如何使用正则表达式为多个属性验证xml架构
我有一个XML文件,如下所示,我需要验证。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>
<MyAttributes
Att1="00:00:00"
Att2="00:05:00"
Att3="00:05:00"
Att4="foo,bar,true,true,,,0253d1f0-27d6-4d90-9d35-e396007db787"
Att5="abc,def,false,true,,,4534234-65d6-6590-5535-da2007db787"
....
..../>
我想使用XSD架构文件验证xml文件,如下所示。
MyAttributes包含Att1,Att2和Att3 2. Att1,Att2和Att3的值属于TimeSpan类型 3. MyAttributes中的所有其他属性都具有贝尔格式。
- 所有其他属性的格式如下
带有7列的csv格式
第一列和第二列应该是非空字符串 col3和col4应该是布尔值 col5和col6是strings.can为空 col7应为GUID类型
有没有办法可以使用XSD 1.1通过某种正则表达式断言来验证这一点?
3 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:2)
xs:time类型将验证时间跨度字段。对于其他字段,您可以使用regexp对xs:string类型进行限制。此XSD将验证您发布的示例XML:
<xs:schema xmlns:xs="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" elementFormDefault="qualified">
<xs:simpleType name="CsvType">
<xs:restriction base="xs:string">
<xs:pattern value="\w+,\w+,(true|false),(true|false),\w*,\w*,[A-Fa-f0-9]{7,8}(-[A-Fa-f0-9]{4}){3}-[A-Fa-f0-9]{11,12}"></xs:pattern>
</xs:restriction>
</xs:simpleType>
<xs:element name="MyAttributes">
<xs:complexType>
<xs:attribute name="Att1" type="xs:time" />
<xs:attribute name="Att2" type="xs:time" />
<xs:attribute name="Att3" type="xs:time" />
<xs:attribute name="Att4" type="CsvType" />
<xs:attribute name="Att5" type="CsvType" />
</xs:complexType>
</xs:element>
</xs:schema>
你真的不需要XSD 1.1断言,除非你想验证一个属性的内容与另一个属性的内容有关。
答案 1 :(得分:0)
此正则表达式验证您的TimeSpan行:
"(\d\d):(60|([0-5][0-9])):(60|([0-5][0-9]))"
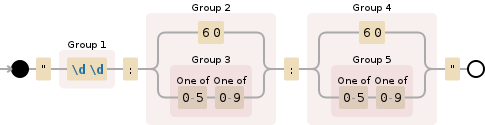
如果匹配,则该行有效。我从this question的第一个答案得到了正则表达式。
对于您的GUID行,如果这与该行匹配,那么它有效:
"(?:\w+,){2}(?:(?:true|false),){2}(?:\w*,){2}(?:[0-9a-fA-F]{7,8}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{4}\-[0-9a-fA-F]{11,12})"

虽然您的演示输入行中的第一个GUID与this question中第一个答案的正则表达式匹配,但第二个不匹配,因为它在某些元素中具有不同数量的字符。我改了它,所以它匹配两者。
答案 2 :(得分:0)
您可以使用xs:anyAttribute来允许任何属性,但是您无法控制属性的名称或类型。您只能定义在架构中显式命名的属性的类型。如你所知,要处理一般情况,你需要一个XSD 1.1断言。这可以是以下形式:
test="every $a in @* satisfies (
(name($a) = ('Att1', 'Att2', 'Att3') and $a castable as xs:time) or
(matches(name($a), 'Att\d+') and matches($a, some-regex))"/>
其中some-regex是其他人提供的正则表达式,在开始时以^结尾,在结尾处以$结尾,因此它匹配整个字符串而不是某些子字符串。
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?