使用按位运算将Int转换为Float或Float转换为Int(软件浮点)
我想知道你是否可以帮助解释将整数转换为float或float转换为整数的过程。对于我的课程,我们只使用按位运算符来完成此操作,但我认为从类型到类型的强制理解将在这个阶段帮助我更多。
据我所知,到目前为止,对于int要浮动,你必须将整数转换为二进制,通过查找有效数,指数和分数来规范化整数的值,然后从那里输出float中的值?
对于float to int,你必须将值分成有效数,指数和分数,然后反转上面的指令得到一个int值?
我尝试按照此问题的说明进行操作:Casting float to int (bitwise) in C 但我真的不能理解它。
另外,有人可以解释为什么在将int转换为float时大于23位的值需要舍入?
3 个答案:
答案 0 :(得分:17)
首先,如果你想更好地理解浮点弱点,你应该考虑阅读一篇论文:“每个计算机科学家应该知道的关于浮点运算的内容”,http://www.validlab.com/goldberg/paper.pdf
现在对某些人来说。
以下代码是简单的,并试图从unsigned int生成一个范围为0< {0}的IEEE-754单精度浮点数。价值< 2 24 。这是您在现代硬件上最有可能遇到的格式,它是您在原始问题中引用的格式。
IEEE-754单精度浮点数分为三个字段:单符号位,8位指数和23位有效数(有时称为尾数)。 IEEE-754使用隐藏1 有效数字,这意味着有效数字实际上是24位。这些位从左到右打包,符号位在第31位,指数在第30位...... 23位,有效位在位22 .. 0中。来自维基百科的下图说明:
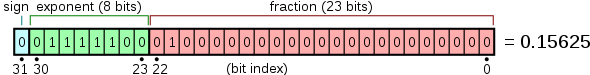
指数的偏差为127,这意味着与浮点数关联的实际指数比指数字段中存储的值小127。因此,指数0将被编码为127。
(注意:完整的维基百科文章可能对您有意思。参考:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_precision_floating-point_format)
因此,IEEE-754号码0x40000000解释如下:
- 位31 = 0:正值
- 位30 .. 23 = 0x80:指数= 128 - 127 = 1(又名.2 1 )
- 位22 .. 0均为0:显着= 1.00000000_00000000_0000000。 (注意我恢复了隐藏的1)。
因此该值为1.0 x 2 1 = 2.0。
要将上面给出的有限范围内的unsigned int转换为IEEE-754格式的内容,您可以使用如下所示的函数。它需要以下步骤:
- 将整数的前导1与浮点表示中隐藏 1的位置对齐。
- 在对齐整数时,记录所做的轮班总数。
- 掩盖隐藏的1。
- 使用所做的班次数,计算指数并将其附加到数字上。
- 使用
reinterpret_cast,将生成的位模式转换为float。这部分是一个丑陋的黑客,因为它使用类型惩罚指针。你也可以通过滥用union来做到这一点。有些平台提供了一种内在操作(例如_itof),使这种重新解释不那么难看。
有更快的方法可以做到这一点;如果不是超级有效的话,这个意图在教学上是有用的:
float uint_to_float(unsigned int significand)
{
// Only support 0 < significand < 1 << 24.
if (significand == 0 || significand >= 1 << 24)
return -1.0; // or abort(); or whatever you'd like here.
int shifts = 0;
// Align the leading 1 of the significand to the hidden-1
// position. Count the number of shifts required.
while ((significand & (1 << 23)) == 0)
{
significand <<= 1;
shifts++;
}
// The number 1.0 has an exponent of 0, and would need to be
// shifted left 23 times. The number 2.0, however, has an
// exponent of 1 and needs to be shifted left only 22 times.
// Therefore, the exponent should be (23 - shifts). IEEE-754
// format requires a bias of 127, though, so the exponent field
// is given by the following expression:
unsigned int exponent = 127 + 23 - shifts;
// Now merge significand and exponent. Be sure to strip away
// the hidden 1 in the significand.
unsigned int merged = (exponent << 23) | (significand & 0x7FFFFF);
// Reinterpret as a float and return. This is an evil hack.
return *reinterpret_cast< float* >( &merged );
}
使用检测数字中前导1的函数,可以提高此过程的效率。 (对于“计数前导零”,有时使用clz之类的名称,或者对于“正常化”使用norm。)
你也可以通过记录符号,取整数的绝对值,执行上述步骤,然后将符号放入数字的第31位,将其扩展为带符号的数字。
对于整数&gt; = 2 24 ,整个整数不适合32位浮点格式的有效数字段。这就是你需要“舍入”的原因:你失去了LSB以使价值合适。因此,多个整数将最终映射到相同的浮点模式。确切的映射取决于舍入模式(向-Inf舍入,向+ Inf舍入,向零舍入,向最近偶数舍入)。但事实是你不能将24位变成少于24位而没有一些损失。
您可以根据上面的代码看到这一点。它的工作原理是将前导1对齐到隐藏的1位置。如果值>> 2 24 ,则代码需要移位右,而不是 left ,这必然会使LSB移位。舍入模式只是告诉你如何处理移走的位。
答案 1 :(得分:3)
Joe Z的答案很优雅,但输入值的范围非常有限。 32位浮点数可以存储以下范围内的所有整数值:
[ - 2 24 ... + 2 24 ] = [-16777216 ... + 16777216]
以及此范围之外的其他一些值。
整个范围将由此涵盖:
float int2float(int value)
{
// handles all values from [-2^24...2^24]
// outside this range only some integers may be represented exactly
// this method will use truncation 'rounding mode' during conversion
// we can safely reinterpret it as 0.0
if (value == 0) return 0.0;
if (value == (1U<<31)) // ie -2^31
{
// -(-2^31) = -2^31 so we'll not be able to handle it below - use const
// value = 0xCF000000;
return (float)INT_MIN; // *((float*)&value); is undefined behaviour
}
int sign = 0;
// handle negative values
if (value < 0)
{
sign = 1U << 31;
value = -value;
}
// although right shift of signed is undefined - all compilers (that I know) do
// arithmetic shift (copies sign into MSB) is what I prefer here
// hence using unsigned abs_value_copy for shift
unsigned int abs_value_copy = value;
// find leading one
int bit_num = 31;
int shift_count = 0;
for(; bit_num > 0; bit_num--)
{
if (abs_value_copy & (1U<<bit_num))
{
if (bit_num >= 23)
{
// need to shift right
shift_count = bit_num - 23;
abs_value_copy >>= shift_count;
}
else
{
// need to shift left
shift_count = 23 - bit_num;
abs_value_copy <<= shift_count;
}
break;
}
}
// exponent is biased by 127
int exp = bit_num + 127;
// clear leading 1 (bit #23) (it will implicitly be there but not stored)
int coeff = abs_value_copy & ~(1<<23);
// move exp to the right place
exp <<= 23;
union
{
int rint;
float rfloat;
}ret = { sign | exp | coeff };
return ret.rfloat;
}
当然还有其他方法可以找到int(无分支)的abs值。类似地,也可以在没有分支的情况下完成couting前导零,因此将此示例视为示例; - )。
答案 2 :(得分:2)
您检查过IEEE 754浮点表示吗?
在32位标准化形式中,它具有(尾数&#39; s)符号位,8位指数(超过127,我认为)和23位尾数&#34;十进制&#34;除了&#34; 0。&#34;被丢弃(总是以那种形式)并且基数是2,而不是10.即:MSB值是1/2,下一位是1/4,依此类推。
- 我写了这段代码,但我无法理解我的错误
- 我无法从一个代码实例的列表中删除 None 值,但我可以在另一个实例中。为什么它适用于一个细分市场而不适用于另一个细分市场?
- 是否有可能使 loadstring 不可能等于打印?卢阿
- java中的random.expovariate()
- Appscript 通过会议在 Google 日历中发送电子邮件和创建活动
- 为什么我的 Onclick 箭头功能在 React 中不起作用?
- 在此代码中是否有使用“this”的替代方法?
- 在 SQL Server 和 PostgreSQL 上查询,我如何从第一个表获得第二个表的可视化
- 每千个数字得到
- 更新了城市边界 KML 文件的来源?