遗传算法中的轮盘选择
任何人都可以为轮盘选择功能提供一些伪代码吗?我将如何实现这一点:
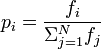
我真的不明白如何阅读这个数学符号。我从未接受过任何概率或统计数据。
14 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:37)
自从我自己完成这项工作已有几年了,但是谷歌上发现了以下伪代码。
for all members of population
sum += fitness of this individual
end for
for all members of population
probability = sum of probabilities + (fitness / sum)
sum of probabilities += probability
end for
loop until new population is full
do this twice
number = Random between 0 and 1
for all members of population
if number > probability but less than next probability
then you have been selected
end for
end
create offspring
end loop
如果您需要更多详细信息,可以找到here来自的网站。
答案 1 :(得分:15)
已经有很多正确的解决方案,但我认为这段代码更清晰。
def select(fs):
p = random.uniform(0, sum(fs))
for i, f in enumerate(fs):
if p <= 0:
break
p -= f
return i
此外,如果累积fs,您可以生成更有效的解决方案。
cfs = [sum(fs[:i+1]) for i in xrange(len(fs))]
def select(cfs):
return bisect.bisect_left(cfs, random.uniform(0, cfs[-1]))
这既快又简洁,而且代码非常简洁。如果这是您正在使用的语言,则C ++中的STL具有类似的二分算法。
答案 2 :(得分:12)
发布的伪代码包含一些不清楚的元素,它增加了生成后代的复杂性,而不是执行纯粹的选择。这是一个伪代码的简单python实现:
def roulette_select(population, fitnesses, num):
""" Roulette selection, implemented according to:
<http://stackoverflow.com/questions/177271/roulette
-selection-in-genetic-algorithms/177278#177278>
"""
total_fitness = float(sum(fitnesses))
rel_fitness = [f/total_fitness for f in fitnesses]
# Generate probability intervals for each individual
probs = [sum(rel_fitness[:i+1]) for i in range(len(rel_fitness))]
# Draw new population
new_population = []
for n in xrange(num):
r = rand()
for (i, individual) in enumerate(population):
if r <= probs[i]:
new_population.append(individual)
break
return new_population
答案 3 :(得分:8)
这通过随机接受来称为轮盘赌选择:
/// \param[in] f_max maximum fitness of the population
///
/// \return index of the selected individual
///
/// \note Assuming positive fitness. Greater is better.
unsigned rw_selection(double f_max)
{
for (;;)
{
// Select randomly one of the individuals
unsigned i(random_individual());
// The selection is accepted with probability fitness(i) / f_max
if (uniform_random_01() < fitness(i) / f_max)
return i;
}
}
单次选择所需的平均尝试次数为:
τ= f max / avg(f)
- f max 是人口的最大适应度
- avg(f)是平均适合度
τ并不明确依赖于人口中的个体数量(N),但该比率可以随N而变化。
然而,在许多应用中(适应度保持有限且平均适应度不会因为增加N而减小到0)τ不会随着N无限增加,因此此算法的典型复杂度为O(1 )(使用搜索算法的轮盘赌选择具有O(N)或O(log N)复杂度)。
此程序的概率分布确实与传统的轮盘选择相同。
有关详细信息,请参阅:
- 通过随机接受选择轮盘赌(Adam Liposki,Dorota Lipowska - 2011)
答案 4 :(得分:5)
以下是C中的一些代码:
// Find the sum of fitnesses. The function fitness(i) should
//return the fitness value for member i**
float sumFitness = 0.0f;
for (int i=0; i < nmembers; i++)
sumFitness += fitness(i);
// Get a floating point number in the interval 0.0 ... sumFitness**
float randomNumber = (float(rand() % 10000) / 9999.0f) * sumFitness;
// Translate this number to the corresponding member**
int memberID=0;
float partialSum=0.0f;
while (randomNumber > partialSum)
{
partialSum += fitness(memberID);
memberID++;
}
**// We have just found the member of the population using the roulette algorithm**
**// It is stored in the "memberID" variable**
**// Repeat this procedure as many times to find random members of the population**
答案 5 :(得分:1)
从上面的回答中,我得到了以下内容,这对我来说比答案本身更清晰。
举个例子:
随机(和)::随机(12) 通过对人口进行迭代,我们检查以下内容:random&lt;总和
让我们选择7作为随机数。
Index | Fitness | Sum | 7 < Sum
0 | 2 | 2 | false
1 | 3 | 5 | false
2 | 1 | 6 | false
3 | 4 | 10 | true
4 | 2 | 12 | ...
通过这个例子,最合适(指数3)的选择百分比最高(33%);因为随机数只需要落在6-> 10之内,就可以选择它。
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sets.size();i++) {
sum += sets[i].eval();
}
double rand = (((double)rand() / (double)RAND_MAX) * sum);
sum = 0;
for (unsigned int i=0;i<sets.size();i++) {
sum += sets[i].eval();
if (rand < sum) {
//breed i
break;
}
}
答案 6 :(得分:1)
教授。斯坦福人工智能实验室的Thrun还在他的CS373 of Udacity期间在python中提出了一个快速(呃?)重采样代码。谷歌搜索结果导致以下链接:
http://www.udacity-forums.com/cs373/questions/20194/fast-resampling-algorithm
希望这有帮助
答案 7 :(得分:1)
这是我最近为轮盘选择写的一个紧凑的java实现,希望可以使用。
public static gene rouletteSelection()
{
float totalScore = 0;
float runningScore = 0;
for (gene g : genes)
{
totalScore += g.score;
}
float rnd = (float) (Math.random() * totalScore);
for (gene g : genes)
{
if ( rnd>=runningScore &&
rnd<=runningScore+g.score)
{
return g;
}
runningScore+=g.score;
}
return null;
}
答案 8 :(得分:1)
MatLab中的轮盘赌轮选择:
TotalFitness=sum(Fitness);
ProbSelection=zeros(PopLength,1);
CumProb=zeros(PopLength,1);
for i=1:PopLength
ProbSelection(i)=Fitness(i)/TotalFitness;
if i==1
CumProb(i)=ProbSelection(i);
else
CumProb(i)=CumProb(i-1)+ProbSelection(i);
end
end
SelectInd=rand(PopLength,1);
for i=1:PopLength
flag=0;
for j=1:PopLength
if(CumProb(j)<SelectInd(i) && CumProb(j+1)>=SelectInd(i))
SelectedPop(i,1:IndLength)=CurrentPop(j+1,1:IndLength);
flag=1;
break;
end
end
if(flag==0)
SelectedPop(i,1:IndLength)=CurrentPop(1,1:IndLength);
end
end
答案 9 :(得分:0)
Based on my research ,Here is another implementation in C# if there is a need for it:
//those with higher fitness get selected wit a large probability
//return-->individuals with highest fitness
private int RouletteSelection()
{
double randomFitness = m_random.NextDouble() * m_totalFitness;
int idx = -1;
int mid;
int first = 0;
int last = m_populationSize -1;
mid = (last - first)/2;
// ArrayList's BinarySearch is for exact values only
// so do this by hand.
while (idx == -1 && first <= last)
{
if (randomFitness < (double)m_fitnessTable[mid])
{
last = mid;
}
else if (randomFitness > (double)m_fitnessTable[mid])
{
first = mid;
}
mid = (first + last)/2;
// lies between i and i+1
if ((last - first) == 1)
idx = last;
}
return idx;
}
答案 10 :(得分:0)
好的,轮盘选择实施有两种方法:常用和随机接受。
常用算法:
# there will be some amount of repeating organisms here.
mating_pool = []
all_organisms_in_population.each do |organism|
organism.fitness.times { mating_pool.push(organism) }
end
# [very_fit_organism, very_fit_organism, very_fit_organism, not_so_fit_organism]
return mating_pool.sample #=> random, likely fit, parent!
随机接受算法:
max_fitness_in_population = all_organisms_in_population.sort_by(:fitness)[0]
loop do
random_parent = all_organisms_in_population.sample
probability = random_parent.fitness/max_fitness_in_population * 100
# if random_parent's fitness is 90%,
# it's very likely that rand(100) is smaller than it.
if rand(100) < probability
return random_parent #=> random, likely fit, parent!
else
next #=> or let's keep on searching for one.
end
end
您可以选择其中之一,他们将返回相同的结果。
有用的资源:
http://natureofcode.com/book/chapter-9-the-evolution-of-code - 关于遗传算法的初学者友好且清晰的章节。解释轮盘赌轮选择作为一桶木制字母(你输入的越多 - 选择A,常用算法的机会就越大)。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fitness_proportionate_selection - 描述随机接受算法。
答案 11 :(得分:0)
此 Swift 4 数组扩展实现了加权随机选择,也就是从其元素中进行的轮盘赌选择:
public extension Array where Element == Double {
/// Consider the elements as weight values and return a weighted random selection by index.
/// a.k.a Roulette wheel selection.
func weightedRandomIndex() -> Int {
var selected: Int = 0
var total: Double = self[0]
for i in 1..<self.count { // start at 1
total += self[i]
if( Double.random(in: 0...1) <= (self[i] / total)) { selected = i }
}
return selected
}
}
例如,给出两个元素数组:
[0.9, 0.1]
weightedRandomIndex()将在90%的时间内返回零,在10%的时间内返回1。
这是一个更完整的测试:
let weights = [0.1, 0.7, 0.1, 0.1]
var results = [Int:Int]()
let n = 100000
for _ in 0..<n {
let index = weights.weightedRandomIndex()
results[index] = results[index, default:0] + 1
}
for (key,val) in results.sorted(by: { a,b in weights[a.key] < weights[b.key] }) {
print(weights[key], Double(val)/Double(n))
}
输出:
0.1 0.09906
0.1 0.10126
0.1 0.09876
0.7 0.70092
此答案与此处的Andrew Mao的答案基本相同: https://stackoverflow.com/a/15582983/74975
答案 12 :(得分:0)
这是python中的代码。该代码还可以处理Fitness的负值。
from numpy import min, sum, ptp, array
from numpy.random import uniform
list_fitness1 = array([-12, -45, 0, 72.1, -32.3])
list_fitness2 = array([0.5, 6.32, 988.2, 1.23])
def get_index_roulette_wheel_selection(list_fitness=None):
""" It can handle negative also. Make sure your list fitness is 1D-numpy array"""
scaled_fitness = (list_fitness - min(list_fitness)) / ptp(list_fitness)
minimized_fitness = 1.0 - scaled_fitness
total_sum = sum(minimized_fitness)
r = uniform(low=0, high=total_sum)
for idx, f in enumerate(minimized_fitness):
r = r + f
if r > total_sum:
return idx
get_index_roulette_wheel_selection(list_fitness1)
get_index_roulette_wheel_selection(list_fitness2)
- 确保您的健康列表是一维数字数组
- 将适应度列表缩放到[0,1]范围
- 将最大问题转换为最小问题1.0-scaled_fitness_list
- 随机分配一个介于0和和之间的数字(minimizzed_fitness_list)
- 在最小适合度列表中保留添加元素,直到获得大于总和的值
- 您可以看到适应度是否较小->在minimumed_fitness中具有较大的值->它具有更大的机会添加和使该值大于总和。
答案 13 :(得分:-1)
我在C#中写了一个版本,我真的在寻找确认它确实是正确的:
(roulette_selector是一个随机数,范围在0.0到1.0之间)
private Individual Select_Roulette(double sum_fitness)
{
Individual ret = new Individual();
bool loop = true;
while (loop)
{
//this will give us a double within the range 0.0 to total fitness
double slice = roulette_selector.NextDouble() * sum_fitness;
double curFitness = 0.0;
foreach (Individual ind in _generation)
{
curFitness += ind.Fitness;
if (curFitness >= slice)
{
loop = false;
ret = ind;
break;
}
}
}
return ret;
}
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?