试图找到/理解Harris Corners的正确实现
我试图了解如何计算Harris Corner M,如中所定义 https://courses.cs.washington.edu/courses/cse455/07wi/homework/hw3/
似乎你需要总结一堆补丁。
但是,我看到很多实现都是这样的:
R = (Ix2.*Iy2 - Ixy.^2) - k*(Ix2 + Iy2).^2;
来自:http://web.engr.illinois.edu/~slazebni/spring14/harris.m
没有总结,你永远不会看补丁。
这些看起来并不等同于我。例如," R"像素5,5的值仅为该像素的Ix2,Iy2和Ixy值的平方。然而,数学似乎建议你总结一个补丁,比如像素5,5。哪种实施是正确的?都?它们是等价的吗?
注意:Ix2 =图像I在x方向上的平方梯度 除y方向外,Iy2是相同的 Ixy = Ix。* Iy
此外,。*或。^是matlab表示法,表示逐点乘法或取幂。
1 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:11)
对于自我控制,Harris Corners的计算基于相关矩阵M的计算:
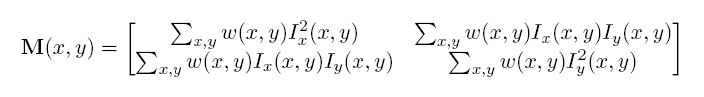
对于图像中的每个像素,您希望收集按高斯权重加权的N x N像素窗口,并计算图像中R位置的响应值(x,y): / p>
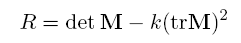
超过阈值的R值被视为兴趣点。 Ix和Iy分别是水平和垂直导数。现在,您关注的代码我将把它放入这篇文章中以进行自我遏制。顺便说一下,这应归功于Peter Kovesi谁将原始函数编写为你帖子中的链接:
% HARRIS - Harris corner detector
%
% Usage: [cim, r, c] = harris(im, sigma, thresh, radius, disp)
%
% Arguments:
% im - image to be processed.
% sigma - standard deviation of smoothing Gaussian. Typical
% values to use might be 1-3.
% thresh - threshold (optional). Try a value ~1000.
% radius - radius of region considered in non-maximal
% suppression (optional). Typical values to use might
% be 1-3.
% disp - optional flag (0 or 1) indicating whether you want
% to display corners overlayed on the original
% image. This can be useful for parameter tuning.
%
% Returns:
% cim - binary image marking corners.
% r - row coordinates of corner points.
% c - column coordinates of corner points.
%
% If thresh and radius are omitted from the argument list 'cim' is returned
% as a raw corner strength image and r and c are returned empty.
% Reference:
% C.G. Harris and M.J. Stephens. "A combined corner and edge detector",
% Proceedings Fourth Alvey Vision Conference, Manchester.
% pp 147-151, 1988.
%
% Author:
% Peter Kovesi
% Department of Computer Science & Software Engineering
% The University of Western Australia
% pk@cs.uwa.edu.au www.cs.uwa.edu.au/~pk
%
% March 2002
function [cim, r, c] = harris(im, sigma, thresh, radius, disp)
error(nargchk(2,5,nargin));
dx = [-1 0 1; -1 0 1; -1 0 1]; % Derivative masks
dy = dx'; %'
Ix = conv2(im, dx, 'same'); % Image derivatives
Iy = conv2(im, dy, 'same');
% Generate Gaussian filter of size 6*sigma (+/- 3sigma) and of
% minimum size 1x1.
g = fspecial('gaussian',max(1,fix(6*sigma)), sigma);
Ix2 = conv2(Ix.^2, g, 'same'); % Smoothed squared image derivatives
Iy2 = conv2(Iy.^2, g, 'same');
Ixy = conv2(Ix.*Iy, g, 'same');
cim = (Ix2.*Iy2 - Ixy.^2)./(Ix2 + Iy2 + eps); % Harris corner measure
% Alternate Harris corner measure used by some. Suggested that
% k=0.04 - I find this a bit arbitrary and unsatisfactory.
% cim = (Ix2.*Iy2 - Ixy.^2) - k*(Ix2 + Iy2).^2;
if nargin > 2 % We should perform nonmaximal suppression and threshold
% Extract local maxima by performing a grey scale morphological
% dilation and then finding points in the corner strength image that
% match the dilated image and are also greater than the threshold.
sze = 2*radius+1; % Size of mask.
mx = ordfilt2(cim,sze^2,ones(sze)); % Grey-scale dilate.
cim = (cim==mx)&(cim>thresh); % Find maxima.
[r,c] = find(cim); % Find row,col coords.
if nargin==5 & disp % overlay corners on original image
figure, imagesc(im), axis image, colormap(gray), hold on
plot(c,r,'ys'), title('corners detected');
end
else % leave cim as a corner strength image and make r and c empty.
r = []; c = [];
end
cim是为图像中的每个像素位置M(x,y)计算的相关矩阵,或(x,y)。我可以看到你的混乱来源。在此代码中,计算M(x,y)的窗口假定为1 x 1.在您引用我的链接中,对于您在代码中查看的每个点,窗口实际上是5 x 5。如果你想扩展它以使相关矩阵包含5 x 5像素,我想到这样的事情:
%//.........
%// From before - Need to modify to accommodate for window size
% Generate Gaussian filter of size 5 x 5 with sigma value
g = fspecial('gaussian', 5, sigma);
Ix2 = conv2(Ix.^2, g, 'same'); % Smoothed squared image derivatives
Iy2 = conv2(Iy.^2, g, 'same');
Ixy = conv2(Ix.*Iy, g, 'same');
%// New - add this before the computation of cim
kernel = ones(5,5);
Ix2 = conv2(Ix2, kernel, 'same'); % To incorporate 5 x 5 patches
Iy2 = conv2(Iy2, kernel, 'same');
Ixy = conv2(Ixy, kernel, 'same');
%// Continue with original code....
cim = (Ix2.*Iy2 - Ixy.^2)./(Ix2 + Iy2 + eps); % Harris corner measure
%//.....
conv2在输入和kernel之间执行卷积,Ix2是本地补丁和内核的加权和。在这种情况下,我们需要对Iy2,Ixy和M中的每一个进行求和,以尊重cim中的符号。如果我们在5 x 5窗口中将内核指定为全1,则实际上这是将所有值一起添加并为图像中的每个位置输出此总和。现在,在链接中它表示内核是高斯。文档说你可以用高斯预过滤你的图像,然后只是累积窗口,而代码当前正在这样做。但是,您需要确保Gaussian的窗口大小与文档所说的相同,因此我们也将其更改为5 x 5。
您现在可以正常计算M(x,y)或相关矩阵Ix2,现在应该合并Iy2,Ixy和Ix2的5 x 5窗口的像素总和Iy2仅使用按元素操作。一旦我们更改代码,Ixy,cim和M(x,y)的每个元素都会计算5 x 5窗口内的导数值的总和,其中每个变量中的每个像素都标记该位置所服务的总和作为中心。在此之后,一旦您计算im,这将为sze = 2*radius+1; % Size of mask.
mx = ordfilt2(cim,sze^2,ones(sze)); % Grey-scale dilate.
cim = (cim==mx)&(cim>thresh); % Find maxima.
中的每个像素提供sze^2。
现在,其余代码执行所谓的非最大抑制。这可确保您删除可能存在误报的角点。这意味着您要查看图像补丁并确定此补丁中的最大值。如果此修补程序中的此最大值等于此修补程序的中心 和,如果此最大值超过阈值,则保留此点。这正是代码的这一部分所做的:
sze x sze = ones(sze) ordfilt2是一个订单统计过滤器,其中第一个输入是您想要的图像,第二个输入是您要查找的 order-statistic ,第三个输入是邻域您要处理的像素数。这告诉我们您需要最大订单统计或[r,c] = find(cim); % Find row,col coords.
if nargin==5 & disp % overlay corners on original image
figure, imagesc(im), axis image, colormap(gray), hold on
plot(c,r,'ys'), title('corners detected');
end
,这与startwork邻域中包含的最大值相对应。< / p>
代码的下一部分:
WorkStartup()...找到通过非最大抑制的那些点的确切行和列坐标,并在需要时在图像上显示这些点。
简而言之,这就解释了Harris Corner Detection ......希望有所帮助!
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?