匹配ROI或形状在几个图像中进行分析
我有很多图像可供使用。但是这个问题我将使用第一张和最后一张图片。
图片1 of 83
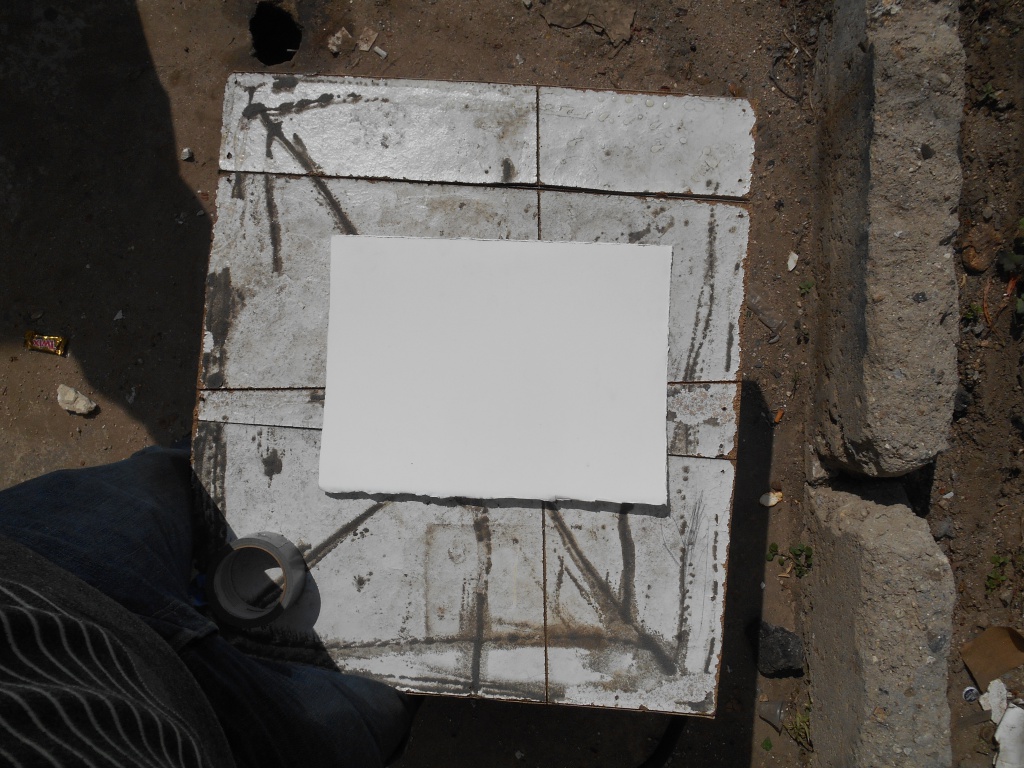

图83/83
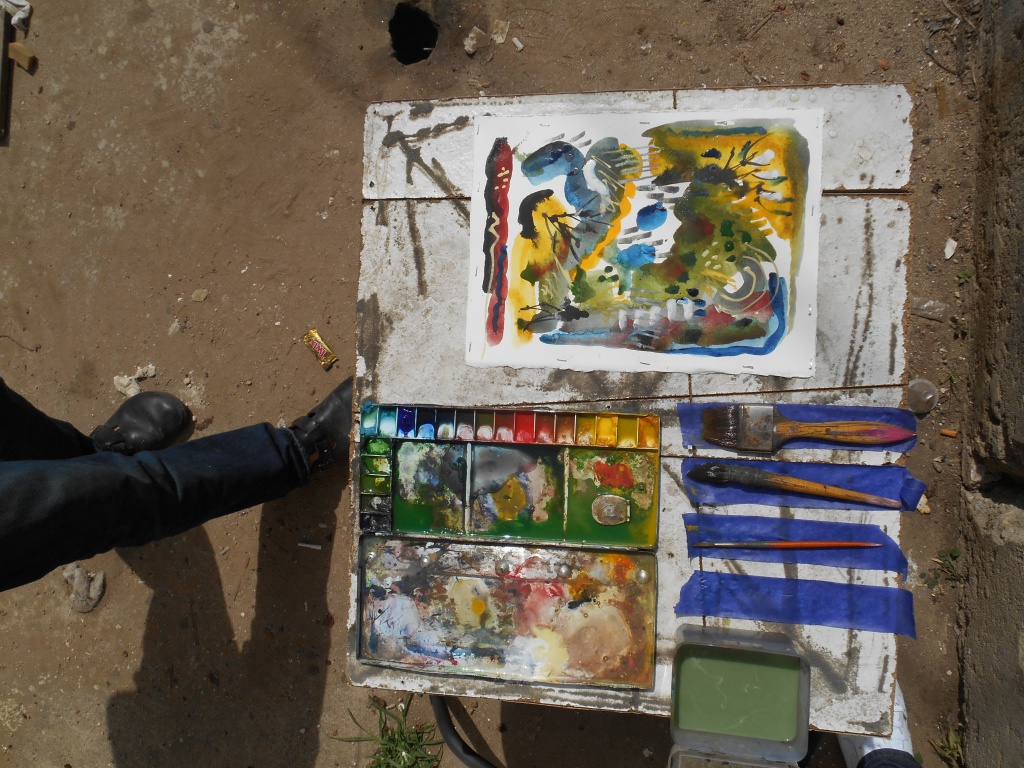

我通过此代码运行了Image 1
import numpy as np
import cv2
def process(filename, key):
gwash = cv2.imread(filename)
gwashBW = cv2.cvtColor(gwash, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret,thresh1 = cv2.threshold(gwashBW,179,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
kernel = np.ones((1,1),np.uint8)
erosion = cv2.erode(thresh1, kernel,iterations = 1)
opening = cv2.morphologyEx(erosion, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(opening, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
_, contours ,_ = cv2.findContours(closing,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
areas = [cv2.contourArea(c) for c in contours]
idx = np.argmax(areas)
cnt = contours[idx]
mask = np.zeros_like(gwash)
cv2.drawContours(mask, contours, idx, (255,255,255), -1)
out = np.zeros_like(gwash)
out[mask == 255] = gwash[mask == 255]
cv2.imwrite('img/out{}.jpg'.format(key),out)
print idx
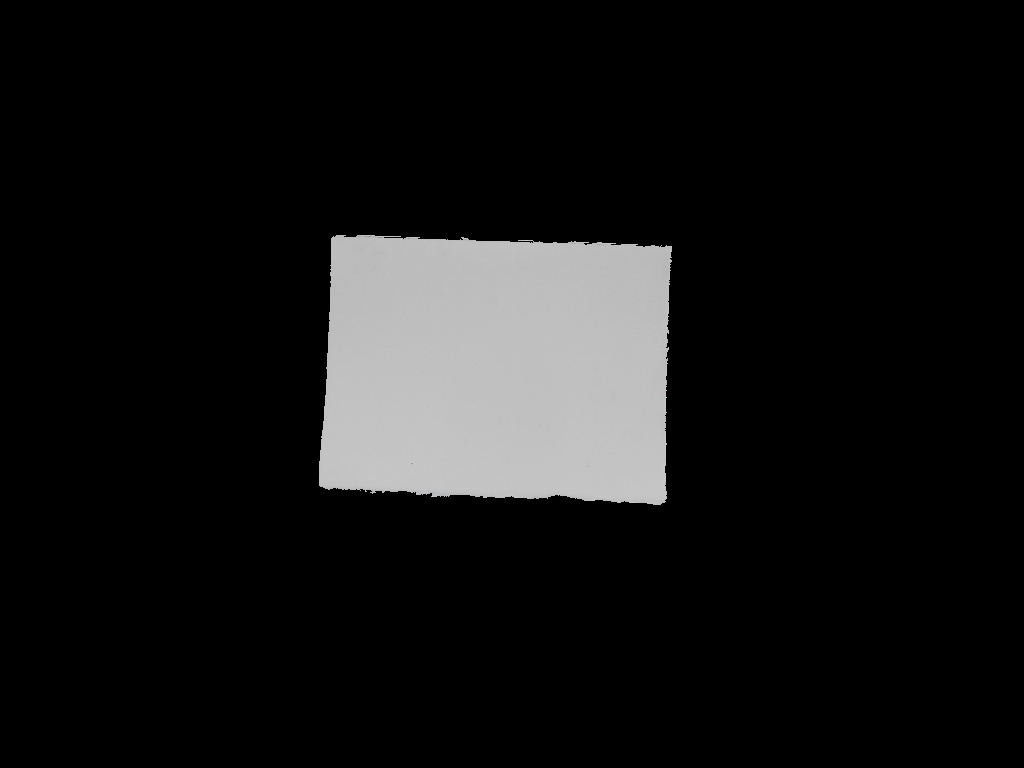

这一结果我得到了更好,最差的结果。
这是我使用的轮廓代码和结果
import cv2
import numpy as np
import imutils
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def process(filename, key):
image = cv2.imread(filename)
resized = imutils.resize(image, width=600)
ratio = image.shape[0] / float(resized.shape[0])
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(resized, (5, 5), 0)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(blurred, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
lab = cv2.cvtColor(resized, cv2.COLOR_BGR2LAB)
thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 180, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
imagem = cv2.bitwise_not(thresh)
th4 = cv2.threshold(gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY+cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
th3 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray,255,cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C, cv2.THRESH_BINARY,11,2)
gray_2 = cv2.cvtColor(resized, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray_blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (15, 15), 0)
thresh_2 = cv2.adaptiveThreshold(gray_blur, 255, cv2.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV, 11, 1)
kernel = np.ones((1, 1), np.uint8)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel, iterations=500)
cnts = cv2.findContours(closing.copy(), cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts2 = cv2.findContours(closing.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL ,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if imutils.is_cv2() else cnts[1]
cnts2 = cnts2[0] if imutils.is_cv2() else cnts2[1]
# loop over the contours
for c in cnts:
# compute the center of the contour
M = cv2.moments(c)
if M["m00"] != 0:
cX = int(M["m10"] / M["m00"])
cY = int(M["m01"] / M["m00"])
else:
cX, cY = 0, 0
# multiply the contour (x, y)-coordinates by the resize ratio,
# then draw the contours and the name of the shape and labeled
# color on the image
c = c.astype("float")
c *= ratio
c = c.astype("int")
cX *= ratio
cY *= ratio
cv2.drawContours(image, [c], -1, (0, 255, 0), 5)
cv2.circle(image, (int(cX),int(cY)),5,300,3)
#r = 100.0 / image.shape[1]
#dim = (100, int(image.shape[0] *r))
#imageresized = cv2.resize(image,(2048,2048),dim,interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
cv2.imwrite( 'i/image_{}.jpg'.format(key) ,QR_final )
print 'image_{}.jpg'.format(key)
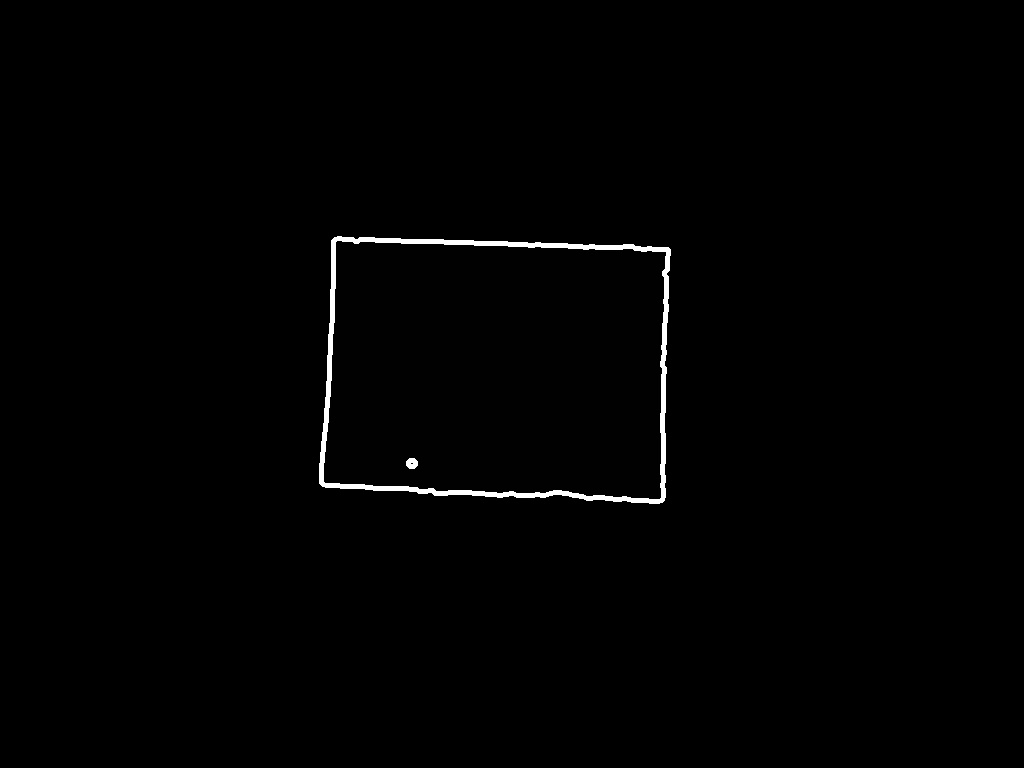
所以我的问题是使用python在所有照片中准确找到画布形状的最佳方法是什么?
0 个答案:
没有答案
相关问题
最新问题
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?