PHP中读取文件最后几行的最佳方法是什么?
在我的PHP应用程序中,我需要从结尾开始读取多行
许多文件(主要是日志)。有时我只需要最后一个,有时我需要
几十或几百。基本上,我想要一些像Unix tail一样灵活的东西
命令。
这里有关于如何从文件中获取单个最后一行的问题(但是 我需要 N 行,并给出了不同的解决方案。我不确定哪个 一个是最好的,哪个表现更好。
7 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:226)
方法概述
在互联网上搜索,我遇到了不同的解决方案。我可以将它们分组 有三种方法:
- 天真使用
file()PHP函数的 - 作弊在系统上运行
tail命令的那些; - 强大使用
fseek()快乐地跳转到已打开文件的人。
我最终选择(或写)五个解决方案,天真一个,作弊一个 和三个强大的。
- 最简洁的naive solution, 使用内置数组函数。
- only possible solution based on
tailcommand,有 一个小问题:如果tail不可用,它就不会运行 非Unix(Windows)或不允许系统的受限环境 功能。 - 从文件搜索结束时读取单字节的解决方案 用于(和计算)换行符,找到 here 。
- 找到针对大型文件优化的多字节缓冲解决方案 的 here 即可。
- 缓冲区长度略微modified version of solution #4 动态,根据要检索的行数决定。
所有解决方案工作。从某种意义上说,他们返回了预期的结果 我们要求的任何文件和任意数量的行(解决方案#1除外) 在大文件的情况下打破PHP内存限制,什么都不返回)。但是哪一个 更好吗?
性能测试
要回答我运行测试的问题。这就是这些事情的完成方式,不是吗?
我准备了一个样本 100 KB文件,将不同的文件连接在一起
我的/var/log目录。然后我写了一个PHP脚本,它使用了每一个
五个解决方案来检索 1,2,...,10,20,... 100,200,...,1000 行
从文件的末尾。每个单独的测试重复十次(即
例如 5×28×10 = 1400 测试),测量平均值
时间,以微秒为单位。
我在本地开发机器上运行脚本(Xubuntu 12.04, 使用PHP命令行的PHP 5.3.10,2.70 GHz双核CPU,2 GB RAM) 翻译。结果如下:
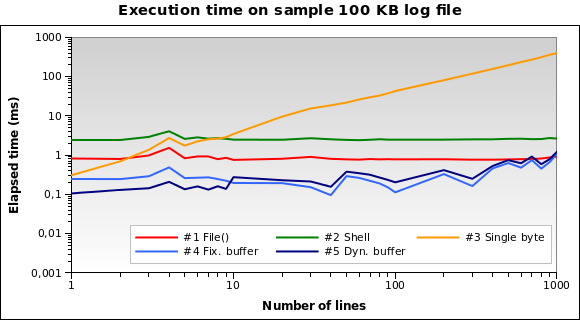
解决方案#1和#2似乎是更糟糕的。只有当我们需要时,解决方案#3才是好的 阅读几行。 解决方案#4和#5似乎是最好的。 注意动态缓冲区大小如何优化算法:执行时间稍长 由于减少了缓冲,因此对于少数几行较小。
让我们尝试更大的文件。如果我们必须阅读 10 MB 日志文件怎么办?
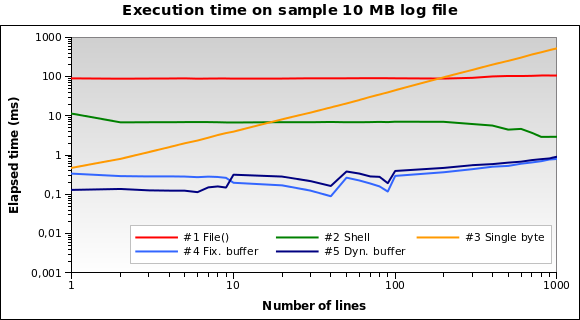
现在解决方案#1是最糟糕的一个:事实上,加载整个10 MB文件 进入记忆并不是一个好主意。我也在1MB和100MB文件上运行测试, 它的情况几乎相同。
对于微小的日志文件?这是 10 KB 文件的图表:
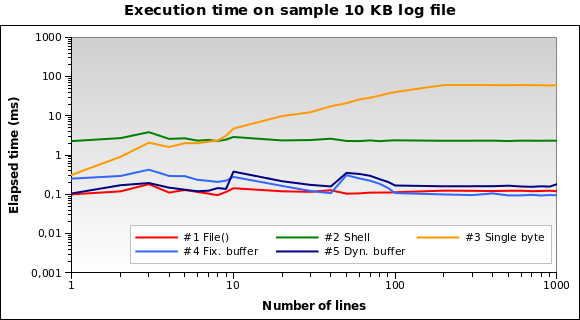
解决方案#1现在是最好的!将10 KB加载到内存中并不是什么大问题 对于PHP。 #4和#5表现也不错。然而,这是一个边缘情况:10 KB日志 意味着像150/200行......
您可以下载我的所有测试文件,来源和结果 here 的
最后的想法
对于一般用例,强烈建议Solution #5 :效果很好 每个文件大小,读取几行时表现特别好。
如果你这样做,请避免使用 solution #1 应该读取大于10 KB的文件。
解决方案 #2 和 #3 对于我运行的每个测试来说,它们不是最好的:#2永远不会运行 2ms,#3受到数量的影响很大 你问的那条线(只用1或2行才能很好地工作)。
答案 1 :(得分:4)
这是一个修改后的版本,也可以跳过最后一行:
/**
* Modified version of http://www.geekality.net/2011/05/28/php-tail-tackling-large-files/ and of https://gist.github.com/lorenzos/1711e81a9162320fde20
* @author Kinga the Witch (Trans-dating.com), Torleif Berger, Lorenzo Stanco
* @link http://stackoverflow.com/a/15025877/995958
* @license http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/
*/
function tailWithSkip($filepath, $lines = 1, $skip = 0, $adaptive = true)
{
// Open file
$f = @fopen($filepath, "rb");
if (@flock($f, LOCK_SH) === false) return false;
if ($f === false) return false;
if (!$adaptive) $buffer = 4096;
else {
// Sets buffer size, according to the number of lines to retrieve.
// This gives a performance boost when reading a few lines from the file.
$max=max($lines, $skip);
$buffer = ($max < 2 ? 64 : ($max < 10 ? 512 : 4096));
}
// Jump to last character
fseek($f, -1, SEEK_END);
// Read it and adjust line number if necessary
// (Otherwise the result would be wrong if file doesn't end with a blank line)
if (fread($f, 1) == "\n") {
if ($skip > 0) { $skip++; $lines--; }
} else {
$lines--;
}
// Start reading
$output = '';
$chunk = '';
// While we would like more
while (ftell($f) > 0 && $lines >= 0) {
// Figure out how far back we should jump
$seek = min(ftell($f), $buffer);
// Do the jump (backwards, relative to where we are)
fseek($f, -$seek, SEEK_CUR);
// Read a chunk
$chunk = fread($f, $seek);
// Calculate chunk parameters
$count = substr_count($chunk, "\n");
$strlen = mb_strlen($chunk, '8bit');
// Move the file pointer
fseek($f, -$strlen, SEEK_CUR);
if ($skip > 0) { // There are some lines to skip
if ($skip > $count) { $skip -= $count; $chunk=''; } // Chunk contains less new line symbols than
else {
$pos = 0;
while ($skip > 0) {
if ($pos > 0) $offset = $pos - $strlen - 1; // Calculate the offset - NEGATIVE position of last new line symbol
else $offset=0; // First search (without offset)
$pos = strrpos($chunk, "\n", $offset); // Search for last (including offset) new line symbol
if ($pos !== false) $skip--; // Found new line symbol - skip the line
else break; // "else break;" - Protection against infinite loop (just in case)
}
$chunk=substr($chunk, 0, $pos); // Truncated chunk
$count=substr_count($chunk, "\n"); // Count new line symbols in truncated chunk
}
}
if (strlen($chunk) > 0) {
// Add chunk to the output
$output = $chunk . $output;
// Decrease our line counter
$lines -= $count;
}
}
// While we have too many lines
// (Because of buffer size we might have read too many)
while ($lines++ < 0) {
// Find first newline and remove all text before that
$output = substr($output, strpos($output, "\n") + 1);
}
// Close file and return
@flock($f, LOCK_UN);
fclose($f);
return trim($output);
}
答案 2 :(得分:1)
这也有效:
$file = new SplFileObject("/path/to/file");
$file->seek(PHP_INT_MAX); // cheap trick to seek to EoF
$total_lines = $file->key(); // last line number
// output the last twenty lines
$reader = new LimitIterator($file, $total_lines - 20);
foreach ($reader as $line) {
echo $line; // includes newlines
}
或没有LimitIterator:
$file = new SplFileObject($filepath);
$file->seek(PHP_INT_MAX);
$total_lines = $file->key();
$file->seek($total_lines - 20);
while (!$file->eof()) {
echo $file->current();
$file->next();
}
不幸的是,你的测试用程序会在我的机器上发生段错误,所以我无法判断它是如何执行的。
答案 3 :(得分:1)
在阅读完所有这些内容后,我的小复制粘贴解决方案。 tail()不会关闭$ fp,因为您必须使用 仍然按Ctrl-C。 usleep可节省您的CPU时间,目前仅在Windows上进行过测试。 您需要将此代码放入类中!
/**
* @param $pathname
*/
private function tail($pathname)
{
$realpath = realpath($pathname);
$fp = fopen($realpath, 'r', FALSE);
$lastline = '';
fseek($fp, $this->tailonce($pathname, 1, false), SEEK_END);
do {
$line = fread($fp, 1000);
if ($line == $lastline) {
usleep(50);
} else {
$lastline = $line;
echo $lastline;
}
} while ($fp);
}
/**
* @param $pathname
* @param $lines
* @param bool $echo
* @return int
*/
private function tailonce($pathname, $lines, $echo = true)
{
$realpath = realpath($pathname);
$fp = fopen($realpath, 'r', FALSE);
$flines = 0;
$a = -1;
while ($flines <= $lines) {
fseek($fp, $a--, SEEK_END);
$char = fread($fp, 1);
if ($char == "\n") $flines++;
}
$out = fread($fp, 1000000);
fclose($fp);
if ($echo) echo $out;
return $a+2;
}
答案 4 :(得分:0)
另一个功能是,您可以使用正则表达式来分隔项目。使用
$last_rows_array = file_get_tail('logfile.log', 100, array(
'regex' => true, // use regex
'separator' => '#\n{2,}#', // separator: at least two newlines
'typical_item_size' => 200, // line length
));
功能:
// public domain
function file_get_tail( $file, $requested_num = 100, $args = array() ){
// default arg values
$regex = true;
$separator = null;
$typical_item_size = 100; // estimated size
$more_size_mul = 1.01; // +1%
$max_more_size = 4000;
extract( $args );
if( $separator === null ) $separator = $regex ? '#\n+#' : "\n";
if( is_string( $file )) $f = fopen( $file, 'rb');
else if( is_resource( $file ) && in_array( get_resource_type( $file ), array('file', 'stream'), true ))
$f = $file;
else throw new \Exception( __METHOD__.': file must be either filename or a file or stream resource');
// get file size
fseek( $f, 0, SEEK_END );
$fsize = ftell( $f );
$fpos = $fsize;
$bytes_read = 0;
$all_items = array(); // array of array
$all_item_num = 0;
$remaining_num = $requested_num;
$last_junk = '';
while( true ){
// calc size and position of next chunk to read
$size = $remaining_num * $typical_item_size - strlen( $last_junk );
// reading a bit more can't hurt
$size += (int)min( $size * $more_size_mul, $max_more_size );
if( $size < 1 ) $size = 1;
// set and fix read position
$fpos = $fpos - $size;
if( $fpos < 0 ){
$size -= -$fpos;
$fpos = 0;
}
// read chunk + add junk from prev iteration
fseek( $f, $fpos, SEEK_SET );
$chunk = fread( $f, $size );
if( strlen( $chunk ) !== $size ) throw new \Exception( __METHOD__.": read error?");
$bytes_read += strlen( $chunk );
$chunk .= $last_junk;
// chunk -> items, with at least one element
$items = $regex ? preg_split( $separator, $chunk ) : explode( $separator, $chunk );
// first item is probably cut in half, use it in next iteration ("junk") instead
// also skip very first '' item
if( $fpos > 0 || $items[0] === ''){
$last_junk = $items[0];
unset( $items[0] );
} // … else noop, because this is the last iteration
// ignore last empty item. end( empty [] ) === false
if( end( $items ) === '') array_pop( $items );
// if we got items, push them
$num = count( $items );
if( $num > 0 ){
$remaining_num -= $num;
// if we read too much, use only needed items
if( $remaining_num < 0 ) $items = array_slice( $items, - $remaining_num );
// don't fix $remaining_num, we will exit anyway
$all_items[] = array_reverse( $items );
$all_item_num += $num;
}
// are we ready?
if( $fpos === 0 || $remaining_num <= 0 ) break;
// calculate a better estimate
if( $all_item_num > 0 ) $typical_item_size = (int)max( 1, round( $bytes_read / $all_item_num ));
}
fclose( $f );
//tr( $all_items );
return call_user_func_array('array_merge', $all_items );
}
答案 5 :(得分:0)
我喜欢以下方法,但不适用于最大2GB的文件。
<?php
function lastLines($file, $lines) {
$size = filesize($file);
$fd=fopen($file, 'r+');
$pos = $size;
$n=0;
while ( $n < $lines+1 && $pos > 0) {
fseek($fd, $pos);
$a = fread($fd, 1);
if ($a === "\n") {
++$n;
};
$pos--;
}
$ret = array();
for ($i=0; $i<$lines; $i++) {
array_push($ret, fgets($fd));
}
return $ret;
}
print_r(lastLines('hola.php', 4));
?>
答案 6 :(得分:0)
对于常规的小型文本文件,只需一根衬纸,就不用担心了:
echo join(array_slice(file("path/to/file"), -5));
根据上下文定义新行,通常这样更容易:
echo join("\n",array_slice(explode("\n",file_get_contents("path/to/file")), -5));
echo join("<br>",array_slice(explode(PHP_EOL,file_get_contents("path/to/file")), -5));
echo join(PHP_EOL,array_slice(explode("\n",file_get_contents("path/to/file")), -5));
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?