让导航中的 DialogFragment 在弹出返回堆栈时不会消失
我有 FragmentA、FragmentB 和 DialogFragment(BottomDialogFragment)。 I 我将它们缩写为 A、B 和 D
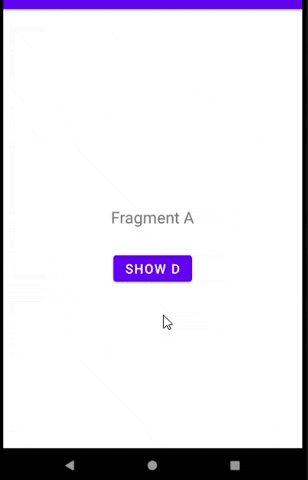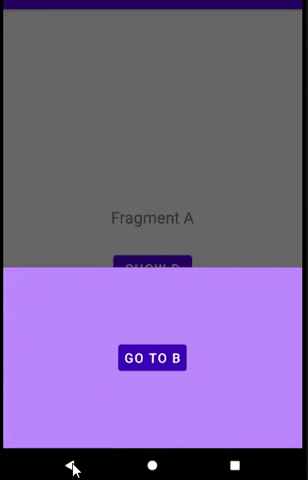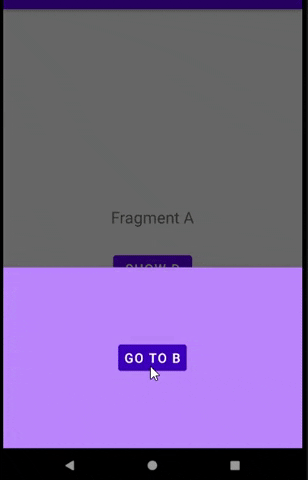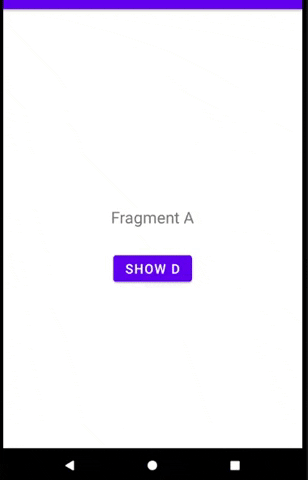
D 将在 A 中的按钮被点击后显示。意思是A -> D
B 将在 D 中的按钮被点击后显示。意思是D -> B
我在 navigation.xml 中配置它们
<fragment
android:id="@+id/A"
android:name="com.example.A">
<action
android:id="@+id/A_D"
app:destination="@id/D" />
</fragment>
<dialog
android:id="@+id/D"
android:name="com.example.D">
<action
android:id="@+id/D_B"
app:destination="@id/B" />
</dialog>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/B"
android:name="com.example.B">
</fragment>
现在当我点击A中的按钮时,片段将跳转到D。
然后我点击D中的按钮,片段将跳转到B。
但是当我在 B 中弹出导航堆栈时,它会返回到 A,并且 D 不会显示。 >
我该怎么办?我希望 D 仍然存在于 A 的表面。
3 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:2)
我该怎么办?我希望 D 仍然存在于 A 的表面。
到目前为止,这是不可能的,因为对话框是在与活动/片段不同的窗口中处理的;因此它们的返回堆栈的处理方式不同这是因为 Dialog 实现了 FloatingWindow interface。
检查 this answer 以获得更多说明。
但是要回答您的问题,请记住两种方法:
- 方法 1: 将片段
B更改为DailogFragment,在这种情况下,B和D都是对话框,因此当您将堆栈从B返回到D,您仍会看到D显示。 - 方法 2: 如果您从
B返回到D,则设置一个标志,如果是,则重新显示D.
实际上,方法 2 并不是那么好,因为当您从 D 转到 D 时,它不会将 B 保留在后堆栈中;这只是一种解决方法;当它从 B 返回到 D 时,用户也会看到对话转换/淡入淡出动画;所以这根本不自然。所以,这里只讨论方法一。
方法 1 的详细信息:
优点:
- 这是非常自然的,并且会保持您想要的后堆栈。
缺点:
DialogFragment B的窗口比普通片段/活动有限。B不再是普通片段,而是DialogFragment,因此您可能会遇到一些其他限制。
解决B窗口受限的问题,可以使用以下主题:
<style name="DialogTheme" parent="Theme.MyApp">
<item name="android:windowNoTitle">true</item>
<item name="android:windowFullscreen">false</item>
<item name="android:windowIsFloating">false</item>
</style>
其中 Theme.MyApp 是您应用的主题。
并使用 B 将其应用于 getTheme():
class FragmentB : DialogFragment() {
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater,
container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
return layoutInflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_b, container, false)
}
override fun getTheme(): Int = R.style.DialogTheme
}
您还需要将导航图中的 B 更改为对话框:
<dialog
android:id="@+id/B"
android:name="com.example.B">
</dialog>
预览:
答案 1 :(得分:1)
有关完整的工作示例,请参阅此 link。
您需要利用 NavigationUI 全局操作(如 here 所述)才能“返回”导航到目的地。将此代码放入 main_graph xml:
<action android:id="@+id/action_global_fragmentD" app:destination="@id/fragmentD"/>
接下来,在您的活动中添加这些以赶回新闻:
class MainActivity: AppCompatActivity {
...
var backPressedListener: OnBackPressedListener? = null
override fun onBackPressed() {
super.onBackPressed()
backPressedListener?.backHaveBeenPressed()
}
}
interface OnBackPressedListener {
fun backHaveBeenPressed()
}
这就像swift中的委托
接下来在 FragmentB 中,添加以下内容:
class FragmentB: Fragment(), OnBackPressedListener {
override fun onCreateView(
inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?,
savedInstanceState: Bundle?
): View? {
// Inflate the layout for this fragment
(activity as MainActivity).backPressedListener = this
return inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_b, container, false)
}
override fun backHaveBeenPressed() {
// show Dialog
findNavController().navigate(R.id.action_global_fragmentD)
}
}
然后您可以根据需要导航回 DialogFragment。这种方法不使用 popBackStack,因为您的用例是一个自定义行为,不由 NavigationUI 框架处理(您需要实现它)。
答案 2 :(得分:0)
不需要使用 controller.popBack() 弹出堆栈,因为堆栈由导航库管理。请注意,堆栈在 LIFO 基础上运行,这就是 Fragment 消失的原因。
您需要添加更多导航图操作:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<navigation xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/navigation"
app:startDestination="@id/A">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/A"
android:name="com.example.A"
android:label="A" >
<action
android:id="@+id/action_A_to_D"
app:destination="@id/D" />
</fragment>
<dialog
android:id="@+id/D"
android:name="com.example.D"
android:label="D" >
<action
android:id="@+id/action_D_to_B"
app:destination="@id/B" />
<action
android:id="@+id/action_D_to_A"
app:destination="@id/A" />
</dialog>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/B"
android:name="com.example.B"
android:label="B" >
<action
android:id="@+id/action_B_to_D"
app:destination="@id/D" />
</fragment>
</navigation>
然后在您的对话框片段中添加以下内容:
确定/是:--
private fun doNav() {
NavHostFragment.findNavController(this).navigate(R.id.action_fragmentD_to_fragmentB)
}
对于取消/否:--
private fun doBackNav() {
NavHostFragment.findNavController(this).navigate(R.id.action_fragmentD_to_fragmentA)
}
最后在 B Fragment 中,覆盖 back press 按钮并执行:
Navigation.findNavController(requireView()).navigate(R.id.action_fragmentB_to_fragmentD)
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?