解决XKCD中的NP完全问题
问题/漫画:http://xkcd.com/287/
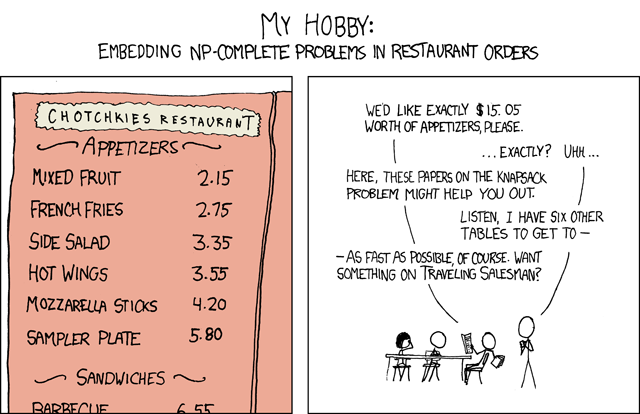
我不确定这是最好的方法,但到目前为止我已经提出了这个问题。我正在使用CFML,但任何人都应该可读。
<cffunction name="testCombo" returntype="boolean">
<cfargument name="currentCombo" type="string" required="true" />
<cfargument name="currentTotal" type="numeric" required="true" />
<cfargument name="apps" type="array" required="true" />
<cfset var a = 0 />
<cfset var found = false />
<cfloop from="1" to="#arrayLen(arguments.apps)#" index="a">
<cfset arguments.currentCombo = listAppend(arguments.currentCombo, arguments.apps[a].name) />
<cfset arguments.currentTotal = arguments.currentTotal + arguments.apps[a].cost />
<cfif arguments.currentTotal eq 15.05>
<!--- print current combo --->
<cfoutput><strong>#arguments.currentCombo# = 15.05</strong></cfoutput><br />
<cfreturn true />
<cfelseif arguments.currentTotal gt 15.05>
<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# > 15.05 (aborting)</cfoutput><br />
<cfreturn false />
<cfelse>
<!--- less than 15.05 --->
<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# < 15.05 (traversing)</cfoutput><br />
<cfset found = testCombo(arguments.currentCombo, arguments.currentTotal, arguments.apps) />
</cfif>
</cfloop>
</cffunction>
<cfset mf = {name="Mixed Fruit", cost=2.15} />
<cfset ff = {name="French Fries", cost=2.75} />
<cfset ss = {name="side salad", cost=3.35} />
<cfset hw = {name="hot wings", cost=3.55} />
<cfset ms = {name="moz sticks", cost=4.20} />
<cfset sp = {name="sampler plate", cost=5.80} />
<cfset apps = [ mf, ff, ss, hw, ms, sp ] />
<cfloop from="1" to="6" index="b">
<cfoutput>#testCombo(apps[b].name, apps[b].cost, apps)#</cfoutput>
</cfloop>
上面的代码告诉我,加起来只有15.05美元的唯一组合是7份混合水果,我需要完成我的testCombo函数的232次执行。
有没有更好的算法来找到正确的解决方案?我找到了正确的解决方案吗?
15 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:30)
它给出了解决方案的所有排列,但我认为我在为代码大小击败其他所有人。
item(X) :- member(X,[215, 275, 335, 355, 420, 580]).
solution([X|Y], Z) :- item(X), plus(S, X, Z), Z >= 0, solution(Y, S).
solution([], 0).
使用swiprolog解决方案:
?- solution(X, 1505).
X = [215, 215, 215, 215, 215, 215, 215] ;
X = [215, 355, 355, 580] ;
X = [215, 355, 580, 355] ;
X = [215, 580, 355, 355] ;
X = [355, 215, 355, 580] ;
X = [355, 215, 580, 355] ;
X = [355, 355, 215, 580] ;
X = [355, 355, 580, 215] ;
X = [355, 580, 215, 355] ;
X = [355, 580, 355, 215] ;
X = [580, 215, 355, 355] ;
X = [580, 355, 215, 355] ;
X = [580, 355, 355, 215] ;
No
答案 1 :(得分:24)
关于NP完全问题的观点并不是它对小数据集很棘手,而是解决它的工作量增长速度大于多项式,即没有O(n ^ x)算法。
如果时间复杂度为O(n!),如(我相信)上面提到的两个问题,那就是NP。
答案 2 :(得分:10)
递归(在Perl中)不是更优雅吗?
#!/usr/bin/perl
use strict;
use warnings;
my @weights = (2.15, 2.75, 3.35, 3.55, 4.20, 5.80);
my $total = 0;
my @order = ();
iterate($total, @order);
sub iterate
{
my ($total, @order) = @_;
foreach my $w (@weights)
{
if ($total+$w == 15.05)
{
print join (', ', (@order, $w)), "\n";
}
if ($total+$w < 15.05)
{
iterate($total+$w, (@order, $w));
}
}
}
输出
marco@unimatrix-01:~$ ./xkcd-knapsack.pl
2.15, 2.15, 2.15, 2.15, 2.15, 2.15, 2.15
2.15, 3.55, 3.55, 5.8
2.15, 3.55, 5.8, 3.55
2.15, 5.8, 3.55, 3.55
3.55, 2.15, 3.55, 5.8
3.55, 2.15, 5.8, 3.55
3.55, 3.55, 2.15, 5.8
3.55, 5.8, 2.15, 3.55
5.8, 2.15, 3.55, 3.55
5.8, 3.55, 2.15, 3.55
答案 3 :(得分:7)
尽管背包是NP Complete,但这是一个非常特殊的问题:通常的动态程序实际上非常出色(http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knapsack_problem)
如果你做了正确的分析,结果是O(nW),n是项目数,W是目标数。问题是当你必须DP超过大W时,就是当我们得到NP行为时。但是在大多数情况下,背包的表现相当好,你可以毫无问题地解决它的大型实例。就NP完全问题而言,背包是最简单的问题之一。
答案 4 :(得分:4)
以下是使用constraint.py
的解决方案>>> from constraint import *
>>> problem = Problem()
>>> menu = {'mixed-fruit': 2.15,
... 'french-fries': 2.75,
... 'side-salad': 3.35,
... 'hot-wings': 3.55,
... 'mozarella-sticks': 4.20,
... 'sampler-plate': 5.80}
>>> for appetizer in menu:
... problem.addVariable( appetizer, [ menu[appetizer] * i for i in range( 8 )] )
>>> problem.addConstraint(ExactSumConstraint(15.05))
>>> problem.getSolutions()
[{'side-salad': 0.0, 'french-fries': 0.0, 'sampler-plate': 5.7999999999999998, 'mixed-fruit': 2.1499999999999999, 'mozarella-sticks': 0.0, 'hot-wings': 7.0999999999999996},
{'side-salad': 0.0, 'french-fries': 0.0, 'sampler-plate': 0.0, 'mixed-fruit': 15.049999999999999, 'mozarella-sticks': 0.0, 'hot-wings': 0.0}]
因此,解决方案是订购一个采样盘,一个混合水果和两个热翅,或订购7个混合水果。
答案 5 :(得分:3)
以下是F#的解决方案:
#light
type Appetizer = { name : string; cost : int }
let menu = [
{name="fruit"; cost=215}
{name="fries"; cost=275}
{name="salad"; cost=335}
{name="wings"; cost=355}
{name="moz sticks"; cost=420}
{name="sampler"; cost=580}
]
// Choose: list<Appetizer> -> list<Appetizer> -> int -> list<list<Appetizer>>
let rec Choose allowedMenu pickedSoFar remainingMoney =
if remainingMoney = 0 then
// solved it, return this solution
[ pickedSoFar ]
else
// there's more to spend
[match allowedMenu with
| [] -> yield! [] // no more items to choose, no solutions this branch
| item :: rest ->
if item.cost <= remainingMoney then
// if first allowed is within budget, pick it and recurse
yield! Choose allowedMenu (item :: pickedSoFar) (remainingMoney - item.cost)
// regardless, also skip ever picking more of that first item and recurse
yield! Choose rest pickedSoFar remainingMoney]
let solutions = Choose menu [] 1505
printfn "%d solutions:" solutions.Length
solutions |> List.iter (fun solution ->
solution |> List.iter (fun item -> printf "%s, " item.name)
printfn ""
)
(*
2 solutions:
fruit, fruit, fruit, fruit, fruit, fruit, fruit,
sampler, wings, wings, fruit,
*)
答案 6 :(得分:2)
答案 7 :(得分:2)
你现在已经拥有了所有正确的组合,但是你仍然需要检查的数量超过你需要的数量(结果显示的许多排列都证明了这一点)。此外,您将省略最后一个达到15.05标记的项目。
我有一个PHP版本,它执行递归调用的209次迭代(如果我获得所有排列,它会执行2012)。如果在循环结束之前,你可以减少你的计数,你可以拉出刚刚检查过的项目。
我不知道CF语法,但它会是这样的:
<cfelse>
<!--- less than 15.50 --->
<!--<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# < 15.05 (traversing)</cfoutput><br />-->
<cfset found = testCombo(CC, CT, arguments.apps) />
------- remove the item from the apps array that was just checked here ------
</cfif>
</cfloop>
编辑:作为参考,这是我的PHP版本:
<?
function rc($total, $string, $m) {
global $c;
$m2 = $m;
$c++;
foreach($m as $i=>$p) {
if ($total-$p == 0) {
print "$string $i\n";
return;
}
if ($total-$p > 0) {
rc($total-$p, $string . " " . $i, $m2);
}
unset($m2[$i]);
}
}
$c = 0;
$m = array("mf"=>215, "ff"=>275, "ss"=>335, "hw"=>355, "ms"=>420, "sp"=>580);
rc(1505, "", $m);
print $c;
?>
输出
mf mf mf mf mf mf mf
mf hw hw sp
209
编辑2:
由于解释了为什么你可以删除这些元素会比我评论中的内容多一点,我在这里添加它。
基本上,每次递归都会找到包含当前搜索元素的所有组合(例如,第一步将找到包括至少一个混合水果的所有内容)。理解它的最简单方法是跟踪执行情况,但由于这将占用大量空间,我会像目标是6.45一样。
MF (2.15)
MF (4.30)
MF (6.45) *
FF (7.05) X
SS (7.65) X
...
[MF removed for depth 2]
FF (4.90)
[checking MF now would be redundant since we checked MF/MF/FF previously]
FF (7.65) X
...
[FF removed for depth 2]
SS (5.50)
...
[MF removed for depth 1]
此时,我们检查了包含任何混合水果的每种组合,因此无需再次检查混合水果。您也可以使用相同的逻辑在每个更深的递归中修剪数组。
这样追踪它实际上提示了另一个节省时间 - 知道价格从低到高排序意味着我们一旦超过目标就不需要继续检查项目。
答案 8 :(得分:2)
我会对算法本身的设计提出一个建议(这就是我如何解释原始问题的意图)。这是我写的解决方案的片段:
....
private void findAndReportSolutions(
int target, // goal to be achieved
int balance, // amount of goal remaining
int index // menu item to try next
) {
++calls;
if (balance == 0) {
reportSolution(target);
return; // no addition to perfect order is possible
}
if (index == items.length) {
++falls;
return; // ran out of menu items without finding solution
}
final int price = items[index].price;
if (balance < price) {
return; // all remaining items cost too much
}
int maxCount = balance / price; // max uses for this item
for (int n = maxCount; 0 <= n; --n) { // loop for this item, recur for others
++loops;
counts[index] = n;
findAndReportSolutions(
target, balance - n * price, index + 1
);
}
}
public void reportSolutionsFor(int target) {
counts = new int[items.length];
calls = loops = falls = 0;
findAndReportSolutions(target, target, 0);
ps.printf("%d calls, %d loops, %d falls%n", calls, loops, falls);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MenuItem[] items = {
new MenuItem("mixed fruit", 215),
new MenuItem("french fries", 275),
new MenuItem("side salad", 335),
new MenuItem("hot wings", 355),
new MenuItem("mozzarella sticks", 420),
new MenuItem("sampler plate", 580),
};
Solver solver = new Solver(items);
solver.reportSolutionsFor(1505);
}
...
(请注意,构造函数 通过提高价格对菜单项进行排序,以便在剩余余额小于任何剩余菜单项时启用固定时间提前终止。)
示例运行的输出是:
7 mixed fruit (1505) = 1505
1 mixed fruit (215) + 2 hot wings (710) + 1 sampler plate (580) = 1505
348 calls, 347 loops, 79 falls
我要强调的设计建议是,在上面的代码中,每个findAndReportSolution(...)的嵌套(递归)调用都会处理由index参数标识的一个菜单项的数量。换句话说,递归嵌套与内嵌嵌套循环集的行为平行;最外面计算第一个菜单项的可能用途,下一个计算第二个菜单项的使用等等(当然,使用递归会释放代码,使其依赖于特定数量的菜单项!)< / p>
我建议这样可以更容易地设计代码,更容易理解每个调用的作用(考虑特定项目的所有可能用途,将菜单的其余部分委托给从属调用)。它还避免了产生多项解决方案的所有排列的组合爆炸(如上述输出的第二行,其仅发生一次,而不是以不同的项目顺序重复)。
我尝试最大化代码的“显而易见性”,而不是尝试最小化某些特定方法的调用次数。例如,上述设计允许委托调用确定是否已达到解决方案,而不是将该检查包围在调用点周围,这将减少调用次数,但代价是使代码混乱。
答案 9 :(得分:1)
由于这显然是要在短时间内通过纸和笔来解决,为什么不将订单总额除以每个项目的价格,看看他们是否有机会订购一件商品的倍数?
例如,
15.05 / 2.15 = 7种混合水果 15.05 / 2.75 = 5.5炸薯条。
然后继续进行简单的组合......
15 /(2.15 + 2.75)= 3.06122449混合水果和炸薯条。换句话说,假设解决方案应该是简单的,并且可由人无法访问计算机来解决。然后测试最简单,最明显(因此隐藏在普通视线中)解决方案是否有效。
我发誓,这个周末我会在当地的康贝拉出这个,当我在俱乐部关闭后的凌晨4:30订购价值4.77美元的开胃菜(含税)。
答案 10 :(得分:1)
在python中 我对“全局变量”有一些问题,所以我将该函数作为对象的方法。它是递归的,它在漫画中的问题上自称29次,在第一次成功的比赛中停止
class Solver(object):
def __init__(self):
self.solved = False
self.total = 0
def solve(s, p, pl, curList = []):
poss = [i for i in sorted(pl, reverse = True) if i <= p]
if len(poss) == 0 or s.solved:
s.total += 1
return curList
if abs(poss[0]-p) < 0.00001:
s.solved = True # Solved it!!!
s.total += 1
return curList + [poss[0]]
ml,md = [], 10**8
for j in [s.solve(p-i, pl, [i]) for i in poss]:
if abs(sum(j)-p)<md: ml,md = j, abs(sum(j)-p)
s.total += 1
return ml + curList
priceList = [5.8, 4.2, 3.55, 3.35, 2.75, 2.15]
appetizers = ['Sampler Plate', 'Mozzarella Sticks', \
'Hot wings', 'Side salad', 'French Fries', 'Mixed Fruit']
menu = zip(priceList, appetizers)
sol = Solver()
q = sol.solve(15.05, priceList)
print 'Total time it runned: ', sol.total
print '-'*30
order = [(m, q.count(m[0])) for m in menu if m[0] in q]
for o in order:
print '%d x %s \t\t\t (%.2f)' % (o[1],o[0][1],o[0][0])
print '-'*30
ts = 'Total: %.2f' % sum(q)
print ' '*(30-len(ts)-1),ts
输出:
Total time it runned: 29
------------------------------
1 x Sampler Plate (5.80)
2 x Hot wings (3.55)
1 x Mixed Fruit (2.15)
------------------------------
Total: 15.05
答案 11 :(得分:0)
实际上,我已经重构了我的算法。我错过了几个正确的组合,这是因为我在成本超过15.05后立即返回 - 我没有费心去检查我可以添加的其他(更便宜的)物品。这是我的新算法:
<cffunction name="testCombo" returntype="numeric">
<cfargument name="currentCombo" type="string" required="true" />
<cfargument name="currentTotal" type="numeric" required="true" />
<cfargument name="apps" type="array" required="true" />
<cfset var a = 0 />
<cfset var found = false />
<cfset var CC = "" />
<cfset var CT = 0 />
<cfset tries = tries + 1 />
<cfloop from="1" to="#arrayLen(arguments.apps)#" index="a">
<cfset combos = combos + 1 />
<cfset CC = listAppend(arguments.currentCombo, arguments.apps[a].name) />
<cfset CT = arguments.currentTotal + arguments.apps[a].cost />
<cfif CT eq 15.05>
<!--- print current combo --->
<cfoutput><strong>#CC# = 15.05</strong></cfoutput><br />
<cfreturn true />
<cfelseif CT gt 15.05>
<!--<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# > 15.05 (aborting)</cfoutput><br />-->
<cfelse>
<!--- less than 15.50 --->
<!--<cfoutput>#arguments.currentCombo# < 15.05 (traversing)</cfoutput><br />-->
<cfset found = testCombo(CC, CT, arguments.apps) />
</cfif>
</cfloop>
<cfreturn found />
</cffunction>
<cfset mf = {name="Mixed Fruit", cost=2.15} />
<cfset ff = {name="French Fries", cost=2.75} />
<cfset ss = {name="side salad", cost=3.35} />
<cfset hw = {name="hot wings", cost=3.55} />
<cfset ms = {name="moz sticks", cost=4.20} />
<cfset sp = {name="sampler plate", cost=5.80} />
<cfset apps = [ mf, ff, ss, hw, ms, sp ] />
<cfset tries = 0 />
<cfset combos = 0 />
<cfoutput>
<cfloop from="1" to="6" index="b">
#testCombo(apps[b].name, apps[b].cost, apps)#
</cfloop>
<br />
tries: #tries#<br />
combos: #combos#
</cfoutput>
输出:
Mixed Fruit,Mixed Fruit,Mixed Fruit,Mixed Fruit,Mixed Fruit,Mixed Fruit,Mixed Fruit = 15.05
Mixed Fruit,hot wings,hot wings,sampler plate = 15.05
Mixed Fruit,hot wings,sampler plate,hot wings = 15.05
Mixed Fruit,sampler plate,hot wings,hot wings = 15.05
false false false hot wings,Mixed Fruit,hot wings,sampler plate = 15.05
hot wings,Mixed Fruit,sampler plate,hot wings = 15.05
hot wings,hot wings,Mixed Fruit,sampler plate = 15.05
hot wings,sampler plate,Mixed Fruit,hot wings = 15.05
false false sampler plate,Mixed Fruit,hot wings,hot wings = 15.05
sampler plate,hot wings,Mixed Fruit,hot wings = 15.05
false
tries: 2014
combos: 12067
我认为这可能有所有正确的组合,但我的问题仍然存在:是否有更好的算法?
答案 12 :(得分:0)
从@rcar's answer学习,以及之后的另一次重构,我得到了以下内容。
正如我编写的许多内容一样,我已经从CFML重构为CFScript,但代码基本相同。
我在数组中添加了一个动态起点的建议(而不是按值传递数组并更改其值以用于将来的递归),这使我获得了相同的统计数据(209次递归,571次组合价格检查) (循环迭代)),然后通过假设数组将按成本排序 - 因为它是 - 并在我们超过目标价格时立即中断来改进。随着中断,我们减少了209次递归和376次循环迭代。
可以对算法做出哪些其他改进?
function testCombo(minIndex, currentCombo, currentTotal){
var a = 0;
var CC = "";
var CT = 0;
var found = false;
tries += 1;
for (a=arguments.minIndex; a <= arrayLen(apps); a++){
combos += 1;
CC = listAppend(arguments.currentCombo, apps[a].name);
CT = arguments.currentTotal + apps[a].cost;
if (CT eq 15.05){
//print current combo
WriteOutput("<strong>#CC# = 15.05</strong><br />");
return(true);
}else if (CT gt 15.05){
//since we know the array is sorted by cost (asc),
//and we've already gone over the price limit,
//we can ignore anything else in the array
break;
}else{
//less than 15.50, try adding something else
found = testCombo(a, CC, CT);
}
}
return(found);
}
mf = {name="mixed fruit", cost=2.15};
ff = {name="french fries", cost=2.75};
ss = {name="side salad", cost=3.35};
hw = {name="hot wings", cost=3.55};
ms = {name="mozarella sticks", cost=4.20};
sp = {name="sampler plate", cost=5.80};
apps = [ mf, ff, ss, hw, ms, sp ];
tries = 0;
combos = 0;
testCombo(1, "", 0);
WriteOutput("<br />tries: #tries#<br />combos: #combos#");
答案 13 :(得分:0)
这是Clojure中的并发实现。计算(items-with-price 15.05)需要大约14次组合生成递归,以及大约10次可能性检查。我花了大约6分钟来计算我的英特尔Q9300上的(items-with-price 100)。
这只会给出第一个找到的答案,如果没有,则为nil,因为这是所有问题的要求。为什么你被告知做更多的工作;)?
;; np-complete.clj
;; A Clojure solution to XKCD #287 "NP-Complete"
;; By Sam Fredrickson
;;
;; The function "items-with-price" returns a sequence of items whose sum price
;; is equal to the given price, or nil.
(defstruct item :name :price)
(def *items* #{(struct item "Mixed Fruit" 2.15)
(struct item "French Fries" 2.75)
(struct item "Side Salad" 3.35)
(struct item "Hot Wings" 3.55)
(struct item "Mozzarella Sticks" 4.20)
(struct item "Sampler Plate" 5.80)})
(defn items-with-price [price]
(let [check-count (atom 0)
recur-count (atom 0)
result (atom nil)
checker (agent nil)
; gets the total price of a seq of items.
items-price (fn [items] (apply + (map #(:price %) items)))
; checks if the price of the seq of items matches the sought price.
; if so, it changes the result atom. if the result atom is already
; non-nil, nothing is done.
check-items (fn [unused items]
(swap! check-count inc)
(if (and (nil? @result)
(= (items-price items) price))
(reset! result items)))
; lazily generates a list of combinations of the given seq s.
; haven't tested well...
combinations (fn combinations [cur s]
(swap! recur-count inc)
(if (or (empty? s)
(> (items-price cur) price))
'()
(cons cur
(lazy-cat (combinations (cons (first s) cur) s)
(combinations (cons (first s) cur) (rest s))
(combinations cur (rest s))))))]
; loops through the combinations of items, checking each one in a thread
; pool until there are no more combinations or the result atom is non-nil.
(loop [items-comb (combinations '() (seq *items*))]
(if (and (nil? @result)
(not-empty items-comb))
(do (send checker check-items (first items-comb))
(recur (rest items-comb)))))
(await checker)
(println "No. of recursions:" @recur-count)
(println "No. of checks:" @check-count)
@result))
答案 14 :(得分:0)
如果您需要优化算法,最好按降序尝试价格。这可以让你先消耗剩余的金额,然后看看如何填写其余的金额。
此外,您可以使用数学计算每次开始的每种食物的最大数量,这样您就不会尝试超过15.05美元目标的组合。
此算法只需要尝试88种组合即可获得完整的答案,这看起来是迄今为止发布的最低答案:
public class NPComplete {
private static final int[] FOOD = { 580, 420, 355, 335, 275, 215 };
private static int tries;
public static void main(String[] ignore) {
tries = 0;
addFood(1505, "", 0);
System.out.println("Combinations tried: " + tries);
}
private static void addFood(int goal, String result, int index) {
// If no more food to add, see if this is a solution
if (index >= FOOD.length) {
tries++;
if (goal == 0)
System.out.println(tries + " tries: " + result.substring(3));
return;
}
// Try all possible quantities of this food
// If this is the last food item, only try the max quantity
int qty = goal / FOOD[index];
do {
addFood(goal - qty * FOOD[index],
result + " + " + qty + " * " + FOOD[index], index + 1);
} while (index < FOOD.length - 1 && --qty >= 0);
}
}
以下是显示两种解决方案的输出:
9 tries: 1 * 580 + 0 * 420 + 2 * 355 + 0 * 335 + 0 * 275 + 1 * 215 88 tries: 0 * 580 + 0 * 420 + 0 * 355 + 0 * 335 + 0 * 275 + 7 * 215 Combinations tried: 88
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?