代理设计模式使用反射
我从以下链接中看到了以下代码:http://javapapers.com/design-patterns/proxy-design-pattern/
我无法理解以下代码:
Animal proxy = (Animal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(realSubject.getClass()
.getClassLoader(), realSubject.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new AnimalInvocationHandler(realSubject));
有人可以提供一些资源/指针来帮助我理解,因为我没有做任何关于反思的工作。
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
interface Animal {
public void getSound();
}
class Lion implements Animal {
public void getSound() {
System.out.println("Roar");
}
}
class AnimalInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private Object realSubject = null;
public AnimalInvocationHandler(Object realSubject) {
this.realSubject = realSubject;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method m, Object[] args) {
Object result = null;
try {
result = m.invoke(realSubject, args);
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
public class ProxyExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal realSubject = new Lion();
Animal proxy = (Animal) Proxy.newProxyInstance(realSubject.getClass()
.getClassLoader(), realSubject.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new AnimalInvocationHandler(realSubject));
proxy.getSound();
}
}
2 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:0)
这是什么意思?它创建一个新的Object(返回类型),使用类的ClassLoader和Interfaces进行代理。最后,它创建了一个新的AnimalInvocationHandler,然后委托(即调用)代理对象。
来自Proxy -
static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)
Returns an instance of a proxy class for the specified interfaces that dispatches method invocations to the specified invocation handler.
“代理人”包裹着“狮子”并像狮子一样行事,尽管它不是“狮子”。
最后,或许这张照片将澄清所涉及的关系 - 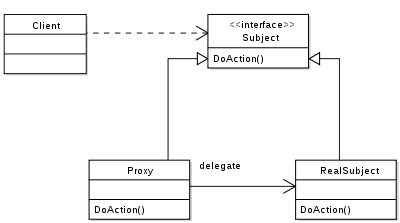
答案 1 :(得分:0)
问题的一部分可能是,正如所写,它似乎没有做任何非常有用的事情: - )
它设置了一个对象,proxy,它实现了Animal,但在源代码中没有可见的实际类定义。相反,对proxy上的任何方法的调用都会进入AnimalInvocationHandler.invoke方法。这是标准的java.lang.Proxy东西,通常在你有许多非常类似的方法实现时使用(相反,你有一段实现代码根据调用的方法做一些稍微不同的东西)。
这里的区别在于,invoke方法直接传递给底层对象上的匹配方法,没有添加任何有用的行为(我猜它会捕获任何异常,但我认为这不是预期的,它们只是吞下了大量的反射教学清晰度相关的东西)。我想这更像是一个真正的代理。
据推测,这个想法是你会在传递给真实方法之前或之后添加一些行为(即在m.invoke(realSubject, args);行的上方或下方) - 如果他们添加了评论说{{}会更加清楚1}}或其他什么。
相关问题
最新问题
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?