10");
int fact = 1;
for (int x=1;x<=10;x++) {
fact=fact*x;
System.out.println(fact);
}
System.out.println(" factorial of 20 ");
double fact1 = 1;
for (double y=1;y<=20;y++){
fact1=fact1*y;
System.out.println(fact1);
}
3 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:2)
您可以使用递归方法计算factorials.Also在解决方案中根据您调整类型。像BigInteger或Long
public class Factorial {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int theNum, theFact;
System.out.println("This program computes the factorial " +
"of a number.");
System.out.print("Enter a number: ");
theNum=Console.in.readInt();
theFact = fact(theNum);
System.out.println(theNum + "! = " + theFact + ".");
}
static int fact(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return 1;
}
else {
return n * fact(n-1);
}
}
}
答案 1 :(得分:1)
您可以将每个计算的阶乘数放入数组,并通过检索数组的最后一个元素来计算新的阶乘值。但是,你知道,你可以计算多达12个!使用int类型因为13!,数字变得大于int的MAX_VALUE(2 ^ 31-1)。您可以使用BigInteger对象作为解决方案。
或者,如果您只需要计算这些特定数字的因子值,您可以调用递归函数,该函数就像上面的解决方案一样。
答案 2 :(得分:1)
使用Stirling approximation进行Gamma功能
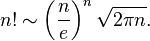
您可以使用此等式来完成这项工作。如果它没有循环,它就不是一种计算机语言。
编辑:或者您可以使用以下代码,无需任何显式循环(借用here)。
import javax.swing.Timer;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class Fac {
public static int fac(final int _n) {
final ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Integer>(1);
final Timer timer = new Timer(0, null);
timer.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
int result = 1;
int n = _n;
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
result *= n;
n--;
if(n == 0) {
try {
queue.put(result);
} catch(Exception ex) {
}
timer.stop();
}
}
});
timer.start();
int result = 0;
try {
result = queue.take();
} catch(Exception ex) {
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(fac(10));
}
}
相关问题
最新问题
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?