C ++性能挑战:整数到std :: string的转换
任何人都可以将我的整数性能提升到std :: string代码,链接如下吗?
已经有几个问题可以解释如何在C ++中将整数转换为std::string,例如this one,但所提供的解决方案都没有效率。
以下是一些可用于竞争的常用方法的编译就绪代码:
- “C ++方式”,使用stringstream:http://ideone.com/jh3Sa
- sprintf,SO-ers通常建议性能意识:http://ideone.com/82kwR
与popular belief相反,boost::lexical_cast有自己的实现(white paper),并且不使用stringstream和数字插入运算符。我真的希望看到它的性能比较,因为this other question suggests that it's miserable。
我自己的贡献,在桌面计算机上具有竞争力,并演示了一种在嵌入式系统上全速运行的方法,与依赖于整数模数的算法不同:
- Ben的算法:http://ideone.com/SsEUW
如果您想使用该代码,我会在简化的BSD许可下提供(允许商业使用,需要归属)。请问。
最后,函数ltoa是非标准的,但可以广泛使用。
- ltoa版本,适用于拥有提供它的编译器的任何人(ideone没有):http://ideone.com/T5Wim
我很快会将我的效果测量结果作为答案发布。
算法规则
- 提供将至少32位有符号和无符号整数转换为十进制的代码。
- 以
std::string生成输出。 - 没有与线程和信号不兼容的技巧(例如,静态缓冲区)。
- 您可以假设ASCII字符集。
- 确保在
INT_MIN上的二进制补码机上测试您的代码,其中绝对值无法表示。 - 理想情况下,输出应该与使用
stringstream,http://ideone.com/jh3Sa的规范C ++版本的字符字符相同,但任何可以理解为正确数字的内容也是正常的。 - 新:虽然您可以使用您想要进行比较的任何编译器和优化器选项(完全禁用除外),但代码还需要在VC ++ 2010和g ++下编译并提供正确的结果。
希望讨论
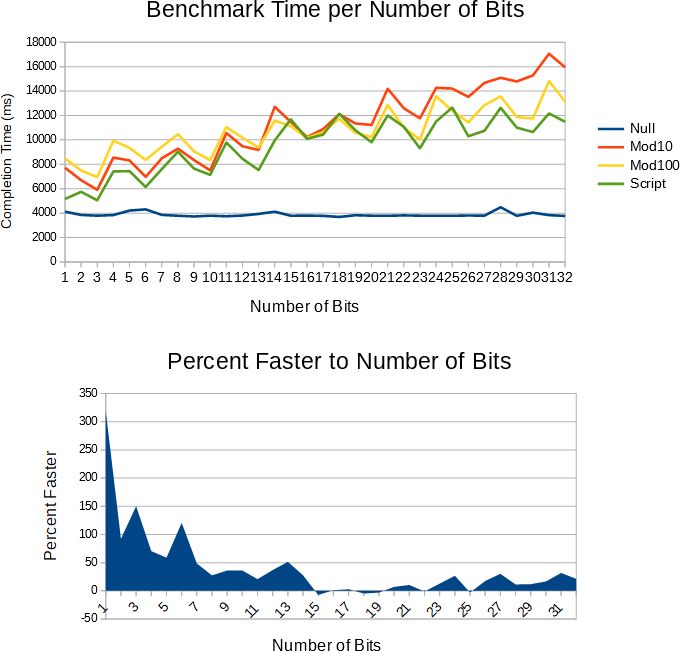
除了更好的算法之外,我还想在几个不同的平台和编译器上获得一些基准测试(让我们使用MB / s吞吐量作为我们的标准测量单位)。我相信我的算法的代码(我知道sprintf基准测试需要一些快捷方式 - 现在已修复)是标准的明确定义的行为,至少在ASCII假设下,但是如果你看到任何未定义的行为或输出无效的输入,请指出。
结论:
不同的算法对g ++和VC2010执行,可能是由于每个算法的std::string实现不同。 VC2010显然在NRVO方面做得更好,摆脱了价值回报只对gcc有帮助。
发现代码的性能比sprintf高出一个数量级。 ostringstream落后50倍甚至更多。
挑战的胜利者是user434507,他在gcc上生成的代码运行速度是我自己的350%。由于SO社区的突发奇想,其他条目将被关闭。
目前(最终?)速度冠军是:
- 对于gcc:user434507,速度比
sprintf快8倍:http://ideone.com/0uhhX - 对于Visual C ++:Timo,比
sprintf快15倍:http://ideone.com/VpKO3
13 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:33)
#include <string>
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
std::string& itostr(int n, std::string& s)
{
if(n==0)
{
s="0";
return s;
}
int sign = -(n<0);
unsigned int val = (n^sign)-sign;
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else
size=1;
}
}
size -= sign;
s.resize(size);
char* c = &s[0];
if(sign)
*c='-';
c += size-1;
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
return s;
}
std::string& itostr(unsigned val, std::string& s)
{
if(val==0)
{
s="0";
return s;
}
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else
size=1;
}
}
s.resize(size);
char* c = &s[size-1];
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
return s;
}
这会破坏禁止未对齐内存访问的系统(在这种情况下,通过*(short*)进行的第一个未对齐分配会导致段错误),但是否则应该非常好用。
要做的一件重要事情是尽量减少std::string的使用。 (讽刺,我知道。)例如,在Visual Studio中,即使在编译器选项中指定/ Ob2,也不会内联对std :: string方法的大多数调用。因此,即使是对std::string::clear()的调用也很简单,你可能期望它非常快,在将CRT作为静态库链接时可以占用100个时钟信号,而当作为DLL链接时可以多达300个时钟信号。
出于同样的原因,通过引用返回更好,因为它避免了赋值,构造函数和析构函数。
答案 1 :(得分:21)
啊,顺便说一句真棒挑战......我对此感到非常有趣。
我有两个提交的算法(如果你想跳过它,代码就在底部)。在我的比较中,我要求函数返回一个字符串,并且它可以处理int和unsigned int。将不构造字符串的事物与那些没有构建字符串的事物进行比较实际上没有意义。
第一个是一个有趣的实现,它不使用任何预先计算的查找表或显式除法/模数。这个与gcc的其他人以及msvc上除了Timo之外的所有人都很有竞争力(我在下面解释的原因很好)。第二种算法是我实际提交的最高性能。在我的测试中,它击败了gcc和msvc上的所有其他人。
我想我知道为什么MSVC上的一些结果非常好。 std :: string有两个相关的构造函数
std::string(char* str, size_t n)
和
std::string(ForwardIterator b, ForwardIterator e)
gcc为它们做同样的事情......就是它使用第二个来实现第一个。第一个构造函数可以比这更有效地实现,MSVC也是如此。这样做的另一个好处是,在某些情况下(比如我的快速代码和Timo代码),可以内联字符串构造函数。事实上,只是在MSVC中切换这些构造函数几乎是我的代码的2倍差异。
我的表现测试结果:
代码来源:
- Voigt
- Timo
- ergosys
- user434507
- user-voigt-timo
- hopman-fun
- hopman-fast
gcc 4.4.5 -O2 on Ubuntu 10.10 64-bit,Core i5
hopman_fun: 124.688 MB/sec --- 8.020 s hopman_fast: 137.552 MB/sec --- 7.270 s voigt: 120.192 MB/sec --- 8.320 s user_voigt_timo: 97.9432 MB/sec --- 10.210 s timo: 120.482 MB/sec --- 8.300 s user: 97.7517 MB/sec --- 10.230 s ergosys: 101.42 MB/sec --- 9.860 s
MSVC 2010 64位/ Ox on Windows 7 64位,Core i5
hopman_fun: 127 MB/sec --- 7.874 s hopman_fast: 259 MB/sec --- 3.861 s voigt: 221.435 MB/sec --- 4.516 s user_voigt_timo: 195.695 MB/sec --- 5.110 s timo: 253.165 MB/sec --- 3.950 s user: 212.63 MB/sec --- 4.703 s ergosys: 78.0518 MB/sec --- 12.812 s
以下是ideone的一些结果和测试/时间框架
http://ideone.com/XZRqp
请注意,ideone是一个32位环境。我的两种算法都受此影响,但是hopman_fast至少仍然具有竞争性。
请注意,对于那些不构造字符串的人,我添加了以下函数模板:
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T t) {
std::string ret;
itostr(t, ret);
return ret;
}
现在我的代码......首先是有趣的一个:
// hopman_fun
template <typename T>
T reduce2(T v) {
T k = ((v * 410) >> 12) & 0x000F000F000F000Full;
return (((v - k * 10) << 8) + k);
}
template <typename T>
T reduce4(T v) {
T k = ((v * 10486) >> 20) & 0xFF000000FFull;
return reduce2(((v - k * 100) << 16) + (k));
}
typedef unsigned long long ull;
inline ull reduce8(ull v) {
ull k = ((v * 3518437209u) >> 45);
return reduce4(((v - k * 10000) << 32) + (k));
}
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T o) {
union {
char str[16];
unsigned short u2[8];
unsigned u4[4];
unsigned long long u8[2];
};
unsigned v = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
u8[0] = (ull(v) * 3518437209u) >> 45;
u8[0] = (u8[0] * 28147497672ull);
u8[1] = v - u2[3] * 100000000;
u8[1] = reduce8(u8[1]);
char* f;
if (u2[3]) {
u2[3] = reduce2(u2[3]);
f = str + 6;
} else {
unsigned short* k = u4[2] ? u2 + 4 : u2 + 6;
f = *k ? (char*)k : (char*)(k + 1);
}
if (!*f) f++;
u4[1] |= 0x30303030;
u4[2] |= 0x30303030;
u4[3] |= 0x30303030;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
return std::string(f, (str + 16) - f);
}
然后快速的那个:
// hopman_fast
struct itostr_helper {
static unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
std::string itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
return std::string(f, (str + 12) - f);
}
答案 2 :(得分:12)
问题中提供的代码的基准数据:
关于ideone(gcc 4.3.4):
- stringstreams:4.4 MB / s
- sprintf:25.0 MB / s
- mine (Ben Voigt):55.8 MB / s
- Timo:58.5 MB / s
- user434507:199 MB / s
- user434507's Ben-Timo-507 hybrid:263 MB / s
Core i7,Windows 7 64位,8 GB RAM,Visual C ++ 2010 32位:
cl /Ox /EHsc
- stringstreams:3.39 MB / s,3.67 MB / s
- sprintf:16.8 MB / s,16.2 MB / s
- 我的:194 MB / s,207 MB / s(启用PGO:250 MB / s)
Core i7,Windows 7 64位,8 GB RAM,64位Visual C ++:
cl /Ox /EHsc
- stringstreams:4.42 MB / s,4.92 MB / s
- sprintf:21.0 MB / s,20.8 MB / s
- 我的:238 MB / s,228 MB / s
Core i7,Windows 7 64位,8 GB RAM,cygwin gcc 4.3.4:
g++ -O3
- stringstreams:2.19 MB / s,2.17 MB / s
- sprintf:13.1 MB / s,13.4 MB / s
- 我的:30.0 MB / s,30.2 MB / s
编辑:我会添加自己的答案,但问题已经关闭,所以我在这里添加。 :)我编写了自己的算法,并设法对Ben的代码进行了不错的改进,虽然我只在MSVC 2010中进行了测试。我还对目前为止提供的所有实现进行了基准测试,使用了Ben的原始版本中的相同测试设置。码。 - 蒂莫
英特尔Q9450,Win XP 32位,MSVC 2010
cl /O2 /EHsc
- stringstream:2.87 MB / s
- sprintf:16.1 MB / s
- Ben:202 MB / s
- Ben(无符号缓冲区):82.0 MB / s
- ergosys(更新版本):64.2 MB / s
- user434507:172 MB / s
- Timo:241 MB / s
-
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
static const int BUFFER_SIZE = 11;
std::string itostr(int val)
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *it = &buf[BUFFER_SIZE-2];
if(val>=0) {
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*val],2);
if(val<10)
it++;
} else {
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[-2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[-2*val],2);
if(val<=-10)
it--;
*it = '-';
}
return std::string(it,&buf[BUFFER_SIZE]-it);
}
std::string itostr(unsigned int val)
{
char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
char *it = (char*)&buf[BUFFER_SIZE-2];
int div = val/100;
while(div) {
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*(val-div*100)],2);
val = div;
it-=2;
div = val/100;
}
memcpy(it,&digit_pairs[2*val],2);
if(val<10)
it++;
return std::string((char*)it,(char*)&buf[BUFFER_SIZE]-(char*)it);
}
答案 3 :(得分:9)
虽然我们在这里得到的算法信息非常好,但我认为问题是“破碎”,我会解释为什么我这么想:
该问题要求考虑int - &gt; std::string转换的效果,并且在比较常用方法(例如不同的字符串流)时,此可能会引起关注实现或boost :: lexical_cast。但是,当要求新代码(一种专门的算法)来执行此操作时,它没有意义。原因是int2string总是涉及来自std :: string的堆分配,如果我们试图挤出转换算法的最后一个,我认为将这些测量与std完成的堆分配混合起来是不合理的: :串。如果我想进行高性能转换,我将总是使用固定大小的缓冲区,当然永远不会在堆上分配任何内容!
总而言之,我认为时间应该分开:
- 首先,最快(int - &gt;固定缓冲区)转换。
- 第二,(固定缓冲区 - &gt; std :: string)复制的时间。
- 第三,检查std :: string分配如何直接用作缓冲区,以保存复制。
这些方面不应该在一个时间内混淆,恕我直言。
答案 4 :(得分:6)
我无法在VS下测试,但这似乎比你的g ++代码要快,大约10%。它可能会被调整, 选择的决策值是猜测。只有,抱歉。
typedef unsigned buf_t;
static buf_t * reduce(unsigned val, buf_t * stp) {
unsigned above = val / 10000;
if (above != 0) {
stp = reduce(above, stp);
val -= above * 10000;
}
buf_t digit = val / 1000;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 1000;
digit = val / 100;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 100;
digit = val / 10;
*stp++ = digit + '0';
val -= digit * 10;
*stp++ = val + '0';
return stp;
}
std::string itostr(int input) {
buf_t buf[16];
if(input == INT_MIN) {
char buf2[16];
std::sprintf(buf2, "%d", input);
return std::string(buf2);
}
// handle negative
unsigned val = input;
if(input < 0)
val = -input;
buf[0] = '0';
buf_t* endp = reduce(val, buf+1);
*endp = 127;
buf_t * stp = buf+1;
while (*stp == '0')
stp++;
if (stp == endp)
stp--;
if (input < 0) {
stp--;
*stp = '-';
}
return std::string(stp, endp);
}
答案 5 :(得分:6)
更新了我的答案... modp_ufast ...
Integer To String Test (Type 1)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 1.1633sec Rate:206308473.0686nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 24.3629sec Rate: 9851045.8556nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 5.2389sec Rate: 45810870.7171nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 3.3126sec Rate: 72450283.7492nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 3.0828sec Rate: 77852152.8820nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 4.7349sec Rate: 50687912.9889nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 5.1689sec Rate: 46431985.1142nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 657777786 Time: 4.6169sec Rate: 51982554.6497nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
Integer To String Test(Type 2)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 0.5072sec Rate:473162716.4618nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 22.3483sec Rate: 10739062.9383nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 4.2471sec Rate: 56509024.3035nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.1683sec Rate:110683636.7123nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.7133sec Rate: 88454602.1423nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.8030sec Rate: 85623453.3872nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 3.4019sec Rate: 70549286.7776nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 660000000 Time: 2.7849sec Rate: 86178023.8743nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
Integer To String Test (type 3)
[modp_ufast]Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 1.6482sec Rate:145610315.7819nums/sec
[sprintf] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 20.7064sec Rate: 11590618.6109nums/sec
[karma] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.3036sec Rate: 55767734.3570nums/sec
[strtk] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 2.9297sec Rate: 81919227.9275nums/sec
[so ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 3.0278sec Rate: 79266003.8158nums/sec
[timo ] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.0631sec Rate: 59068204.3266nums/sec
[voigt] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.5616sec Rate: 52613393.0285nums/sec
[hopman] Numbers: 240000000 Total: 505625000 Time: 4.1248sec Rate: 58184194.4569nums/sec
Press any key to continue . . .
int ufast_utoa10(unsigned int value, char* str)
{
#define JOIN(N) N "0", N "1", N "2", N "3", N "4", N "5", N "6", N "7", N "8", N "9"
#define JOIN2(N) JOIN(N "0"), JOIN(N "1"), JOIN(N "2"), JOIN(N "3"), JOIN(N "4"), \
JOIN(N "5"), JOIN(N "6"), JOIN(N "7"), JOIN(N "8"), JOIN(N "9")
#define JOIN3(N) JOIN2(N "0"), JOIN2(N "1"), JOIN2(N "2"), JOIN2(N "3"), JOIN2(N "4"), \
JOIN2(N "5"), JOIN2(N "6"), JOIN2(N "7"), JOIN2(N "8"), JOIN2(N "9")
#define JOIN4 JOIN3("0"), JOIN3("1"), JOIN3("2"), JOIN3("3"), JOIN3("4"), \
JOIN3("5"), JOIN3("6"), JOIN3("7"), JOIN3("8"), JOIN3("9")
#define JOIN5(N) JOIN(N), JOIN(N "1"), JOIN(N "2"), JOIN(N "3"), JOIN(N "4"), \
JOIN(N "5"), JOIN(N "6"), JOIN(N "7"), JOIN(N "8"), JOIN(N "9")
#define JOIN6 JOIN5(), JOIN5("1"), JOIN5("2"), JOIN5("3"), JOIN5("4"), \
JOIN5("5"), JOIN5("6"), JOIN5("7"), JOIN5("8"), JOIN5("9")
#define F(N) ((N) >= 100 ? 3 : (N) >= 10 ? 2 : 1)
#define F10(N) F(N),F(N+1),F(N+2),F(N+3),F(N+4),F(N+5),F(N+6),F(N+7),F(N+8),F(N+9)
#define F100(N) F10(N),F10(N+10),F10(N+20),F10(N+30),F10(N+40),\
F10(N+50),F10(N+60),F10(N+70),F10(N+80),F10(N+90)
static const short offsets[] = { F100(0), F100(100), F100(200), F100(300), F100(400),
F100(500), F100(600), F100(700), F100(800), F100(900)};
static const char table1[][4] = { JOIN("") };
static const char table2[][4] = { JOIN2("") };
static const char table3[][4] = { JOIN3("") };
static const char table4[][5] = { JOIN4 };
static const char table5[][4] = { JOIN6 };
#undef JOIN
#undef JOIN2
#undef JOIN3
#undef JOIN4
char *wstr;
int remains[2];
unsigned int v2;
if (value >= 100000000) {
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[0] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[1] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
wstr = str;
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
wstr += 4;
} else {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table5[value];
wstr += offsets[value];
}
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[1]];
wstr += 4;
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return (wstr - str);
}
else if (value >= 10000) {
v2 = value / 10000;
remains[0] = value - v2 * 10000;
value = v2;
wstr = str;
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
wstr += 4;
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return 8;
} else {
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table5[value];
wstr += offsets[value];
*(__int32 *) wstr = *(__int32 *) table4[remains[0]];
wstr += 4;
*wstr = 0;
return (wstr - str);
}
}
else {
if (value >= 1000) {
*(__int32 *) str = *(__int32 *) table4[value];
str += 4;
*str = 0;
return 4;
} else if (value >= 100) {
*(__int32 *) str = *(__int32 *) table3[value];
return 3;
} else if (value >= 10) {
*(__int16 *) str = *(__int16 *) table2[value];
str += 2;
*str = 0;
return 2;
} else {
*(__int16 *) str = *(__int16 *) table1[value];
return 1;
}
}
}
int ufast_itoa10(int value, char* str) {
if (value < 0) { *(str++) = '-';
return ufast_utoa10(-value, str) + 1;
}
else return ufast_utoa10(value, str);
}
void ufast_test() {
print_mode("[modp_ufast]");
std::string s;
s.reserve(32);
std::size_t total_length = 0;
strtk::util::timer t;
t.start();
char buf[128];
int len;
for (int i = (-max_i2s / 2); i < (max_i2s / 2); ++i)
{
#ifdef enable_test_type01
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(((i & 1) ? i : -i), const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
#ifdef enable_test_type02
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(max_i2s + i, const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
#ifdef enable_test_type03
s.resize(ufast_itoa10(randval[(max_i2s + i) & 1023], const_cast<char*>(s.c_str())));
total_length += s.size();
#endif
}
t.stop();
printf("Numbers:%10lu\tTotal:%12lu\tTime:%8.4fsec\tRate:%14.4fnums/sec\n",
static_cast<unsigned long>(3 * max_i2s),
static_cast<unsigned long>(total_length),
t.time(),
(3.0 * max_i2s) / t.time());
}
答案 6 :(得分:2)
这是我对这个有趣谜题的小尝试。
我不想使用查找表,而是希望编译器能够全面解决这个问题。特别是在这种情况下 - 如果你看过黑客&#39;很高兴,您可以看到除法和模运算是如何工作的 - 这使得使用SSE / AVX指令进行优化成为可能。
效果基准
至于速度,我的基准测试告诉我它比Timo的工作快了1.5倍(在我的Intel Haswell上运行速度大约为1 GB / s)。
你可以考虑作弊的事情
至于我使用的非制作字符串作弊 - 当然我也考虑了Timo方法的基准测试。
我使用内在:BSR。如果你愿意,你也可以使用DeBruijn表 - 这是我在我最快的2log&#39;中写的很多东西之一。帖子。当然,这确实会带来性能损失(*好吧......如果你做了很多itoa操作,你实际上可以做出更快的BSR,但我猜这不公平......)。
工作方式
首先要做的是弄清楚我们需要多少内存。这基本上是10log,可以通过多种智能方式实现。请参阅频繁引用的&#34; Bit Twiddling Hacks&#34;详情。
接下来要做的是执行数字输出。我为此使用模板递归,因此编译器会弄明白。
我使用&#39; modulo&#39;和&#39; div&#39; div紧挨着。如果你读过Hacker's Delight,你会发现两者密切相关,所以如果你有一个答案,你可能还有另一个答案。我认为编译器可以弄清楚......: - )
代码
使用(修改的)log10获取位数:
struct logarithm
{
static inline int log2(unsigned int value)
{
unsigned long index;
if (!_BitScanReverse(&index, value))
{
return 0;
}
// add 1 if x is NOT a power of 2 (to do the ceil)
return index + (value&(value - 1) ? 1 : 0);
}
static inline int numberDigits(unsigned int v)
{
static unsigned int const PowersOf10[] =
{ 0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000 };
int t = (logarithm::log2(v) + 1) * 1233 >> 12; // (use a lg2 method from above)
return 1 + t - (v < PowersOf10[t]);
}
};
让自己成为字符串:
template <int count>
struct WriteHelper
{
inline static void WriteChar(char* buf, unsigned int value)
{
unsigned int div = value / 10;
unsigned int rem = value % 10;
buf[count - 1] = rem + '0';
WriteHelper<count - 1>::WriteChar(buf, div);
}
};
template <>
struct WriteHelper<1>
{
inline static void WriteChar(char* buf, unsigned int value)
{
buf[0] = '0' + value;
}
};
// Boring code that converts a length into a switch.
// TODO: Test if recursion with an 'if' is faster.
static inline void WriteNumber(char* data, int len, unsigned int val)
{
switch (len) {
case 1:
WriteHelper<1>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 2:
WriteHelper<2>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 3:
WriteHelper<3>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 4:
WriteHelper<4>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 5:
WriteHelper<5>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 6:
WriteHelper<6>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 7:
WriteHelper<7>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 8:
WriteHelper<8>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 9:
WriteHelper<9>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
case 10:
WriteHelper<10>::WriteChar(data, static_cast<unsigned int>(val));
break;
}
}
// The main method you want to call...
static int Write(char* data, int val)
{
int len;
if (val >= 0)
{
len = logarithm::numberDigits(val);
WriteNumber(data, len, unsigned int(val));
return len;
}
else
{
unsigned int v(-val);
len = logarithm::numberDigits(v);
WriteNumber(data+1, len, v);
data[0] = '-';
return len + 1;
}
}
答案 7 :(得分:2)
我已经坐了好一会儿,终于到处张贴了它。
与 hopman_fast 中的双字相比,还有一些方法。结果是针对GCC的短字符串优化的std :: string,否则性能差异会被写时复制字符串管理代码的开销所掩盖。吞吐量的测量方法与本主题中的其他地方相同,循环计数用于将输出缓冲区复制到字符串之前的代码的原始序列化部分。
HOPMAN_FAST - performance reference
TM_CPP, TM_VEC - scalar and vector versions of Terje Mathisen algorithm
WM_VEC - intrinsics implementation of Wojciech Mula's vector algorithm
AK_BW - word-at-a-time routine with a jump table that fills a buffer in reverse
AK_FW - forward-stepping word-at-a-time routine with a jump table in assembly
AK_UNROLLED - generic word-at-a-time routine that uses an unrolled loop
编译时间开关:
-DVSTRING - 为较旧的GCC设置启用SSO字符串
-DBSR1 - 启用快速log10
-DRDTSC - 启用循环计数器
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <limits>
#include <ctime>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/* Uncomment to run */
// #define HOPMAN_FAST
// #define TM_CPP
// #define TM_VEC
// #define WM_VEC
// #define AK_UNROLLED
// #define AK_BW
// #define AK_FW
using namespace std;
#ifdef VSTRING
#include <ext/vstring.h>
typedef __gnu_cxx::__vstring string_type;
#else
typedef string string_type;
#endif
namespace detail {
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define ALIGN(N) __attribute__ ((aligned(N)))
#define PACK __attribute__ ((packed))
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned u) {
struct {
uint32_t count;
uint32_t max;
} static digits[32] ALIGN(64) = {
{ 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 },
{ 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 },
{ 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 },
{ 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 },
{ 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 },
{ 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 },
{ 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 },
{ 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 },
{ 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 },
{ 10, UINT_MAX }, { 10, UINT_MAX }
};
#if (defined(i386) || defined(__x86_64__)) && (defined(BSR1) || defined(BSR2))
size_t l = u;
#if defined(BSR1)
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"bsrl %k0, %k0 \n\t"
"shlq $32, %q1 \n\t"
"movq %c2(,%0,8), %0\n\t"
"cmpq %0, %q1 \n\t"
"seta %b1 \n\t"
"addl %1, %k0 \n\t"
: "+r" (l), "+r"(u)
: "i"(digits)
: "cc"
);
return l;
#else
__asm__ __volatile__ ( "bsr %0, %0;" : "+r" (l) );
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
#else
size_t l = (u != 0) ? 31 - __builtin_clz(u) : 0;
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
}
#else
inline unsigned msb_u32(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned bval[] = { 0,1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,4,4,4,4 };
unsigned base = 0;
if (x & (unsigned) 0xFFFF0000) { base += 32/2; x >>= 32/2; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x0000FF00) { base += 32/4; x >>= 32/4; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x000000F0) { base += 32/8; x >>= 32/8; }
return base + bval[x];
}
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned powertable[] = {
0,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000,10000000,100000000, 1000000000 };
size_t lg_ten = msb_u32(x) * 1233 >> 12;
size_t adjust = (x >= powertable[lg_ten]);
return lg_ten + adjust;
}
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
struct CharBuffer {
class reverse_iterator : public iterator<random_access_iterator_tag, char> {
char* m_p;
public:
reverse_iterator(char* p) : m_p(p - 1) {}
reverse_iterator operator++() { return --m_p; }
reverse_iterator operator++(int) { return m_p--; }
char operator*() const { return *m_p; }
bool operator==( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p == it.m_p; }
bool operator!=( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p != it.m_p; }
difference_type operator-( reverse_iterator it) const { return it.m_p - m_p; }
};
};
union PairTable {
char c[2];
unsigned short u;
} PACK table[100] ALIGN(1024) = {
{{'0','0'}},{{'0','1'}},{{'0','2'}},{{'0','3'}},{{'0','4'}},{{'0','5'}},{{'0','6'}},{{'0','7'}},{{'0','8'}},{{'0','9'}},
{{'1','0'}},{{'1','1'}},{{'1','2'}},{{'1','3'}},{{'1','4'}},{{'1','5'}},{{'1','6'}},{{'1','7'}},{{'1','8'}},{{'1','9'}},
{{'2','0'}},{{'2','1'}},{{'2','2'}},{{'2','3'}},{{'2','4'}},{{'2','5'}},{{'2','6'}},{{'2','7'}},{{'2','8'}},{{'2','9'}},
{{'3','0'}},{{'3','1'}},{{'3','2'}},{{'3','3'}},{{'3','4'}},{{'3','5'}},{{'3','6'}},{{'3','7'}},{{'3','8'}},{{'3','9'}},
{{'4','0'}},{{'4','1'}},{{'4','2'}},{{'4','3'}},{{'4','4'}},{{'4','5'}},{{'4','6'}},{{'4','7'}},{{'4','8'}},{{'4','9'}},
{{'5','0'}},{{'5','1'}},{{'5','2'}},{{'5','3'}},{{'5','4'}},{{'5','5'}},{{'5','6'}},{{'5','7'}},{{'5','8'}},{{'5','9'}},
{{'6','0'}},{{'6','1'}},{{'6','2'}},{{'6','3'}},{{'6','4'}},{{'6','5'}},{{'6','6'}},{{'6','7'}},{{'6','8'}},{{'6','9'}},
{{'7','0'}},{{'7','1'}},{{'7','2'}},{{'7','3'}},{{'7','4'}},{{'7','5'}},{{'7','6'}},{{'7','7'}},{{'7','8'}},{{'7','9'}},
{{'8','0'}},{{'8','1'}},{{'8','2'}},{{'8','3'}},{{'8','4'}},{{'8','5'}},{{'8','6'}},{{'8','7'}},{{'8','8'}},{{'8','9'}},
{{'9','0'}},{{'9','1'}},{{'9','2'}},{{'9','3'}},{{'9','4'}},{{'9','5'}},{{'9','6'}},{{'9','7'}},{{'9','8'}},{{'9','9'}}
};
} // namespace detail
struct progress_timer {
clock_t c;
progress_timer() : c(clock()) {}
int elapsed() { return clock() - c; }
~progress_timer() {
clock_t d = clock() - c;
cout << d / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "."
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 1000 / 100)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 100 / 10)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 10)
<< " s" << endl;
}
};
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
namespace hopman_fast {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
struct itostr_helper {
static ALIGN(1024) unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
string_type itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
str += 12;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(f, str);
}
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
namespace ak {
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
namespace unrolled {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static const size_t MaxValueSize = 16;
static inline char* generate(int value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value < 0 ? unsigned(~value) + 1 : value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
*(b.pc -= (u >= 10)) = '-';
return b.pc + (value >= 0);
}
static inline char* generate(unsigned value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
return b.pc + (u < 10);
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(value_type v) {
char buf[MaxValueSize];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char* p = generate(v, buf);
char* e = buf + MaxValueSize;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(p, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
namespace bw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint64_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
u_type u = v;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 8) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 8: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 6) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 6: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 4) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 4: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 2) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)buffer = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 7) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 7: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 5) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 5: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 3) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 3: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 1) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 1: *buffer = v + 0x30;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + neg;
generate(val, len, e);
e += len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
namespace fw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint32_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
uint16_t w;
uint32_t u;
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"jmp %*T%=(,%3,8) \n\t"
"T%=: .quad L0%= \n\t"
" .quad L1%= \n\t"
" .quad L2%= \n\t"
" .quad L3%= \n\t"
" .quad L4%= \n\t"
" .quad L5%= \n\t"
" .quad L6%= \n\t"
" .quad L7%= \n\t"
" .quad L8%= \n\t"
" .quad L9%= \n\t"
" .quad L10%= \n\t"
"L10%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1441151881, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $57, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L8%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1125899907, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $50, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -8(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L6%=: \n\t"
" imulq $429497, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $32, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -6(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L4%=: \n\t"
" imull $167773, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $24, %1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -4(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L2%=: \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q0,2), %w2 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -2(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L0%=: jmp 1f \n\t"
"L9%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1801439851, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $54, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L7%=: \n\t"
" imulq $43980466, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $42, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -7(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L5%=: \n\t"
" imulq $268436, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $28, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -5(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L3%=: \n\t"
" imull $6554, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $15, %1 \n\t"
" andb $254, %b1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1), %w2 \n\t"
" leal (%1,%1,4), %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -3(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L1%=: \n\t"
" addl $48, %0 \n\t"
" movb %b0, -1(%4,%3) \n\t"
"1: \n\t"
: "+r"(v), "=&q"(u), "=&r"(w)
: "r"(len), "r"(buffer), "i"(detail::table)
: "memory", "cc"
);
#else
u_type u;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1441151881ULL) >> 57; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000000;
case 8: u = (v * 1125899907ULL) >> 50; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 8) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000000;
case 6: u = (v * 429497ULL) >> 32; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 6) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000;
case 4: u = (v * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 4) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 2) = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1801439851ULL) >> 54; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000000;
case 7: u = (v * 43980466ULL) >> 42; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 7) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000;
case 5: u = (v * 268436ULL) >> 28; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 5) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000;
case 3: u = (v * 6554) >> 16; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 3) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10;
case 1: *(buffer + len - 1) = v + 0x30;
}
#endif
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
if (neg) buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + len + neg;
generate(val, len, buf + neg);
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
} // ak
namespace wm {
#ifdef WM_VEC
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned v, char* buf) {
static struct {
unsigned short mul_10[8];
unsigned short div_const[8];
unsigned short shl_const[8];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits =
{
{ // mul_10
10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10
},
{ // div_const
8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000, 8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000
},
{ // shl_const
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15),
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15)
},
{ // to_ascii
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0'
}
};
unsigned x, y, l;
x = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37;
y = v;
l = 0;
if (x) {
unsigned div = 0xd1b71759;
unsigned mul = 55536;
__m128i z, m, a, o;
y -= 100 * x;
z = _mm_cvtsi32_si128(x);
m = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
o = _mm_mul_epu32( z, _mm_cvtsi32_si128(div));
z = _mm_add_epi32( z, _mm_mul_epu32( _mm_cvtsi32_si128(mul), _mm_srli_epi64( o, 45) ) );
z = _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_unpacklo_epi16(z, z), 5 ), 2 );
a = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
z = _mm_mulhi_epu16( _mm_mulhi_epu16( z, *(__m128i*)bits.div_const ), *(__m128i*)bits.shl_const );
z = _mm_sub_epi16( z, _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi16( m, z ), 16 ) );
z = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_packus_epi16( z, _mm_xor_si128(o, o) ), a );
x = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( a, z ) ) );
l = 8 - x;
uint64_t q = _mm_cvtsi128_si64(z) >> (x * 8);
*(uint64_t*)buf = q;
buf += l;
x = 1;
}
v = (y * 6554) >> 16;
l += 1 + (x | (v != 0));
*(unsigned short*)buf = 0x30 + ((l > 1) ? ((0x30 + y - v * 10) << 8) + v : y);
return l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
buf[0] = '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf + neg);
char* e = buf + len + neg;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
inline string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
inline string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#endif
} // wm
namespace tmn {
#ifdef TM_CPP
namespace cpp {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, char* buffer) {
unsigned const f1_10000 = (1 << 28) / 10000;
unsigned tmplo, tmphi;
unsigned lo = v % 100000;
unsigned hi = v / 100000;
tmplo = lo * (f1_10000 + 1) - (lo >> 2);
tmphi = hi * (f1_10000 + 1) - (hi >> 2);
unsigned mask = 0x0fffffff;
unsigned shift = 28;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
buffer[i + 0] = '0' + (char)(tmphi >> shift);
buffer[i + 5] = '0' + (char)(tmplo >> shift);
tmphi = (tmphi & mask) * 5;
tmplo = (tmplo & mask) * 5;
mask >>= 1;
shift--;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char buf[16];
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
char* e = buf + 11;
generate(val, buf + 1);
buf[10 - len] = '-';
len += neg;
char* b = e - len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(b, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned val, char* buffer) {
static struct {
unsigned char mul_10[16];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
unsigned char gather[16];
unsigned char shift[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits = {
{ 10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0 },
{ '0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0' },
{ 3,5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14,15,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 }
};
unsigned u = val / 1000000;
unsigned l = val - u * 1000000;
__m128i x, h, f, m, n;
n = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
x = _mm_set_epi64x( l, u );
h = _mm_mul_epu32( x, _mm_set1_epi32(4294968) );
x = _mm_sub_epi64( x, _mm_srli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi32( h, _mm_set1_epi32(1000) ), 32 ) );
f = _mm_set1_epi32((1 << 28) / 1000 + 1);
m = _mm_srli_epi32( _mm_cmpeq_epi32(m, m), 4 );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_blend_epi16( x, h, 204 ), 177 );
f = _mm_sub_epi32( _mm_mullo_epi32(f, x), _mm_srli_epi32(x, 2) );
h = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
x = _mm_srli_epi32(f, 28);
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 8) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 16) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 24) );
x = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_shuffle_epi8(x, *(__m128i*)bits.gather), h );
l = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( h, x ) ) | (1 << 9) );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi8( x, _mm_add_epi8(*(__m128i*)bits.shift, _mm_set1_epi8(l) ) );
_mm_store_si128( (__m128i*)buffer, x );
return 10 - l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char arena[32];
char* buf = (char*)((uintptr_t)(arena + 16) & ~(uintptr_t)0xf);
*(buf - 1)= '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf) + neg;
buf -= neg;
char* end = buf + len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, end);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
}
bool fail(string in, string_type out) {
cout << "failure: " << in << " => " << out << endl;
return false;
}
#define TEST(x, n) \
stringstream ss; \
string_type s = n::itostr(x); \
ss << (long long)x; \
if (::strcmp(ss.str().c_str(), s.c_str())) { \
passed = fail(ss.str(), s); \
break; \
}
#define test(x) { \
passed = true; \
if (0 && passed) { \
char c = CHAR_MIN; \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != CHAR_MAX); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed char!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (0 && passed) { \
short c = numeric_limits<short>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != numeric_limits<short>::max()); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed short!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
int c = numeric_limits<int>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c += 100000) < numeric_limits<int>::max() - 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed int!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
unsigned c = numeric_limits<unsigned>::max(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c -= 100000) > 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed unsigned int!!!" << endl; \
} \
}
#define time(x, N) \
if (passed) { \
static const int64_t limits[] = \
{0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, \
1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000, 10000000000ULL }; \
long passes = 0; \
cout << #x << ": "; \
progress_timer t; \
uint64_t s = 0; \
if (do_time) { \
for (int n = 0; n < N1; n++) { \
int i = 0; \
while (i < N2) { \
int v = ((NM - i) % limits[N]) | (limits[N] / 10); \
int w = x::itostr(v).size() + \
x::itostr(-v).size(); \
i += w * mult; \
passes++; \
} \
s += i / mult; \
} \
} \
k += s; \
cout << N << " digits: " \
<< s / double(t.elapsed()) * CLOCKS_PER_SEC/1000000 << " MB/sec, " << (x::cycles() / passes >> 1) << " clocks per pass "; \
x::reset(); \
}
#define series(n) \
{ if (do_test) test(n); if (do_time) time(n, 1); if (do_time) time(n, 2); \
if (do_time) time(n, 3); if (do_time) time(n, 4); if (do_time) time(n, 5); \
if (do_time) time(n, 6); if (do_time) time(n, 7); if (do_time) time(n, 8); \
if (do_time) time(n, 9); if (do_time) time(n, 10); }
int N1 = 1, N2 = 500000000, NM = INT_MAX;
int mult = 1; // used to stay under timelimit on ideone
unsigned long long k = 0;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
bool do_time = 1, do_test = 1;
bool passed = true;
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
series(hopman_fast)
#endif
#ifdef WM_VEC
series(wm::vec)
#endif
#ifdef TM_CPP
series(tmn::cpp)
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
series(tmn::vec)
#endif
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
series(ak::unrolled)
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
series(ak::bw)
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
series(ak::fw)
#endif
return k;
}
答案 8 :(得分:1)
我相信我已经创建了最快的整数到字符串算法。它是Modulo 100算法的一种变体,速度提高了约33%,最重要的是它对于较小和较大的数字都更快。它被称为脚本ItoS算法。阅读解释我如何设计算法的论文@see https://github.com/kabuki-starship/kabuki-toolkit/wiki/Engineering-a-Faster-Integer-to-String-Algorithm。您可以使用该算法,但请考虑回馈Kabuki VM并查看Script;特别是如果您对AMIL-NLP和/或软件定义的网络协议感兴趣。
/** Kabuki Toolkit
@version 0.x
@file ~/source/crabs/print_itos.cc
@author Cale McCollough <cale.mccollough@gmail.com>
@license Copyright (C) 2017-2018 Cale McCollough <calemccollough@gmail.com>;
All right reserved (R). Licensed under the Apache License, Version
2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in
compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License
[here](http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0). Unless
required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
implied. See the License for the specific language governing
permissions and limitations under the License.
*/
#include <stdafx.h>
#include "print_itos.h"
#if MAJOR_SEAM >= 1 && MINOR_SEAM >= 1
#if MAJOR_SEAM == 1 && MINOR_SEAM == 1
#define DEBUG 1
#define PRINTF(format, ...) printf(format, __VA_ARGS__);
#define PUTCHAR(c) putchar(c);
#define PRINT_PRINTED\
sprintf_s (buffer, 24, "%u", value); *text_end = 0;\
printf ("\n Printed \"%s\" leaving value:\"%s\":%u",\
begin, buffer, (uint)strlen (buffer));
#define PRINT_BINARY PrintBinary (value);
#define PRINT_BINARY_TABLE PrintBinaryTable (value);
#else
#define PRINTF(x, ...)
#define PUTCHAR(c)
#define PRINT_PRINTED
#define PRINT_BINARY
#define PRINT_BINARY_TABLE
#endif
namespace _ {
void PrintLine (char c) {
std::cout << '\n';
for (int i = 80; i > 0; --i)
std::cout << c;
}
char* Print (uint32_t value, char* text, char* text_end) {
// Lookup table for powers of 10.
static const uint32_t k10ToThe[]{
1, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, 1000000, 10000000, 100000000,
1000000000, ~(uint32_t)0 };
/** Lookup table of ASCII char pairs for 00, 01, ..., 99.
To convert this algorithm to big-endian, flip the digit pair bytes. */
static const uint16_t kDigits00To99[100] = {
0x3030, 0x3130, 0x3230, 0x3330, 0x3430, 0x3530, 0x3630, 0x3730, 0x3830,
0x3930, 0x3031, 0x3131, 0x3231, 0x3331, 0x3431, 0x3531, 0x3631, 0x3731,
0x3831, 0x3931, 0x3032, 0x3132, 0x3232, 0x3332, 0x3432, 0x3532, 0x3632,
0x3732, 0x3832, 0x3932, 0x3033, 0x3133, 0x3233, 0x3333, 0x3433, 0x3533,
0x3633, 0x3733, 0x3833, 0x3933, 0x3034, 0x3134, 0x3234, 0x3334, 0x3434,
0x3534, 0x3634, 0x3734, 0x3834, 0x3934, 0x3035, 0x3135, 0x3235, 0x3335,
0x3435, 0x3535, 0x3635, 0x3735, 0x3835, 0x3935, 0x3036, 0x3136, 0x3236,
0x3336, 0x3436, 0x3536, 0x3636, 0x3736, 0x3836, 0x3936, 0x3037, 0x3137,
0x3237, 0x3337, 0x3437, 0x3537, 0x3637, 0x3737, 0x3837, 0x3937, 0x3038,
0x3138, 0x3238, 0x3338, 0x3438, 0x3538, 0x3638, 0x3738, 0x3838, 0x3938,
0x3039, 0x3139, 0x3239, 0x3339, 0x3439, 0x3539, 0x3639, 0x3739, 0x3839,
0x3939, };
static const char kMsbShift[] = { 4, 7, 11, 14, 17, 21, 24, 27, 30, };
if (!text) {
return nullptr;
}
if (text >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
uint16_t* text16;
char digit;
uint32_t scalar;
uint16_t digits1and2,
digits3and4,
digits5and6,
digits7and8;
uint32_t comparator;
#if MAJOR_SEAM == 1 && MINOR_SEAM == 1
// Write a bunches of xxxxxx to the buffer for debug purposes.
for (int i = 0; i <= 21; ++i) {
*(text + i) = 'x';
}
*(text + 21) = 0;
char* begin = text;
char buffer[256];
#endif
if (value < 10) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[0, 9] length:1 ")
if (text + 1 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '0' + (char)value;
PRINT_PRINTED
return text;
}
if (value < 100) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10, 99] length:2 ")
if (text + 2 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) = kDigits00To99[value];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 2;
}
if (value >> 14) {
if (value >> 27) {
if (value >> 30) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1073741824, 4294967295] length:10")
Print10:
if (text + 10 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
comparator = 100000000;
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)(value / comparator);
PRINTF ("\n digits1and2:%u", digits1and2)
value -= digits1and2 * comparator;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
text += 2;
goto Print8;
}
else {
comparator = 1000000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000000, 1073741823] length:10")
goto Print10;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[134217727, 999999999] length:9")
if (text + 9 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
comparator = 100000000;
digit = (char)(value / comparator);
*text++ = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator * digit;
goto Print8;
}
}
else if (value >> 24) {
comparator = k10ToThe[8];
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000000, 134217728] length:9")
if (text + 9 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[16777216, 9999999] length:8")
if (text + 8 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
Print8:
PRINTF ("\n Print8:")
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 6) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 4) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) =
kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text) =
kDigits00To99[digits7and8];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 8;
}
else if (value >> 20) {
comparator = 10000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000000, 16777215] length:8")
if (text + 8 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1048576, 9999999] length:7")
if (text + 7 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 5) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 3) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) =
kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
*text = (char)digits7and8 + '0';
return text + 7;
}
else if (value >> 17) {
comparator = 1000000;
if (value >= comparator) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100000, 1048575] length:7")
if (text + 7 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
value -= comparator;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[131072, 999999] length:6")
if (text + 6 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
Print6:
scalar = 10000;
digits5and6 = (uint16_t)(value / scalar);
digits1and2 = value - scalar * digits5and6;
digits7and8 = digits5and6 / 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / 100;
digits5and6 -= 100 * digits7and8;
digits1and2 -= 100 * digits3and4;
text16 = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 6);
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 4) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) = kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text ) = kDigits00To99[digits5and6];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 6;
}
else { // (value >> 14)
if (value >= 100000) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[65536, 131071] length:6")
goto Print6;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000, 65535] length:5")
if (text + 5 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
digits5and6 = 10000;
digit = (uint8_t)(value / digits5and6);
value -= digits5and6 * digit;
*text = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
digits5and6 = 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / digits5and6;
digits1and2 -= digits3and4 * digits5and6;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) =
kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
PRINTF ("\n digits1and2:%u", digits1and2)
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 3) =
kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 5;
}
}
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
if (value >> 10) {
digits5and6 = 10000;
if (digits1and2 >= digits5and6) {
if (text + 5 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[10000, 16383] length:5")
*text++ = '1';
PRINT_PRINTED
digits1and2 -= digits5and6;
}
else {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1024, 9999] length:4")
if (text + 4 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
}
digits5and6 = 100;
digits3and4 = digits1and2 / digits5and6;
digits1and2 -= digits3and4 * digits5and6;
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text ) = kDigits00To99[digits3and4];
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 4;
}
else {
if (text + 4 >= text_end) {
return nullptr;
}
digits3and4 = 1000;
if (digits1and2 >= digits3and4) {
PRINTF ("\n Range:[1000, 1023] length:4")
digits1and2 -= digits3and4;
text16 = reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 2);
*text16-- = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
*text16 = (((uint16_t)'1') | (((uint16_t)'0') << 8));
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 4;
}
PRINTF ("\n Range:[100, 999] length:3")
digits1and2 = (uint16_t)value;
digits3and4 = 100;
digit = (char)(digits1and2 / digits3and4);
digits1and2 -= digit * digits3and4;
*text = digit + '0';
PRINT_PRINTED
*reinterpret_cast<uint16_t*> (text + 1) = kDigits00To99[digits1and2];
PRINT_PRINTED
return text + 3;
}
}
} //< namespace _
#undef PRINTF
#undef PRINT_PRINTED
#endif //< MAJOR_SEAM >= 1 && MINOR_SEAM >= 1
作者
- Cale McCollough&lt; cale.mccollough@gmail.com>
答案 9 :(得分:0)
修改user434507的解决方案。修改为使用字符数组而不是C ++字符串。跑得快一点。还将代码中的0检查移动到了...因为这种情况从未发生过我的特殊情况。如果你的情况更常见,请将其移回。
// Int2Str.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
//
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "StopWatch.h"
using namespace std;
const char digit_pairs[201] = {
"00010203040506070809"
"10111213141516171819"
"20212223242526272829"
"30313233343536373839"
"40414243444546474849"
"50515253545556575859"
"60616263646566676869"
"70717273747576777879"
"80818283848586878889"
"90919293949596979899"
};
void itostr(int n, char* c) {
int sign = -(n<0);
unsigned int val = (n^sign)-sign;
int size;
if(val>=10000) {
if(val>=10000000) {
if(val>=1000000000) {
size=10;
}
else if(val>=100000000) {
size=9;
}
else size=8;
}
else {
if(val>=1000000) {
size=7;
}
else if(val>=100000) {
size=6;
}
else size=5;
}
}
else {
if(val>=100) {
if(val>=1000) {
size=4;
}
else size=3;
}
else {
if(val>=10) {
size=2;
}
else if(n==0) {
c[0]='0';
c[1] = '\0';
return;
}
else size=1;
}
}
size -= sign;
if(sign)
*c='-';
c += size-1;
while(val>=100) {
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0) {
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
c[size+1] = '\0';
}
void itostr(unsigned val, char* c)
{
int size;
if(val>=10000)
{
if(val>=10000000)
{
if(val>=1000000000)
size=10;
else if(val>=100000000)
size=9;
else
size=8;
}
else
{
if(val>=1000000)
size=7;
else if(val>=100000)
size=6;
else
size=5;
}
}
else
{
if(val>=100)
{
if(val>=1000)
size=4;
else
size=3;
}
else
{
if(val>=10)
size=2;
else if (val==0) {
c[0]='0';
c[1] = '\0';
return;
}
else
size=1;
}
}
c += size-1;
while(val>=100)
{
int pos = val % 100;
val /= 100;
*(short*)(c-1)=*(short*)(digit_pairs+2*pos);
c-=2;
}
while(val>0)
{
*c--='0' + (val % 10);
val /= 10;
}
c[size+1] = '\0';
}
void test() {
bool foundmismatch = false;
char str[16];
char compare[16];
for(int i = -1000000; i < 1000000; i++) {
int random = rand();
itostr(random, str);
itoa(random, compare, 10);
if(strcmp(str, compare) != 0) {
cout << "Mismatch found: " << endl;
cout << "Generated: " << str << endl;
cout << "Reference: " << compare << endl;
foundmismatch = true;
}
}
if(!foundmismatch) {
cout << "No mismatch found!" << endl;
}
cin.get();
}
void benchmark() {
StopWatch stopwatch;
stopwatch.setup("Timer");
stopwatch.reset();
stopwatch.start();
char str[16];
for(unsigned int i = 0; i < 2000000; i++) {
itostr(i, str);
}
stopwatch.stop();
cin.get();
}
int main( int argc, const char* argv[]) {
benchmark();
}
答案 10 :(得分:0)
我们使用以下代码(对于MSVC):
模板化tBitScanReverse:
#include <intrin.h>
namespace intrin {
#pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse)
#pragma intrinsic(_BitScanReverse64)
template<typename TIntegerValue>
__forceinline auto tBitScanReverse(DWORD * out_index, TIntegerValue mask)
-> std::enable_if_t<(std::is_integral<TIntegerValue>::value && sizeof(TIntegerValue) == 4), unsigned char>
{
return _BitScanReverse(out_index, mask);
}
template<typename TIntegerValue>
__forceinline auto tBitScanReverse(DWORD * out_index, TIntegerValue mask)
-> std::enable_if_t<(std::is_integral<TIntegerValue>::value && sizeof(TIntegerValue) == 8), unsigned char>
{
#if !(_M_IA64 || _M_AMD64)
auto res = _BitScanReverse(out_index, (unsigned long)(mask >> 32));
if (res) {
out_index += 32;
return res;
}
return _BitScanReverse(out_index, (unsigned long)mask);
#else
return _BitScanReverse64(out_index, mask);
#endif
}
}
char / wchar_t helpers:
template<typename TChar> inline constexpr TChar ascii_0();
template<> inline constexpr char ascii_0() { return '0'; }
template<> inline constexpr wchar_t ascii_0() { return L'0'; }
template<typename TChar, typename TInt> inline constexpr TChar ascii_DEC(TInt d) { return (TChar)(ascii_0<TChar>() + d); }
10张牌桌的权力:
static uint32 uint32_powers10[] = {
1,
10,
100,
1000,
10000,
100000,
1000000,
10000000,
100000000,
1000000000
// 123456789
};
static uint64 uint64_powers10[] = {
1ULL,
10ULL,
100ULL,
1000ULL,
10000ULL,
100000ULL,
1000000ULL,
10000000ULL,
100000000ULL,
1000000000ULL,
10000000000ULL,
100000000000ULL,
1000000000000ULL,
10000000000000ULL,
100000000000000ULL,
1000000000000000ULL,
10000000000000000ULL,
100000000000000000ULL,
1000000000000000000ULL,
10000000000000000000ULL
// 1234567890123456789
};
template<typename TUint> inline constexpr const TUint * powers10();
template<> inline constexpr const uint32 * powers10() { return uint32_powers10; }
template<> inline constexpr const uint64 * powers10() { return uint64_powers10; }
实际打印:
template<typename TChar, typename TUInt>
__forceinline auto
print_dec(
TUInt u,
TChar * & buffer) -> typename std::enable_if_t<std::is_unsigned<TUInt>::value>
{
if (u < 10) { // 1-digit, including 0
*buffer++ = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u);
}
else {
DWORD log2u;
intrin::tBitScanReverse(&log2u, u); // log2u [3,31] (u >= 10)
DWORD log10u = ((log2u + 1) * 77) >> 8; // log10u [1,9] 77/256 = ln(2) / ln(10)
DWORD digits = log10u + (u >= powers10<TUInt>()[log10u]); // digits [2,10]
buffer += digits;
auto p = buffer;
for (--digits; digits; --digits) {
auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10;
*--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d);
u = x;
}
*--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u);
}
}
可以展开最后一个循环:
switch (digits) {
case 10: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 9: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 8: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 7: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 6: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 5: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 4: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 3: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; }
case 2: { auto x = u / 10, d = u - x * 10; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(d); u = x; *--p = ascii_DEC<TChar>(u); break; }
default: __assume(0);
}
主要观点与之前建议的@atlaste相同:https://stackoverflow.com/a/29039967/2204001
答案 11 :(得分:0)
由于最近的活动,才碰到了这一点;我确实没有时间添加基准测试,但是我想添加我以前编写的内容,以便在需要快速将整数转换为字符串时使用...
https://github.com/CarloWood/ai-utils/blob/master/itoa.h
https://github.com/CarloWood/ai-utils/blob/master/itoa.cxx
这里使用的技巧是用户必须提供一个很大的std :: array 足够(在他们的堆栈上),并且此代码将字符串写入其中 向后,从单位开始,然后将指针返回到数组中,指针指向结果实际开始的位置。
因此,这不会分配或移动内存,但仍需要对每个结果位进行除法和模运算(我相信这是足够快的,因为这仅仅是在CPU内部运行代码;内存访问通常是恕我直言的问题) )。
答案 12 :(得分:-1)
当需要商和余数时,为什么没有人使用stdlib中的div函数? 使用Timo的源代码,我得到了类似的东西:
if(val >= 0)
{
div_t d2 = div(val,100);
while(d2.quot)
{
COPYPAIR(it,2 * d2.rem);
it-=2;
d2 = div(d2.quot,100);
}
COPYPAIR(it,2*d2.rem);
if(d2.quot<10)
it++;
}
else
{
div_t d2 = div(val,100);
while(d2.quot)
{
COPYPAIR(it,-2 * d2.rem);
it-=2;
d2 = div(d2.quot,100);
}
COPYPAIR(it,-2*d2.rem);
if(d2.quot<=-10)
it--;
*it = '-';
}
好的,对于unsigned int,不能使用div函数,但可以单独处理unsigned's。 我已经将COPYPAIR宏定义如下,以测试如何从digit_pairs复制2个字符的变体(找不到任何这些方法的明显优势):
#define COPYPAIR0(_p,_i) { memcpy((_p), &digit_pairs[(_i)], 2); }
#define COPYPAIR1(_p,_i) { (_p)[0] = digit_pairs[(_i)]; (_p)[1] = digit_pairs[(_i)+1]; }
#define COPYPAIR2(_p,_i) { unsigned short * d = (unsigned short *)(_p); unsigned short * s = (unsigned short *)&digit_pairs[(_i)]; *d = *s; }
#define COPYPAIR COPYPAIR2
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?