如何在IPython Notebook中编写LaTeX?
如何在IPython Notebook中显示LaTeX代码?
14 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:255)
IPython笔记本使用MathJax在html / markdown中呈现LaTeX。只需将您的LaTeX数学放在$$。
$$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}$$
或者您可以显示Python的LaTeX / Math输出,如notebook tour末尾所示:
from IPython.display import display, Math, Latex
display(Math(r'F(k) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x) e^{2\pi i k} dx'))

答案 1 :(得分:119)
这出现在我正在进行的搜索中,通过更多搜索找到了更好的解决方案,IPython笔记本现在具有%%latex魔法,使得整个单元格Latex没有每个$$包装器线。
答案 2 :(得分:55)
LaTeX参考文献:
Udacity的博客有最佳 LaTeX Primer 我看过:它清楚地展示了如何使用LaTeX命令轻松阅读,而且容易记住! 强烈推荐。
This Link has Excellent Examples 显示代码和渲染结果!
您可以使用此站点快速了解如何通过示例编写LaTeX。
并且,这是一个快速Reference for LaTeX命令/符号。
总结:在Jupyter / IPython中表示LaTeX的各种方法:
Markdown CellExamples:
内联,换入:$
The equation used depends on whether the the value of
$Vmax$ is R, G, or B.
阻止,换入:$$
$$H← 0 + \frac{30(G−B)}{Vmax−Vmin} , if Vmax = R$$
阻止,换入:\begin{equation} 和\end{equation}
\begin{equation}
H← 60 + \frac{30(B−R)}{Vmax−Vmin} , if Vmax = G
\end{equation}
阻止,换入:\begin{align} 和\end{align}
\begin{align}
H←120 + \frac{30(R−G)}{Vmax−Vmin} , if Vmax = B
\end{align}
Examples:
LaTex Cell: %%latex magic命令将整个单元转换为 LaTeX Cell < / p>
%%latex
\begin{align}
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{align}
数学对象传入原始LaTeX字符串:
from IPython.display import Math
Math(r'F(k) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x) e^{2\pi i k} dx')
乳胶类。注意:您必须自己包含分隔符。这允许您使用其他LaTeX模式,例如eqnarray:
from IPython.display import Latex
Latex(r"""\begin{eqnarray}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{eqnarray}""")
Docs for 原始单元格:
(对不起,这里没有例子,只是文档)
原始细胞 原始单元格提供了一个可以直接写入输出的位置。笔记本不评估原始单元格。当通过
nbconvert时,原始单元格以未修改的目标格式到达。例如,这允许您将完整的LaTeX键入原始单元格,只有在nbconvert转换后才由LaTeX呈现。
其他文档:
对于Markdown Cells,引自Jupyter Notebook docs:
在Markdown单元格中,您还可以使用标准的LaTeX表示法以简单的方式包含数学: $ ... $用于内联数学和 $$ ... $$用于显示数学即可。执行Markdown单元格时,LaTeX部分会自动在HTML输出中呈现为具有高质量排版的方程式。这可以通过MathJax实现,它支持大量的LaTeX功能
LaTeX和AMS-LaTeX(amsmath包)定义的标准数学环境也有效,例如 \ begin {equation} ... \ end {equation} 和 \ begin {对齐} ... \ {端对齐} 即可。新的LaTeX宏可以使用标准方法定义,例如\ newcommand,通过将它们放在Markdown单元格中的数学分隔符之间的任何位置。然后,在整个IPython会话的其余部分都可以使用这些定义。
答案 3 :(得分:30)
如果您希望数学出现在一行中,请使用$$,例如
$$a = b + c$$ (line break after the equation)
如果您在数学后不需要换行符,请使用单个美元符号$,例如
$a = b + c$ (no line break after the equation)
答案 4 :(得分:20)
您可以选择要标记的单元格,然后编写由mathjax解释的乳胶代码,如上面的响应者之一所述。
或者,iPython笔记本教程的Latex部分很好地解释了这一点。
您可以这样做:
from IPython.display import Latex
Latex(r"""\begin{eqnarray}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{eqnarray}""")
或者这样做:
%%latex
\begin{align}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{align}
在此link
中找到更多信息答案 5 :(得分:9)
答案 6 :(得分:7)
因为即使在使用%% latex关键字或$ .. $限制器之后我也无法使用Code中的所有latex命令,我安装了nbextensions,我可以在Markdown中使用latex命令。按照此处的说明操作后:the dup2() man page然后重新启动Jupyter然后重新启动localhost:8888 / nbextensions,然后激活&#34; Latep Environment for Jupyter&#34;,我可以运行许多Latex命令。示例如下:https://github.com/ipython-contrib/IPython-notebook-extensions/blob/master/README.md
\section{First section}
\textbf{Hello}
$
\begin{equation}
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
\end{equation}
$
\begin{itemize}
\item First item
\item Second item
\end{itemize}
\textbf{World}
如您所见,我仍然无法使用usepackage。但也许它将来会得到改善。
https://rawgit.com/jfbercher/latex_envs/master/doc/latex_env_doc.html
答案 7 :(得分:4)
minrk给出的答案(包括完整性)是好的,但我还有另外一种方式。
您还可以通过键入LaTeX作为文本单元格中的第一行,将整个单元格呈现为%%latex。如果您
- 想要更多控制,
- 想要的不仅仅是数学环境,
- 或者如果你打算在一个单元格中写下很多数学。
minrk回答:
IPython笔记本使用MathJax进行渲染 LaTeX里面的html / markdown。只需将您的LaTeX数学放在
中$$。$$c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}$$
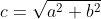
或者您可以从Python中显示LaTeX / Math输出 notebook tour的结尾:
from IPython.display import display, Math, Latex display(Math(r'F(k) = \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} f(x) e^{2\pi i k} dx'))

答案 8 :(得分:3)
您需要将它们括在美元符号中。
- 要向左对齐,请使用一个美元符号。
$P(A)=\frac{n(A)}{n(U)}$
- 要对齐中心,请使用双美元($$)符号。
$$P(A)=\frac{n(A)}{n(U)}$$
-
对
\limits,\lim和\sum使用\int可以在每个符号的顶部和底部添加限制。 -
使用反斜杠转义LaTeX特殊词,例如数学符号,拉丁词,文本等。
尝试这个。
$$\overline{x}=\frac{\sum \limits _{i=1} ^k f_i x_i}{n} \text{, where } n=\sum \limits _{i=1} ^k f_i $$
- 矩阵
- Piecewise函数
$$
\begin{align}
\text{Probability density function:}\\
\begin{cases}
\frac{1}{b-a}&\text{for $x\in[a,b]$}\\
0&\text{otherwise}\\
\end{cases}
\\
\text{Cumulative distribution function:}\\
\begin{cases}
0&\text{for $x<a$}\\
\frac{x-a}{b-a}&\text{for $x\in[a,b)$}\\
1&\text{for $x\ge b$}\\
\end{cases}
\end{align}
$$
上面的代码将创建它。
如果您想知道如何在方程式中添加编号并对齐方程式,请阅读this article for details。
答案 9 :(得分:2)
如果您的主要目标是进行数学运算,SymPy会为看起来很棒的功能性乳胶表达提供an excellent approach。
答案 10 :(得分:1)
直接在Markdown单元中使用LaTeX语法对我有用。我正在使用Jypiter 4.4.0。
我坚持,我不必使用%%latex魔术命令,只需使用一个markdown单元格即可:
\begin{align}
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{B}} -\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{E}}}{\partial t} & = \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{\mathbf{j}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{E}} & = 4 \pi \rho \\
\nabla \times \vec{\mathbf{E}}\, +\, \frac1c\, \frac{\partial\vec{\mathbf{B}}}{\partial t} & = \vec{\mathbf{0}} \\
\nabla \cdot \vec{\mathbf{B}} & = 0
\end{align}
渲染至:
答案 11 :(得分:0)
我有一天用colab遇到了这个问题。而且我发现最轻松的方法是在打印之前运行此代码。一切都像魅力一样。
from IPython.display import Math, HTML
def load_mathjax_in_cell_output():
display(HTML("<script src='https://www.gstatic.com/external_hosted/"
"mathjax/latest/MathJax.js?config=default'></script>"))
get_ipython().events.register('pre_run_cell', load_mathjax_in_cell_output)
import sympy as sp
sp.init_printing()
结果如下:
答案 12 :(得分:0)
我正在使用Jupyter笔记本。 我不得不写
%%latex
$sin(x)/x$
获取LaTex字体。
答案 13 :(得分:0)
当您想要控制文档序言时的另一种解决方案。写一个完整的文档,发送到系统latex,将pdf转成png,使用IPython.display加载显示。
import tempfile
import os.path
import subprocess
from IPython.display import Image, display
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory(prefix="texinpy_") as tmpdir:
path = os.path.join(tmpdir, "document.tex")
with open(path, 'w') as fp:
fp.write(r"""
\documentclass[12pt]{standalone}
\begin{document}
\LaTeX{}
\end{document}
""")
subprocess.run(["lualatex", path], cwd=tmpdir)
subprocess.run(["pdftocairo", "-singlefile", "-transp", "-r", "100", "-png", "document.pdf", "document"], cwd=tmpdir)
im = Image(filename=os.path.join(tmpdir, "document.png"))
display(im)
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?





